Considering the symmetry of teeth in spur gears, in order to reduce the amount of calculation, one single tooth is still cut as the research object. The material parameters and tooth profile of the semi elliptical flake crack are the same as before. In the static analysis, it can be known that the initial crack is located at the midpoint of the tooth width of the spur gear and parallel to the XZ plane. When analyzing the influence of crack location on crack propagation life, rotate the semi elliptical sheet crack around the z-axis for a certain angle, and then conduct crack propagation analysis and crack propagation life prediction. In this section, the initial crack rotation angle around the z-axis is selected as 15 °, 30 °, 45 ° and 60 °, and then predict the fatigue crack propagation life for these four cases respectively, The results of straight cylindrical gear embedded with initial crack at the dangerous position of single tooth root are shown in Figure 1.
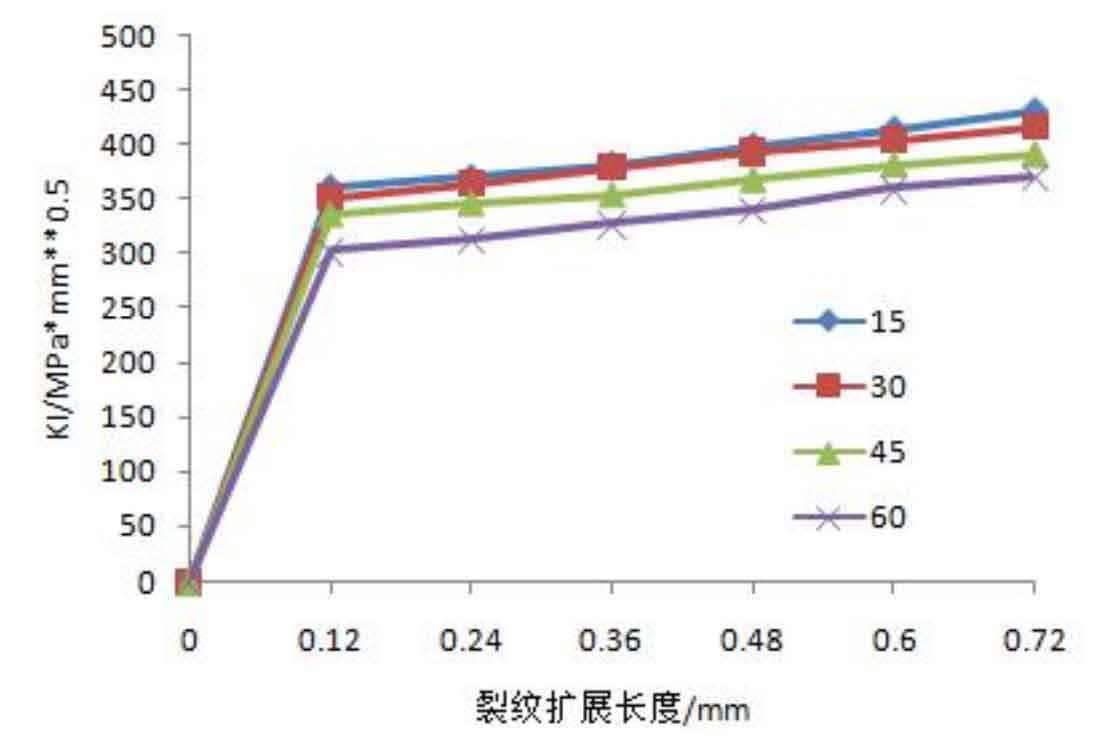
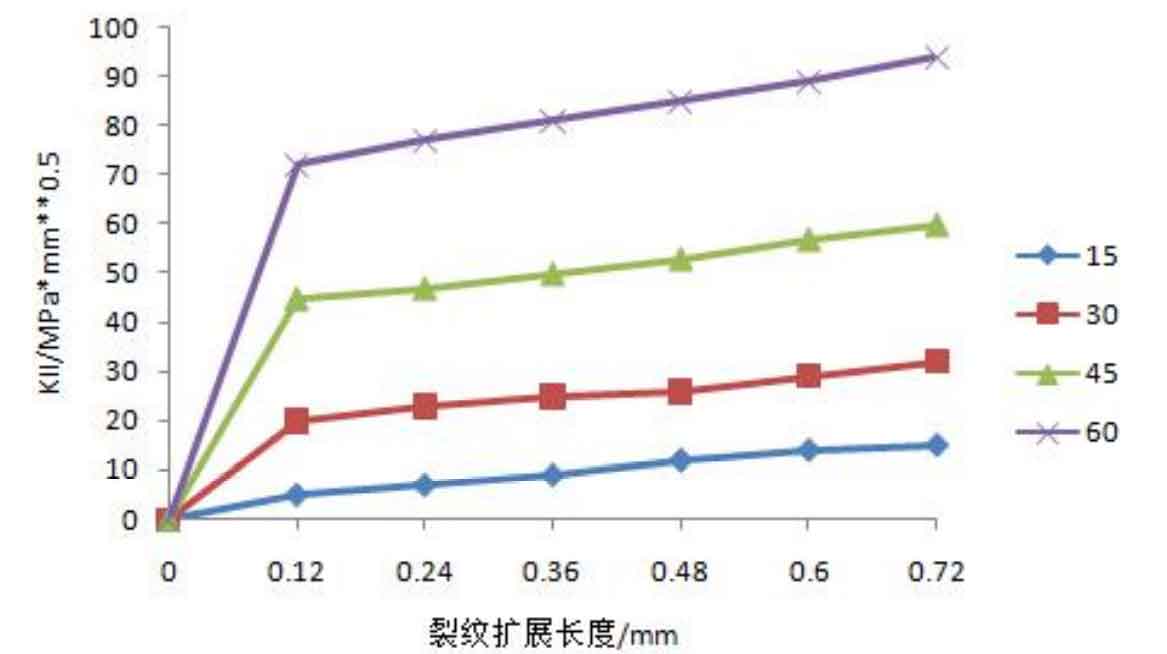
According to the simulation of the crack propagation process of spur gear, it can be seen that the size and the ratio of long and short axes of ellipse are constantly changing during the propagation process of semi elliptical sheet initial crack, which leads to the change of stress intensity factor at the crack front. In, the pointing line at the crack front is still selected as the path to obtain the value of stress intensity factor, and the results are shown in Fig. 2.
It can be seen from Fig. 2 (a) that the value of Ki is increasing during the crack propagation of spur gear; The Ki value at different angles decreases with the increase of the included angle. In Fig. 2 (b), under a fixed included angle, like Ki, the value of Kii increases with the crack propagation; However, it is worth noting that the variation law of Kii value under different included angles is just opposite to Ki, that is, Kii increases with the increase of included angle. It can be seen from Figure 2 (c) that the value of kiII is very small compared with KI and Kii, which will not be discussed here.
In general, among Ki, Kii and kiII, the value of Ki is the largest, and the crack propagation of spur gear is still dominated by open type. One thing to note: from figures (a) and (b), we can see that Ki and Kii change regularly with the change of the included angle. For example, Ki is inversely proportional to the included angle, and Kii is directly proportional to the included angle before the intersection. From the perspective of composite crack growth theory, Kii and kiII are much smaller than ki. Therefore, Kii and kiII have little influence on the equivalent stress intensity factor, so it can be judged that they have little influence on the crack fatigue life, which can be verified in the following contents.