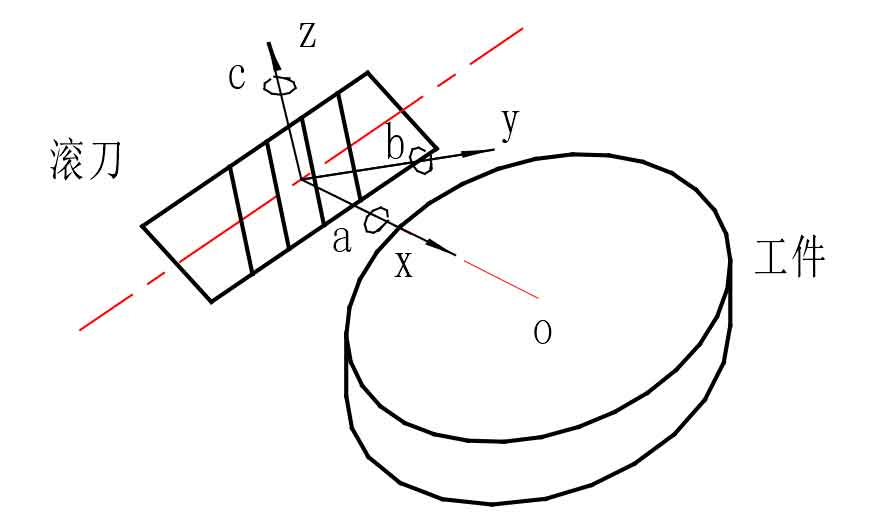
There are 24 errors affecting the mutual position of gear hob and workpiece, including 12 motion errors and 12 installation errors. In the analysis, the univariate method is used to study the influence of each error on gear accuracy. Firstly, the theoretical model of machining workpiece with gear hobbing hob is established. As shown in Figure 1. Taking the machining of helical gear as an example for modeling, because the spur gear can be expressed as a special case of helical gear with zero helix angle. The model takes the horizontal vertical line from the center of the workpiece to the central axis of the gear hobbing hob as the X axis and the helix direction of the vertical gear hobbing hob as the Y axis to establish the spatial coordinate system. In the model, the gear hobbing hob and the workpiece have 6 degrees of freedom respectively, There are errors in installation and movement. The influence of errors on machining accuracy is analyzed below.
Gear error mainly includes: pitch error, tooth profile error, helix error, radial error, tangential error, etc.
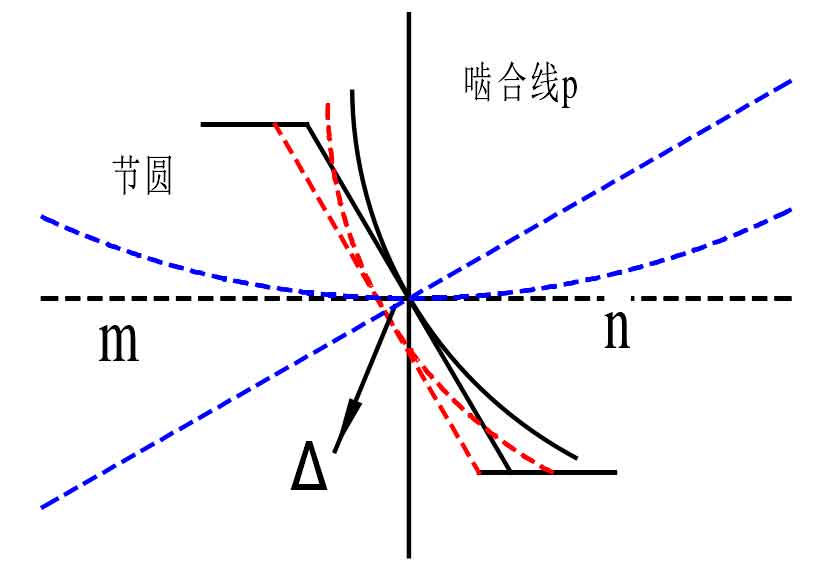
The meshing error is shown by the dotted line P and the meshing error on the end face of the gear, as shown in the figure 2. The meshing error is shown by the dotted line on the gear. It can be seen from the schematic diagram that when there is an error ∆ in the meshing line P direction of the gear hobbing hob, the error will be transmitted to the tooth profile of the machined gear, which is the basic principle of analyzing the machining accuracy of gear hobbing.