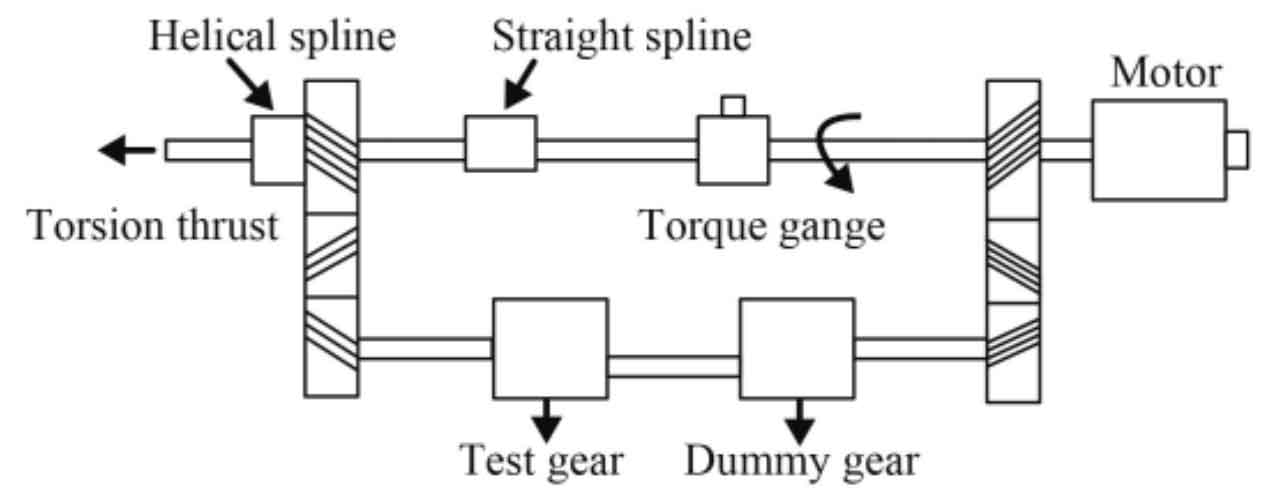
Automotive automatic transmission lubricating oil (ATF) not only meets the lubrication of automotive helical gears and bearings, but also undertakes the lubrication and cooling of hydraulic control oil, clutch and other components and the control of action stability. It has very strict requirements for the dynamic friction coefficient, static friction coefficient and oxidation durability of oil products. In recent years, due to the improvement of the requirements of automotive automatic transmission on the accuracy and slip of the control system, the lubrication of automotive helical gear system by oil products is facing great challenges. The table shows the representative properties of two different oil products of automobile automatic transmission. The automobile helical gear pair used for the test was treated with composite shot peening and manganese phosphate respectively. Figure 1 shows the power cycle automobile helical gear fatigue test-bed.
| Factor | ATF-A | ATF-B |
| Density / (g·cm−3) @15 ℃ | 0.867 | 0.857 |
| Dynamic viscosity / cSt @40 ℃ | 34.1 | 33.9 |
| Dynamic viscosity / cSt @100 ℃ | 7.55 | 7.34 |
| Mean dynamic friction coefficient | 0.128 | 0.137 |
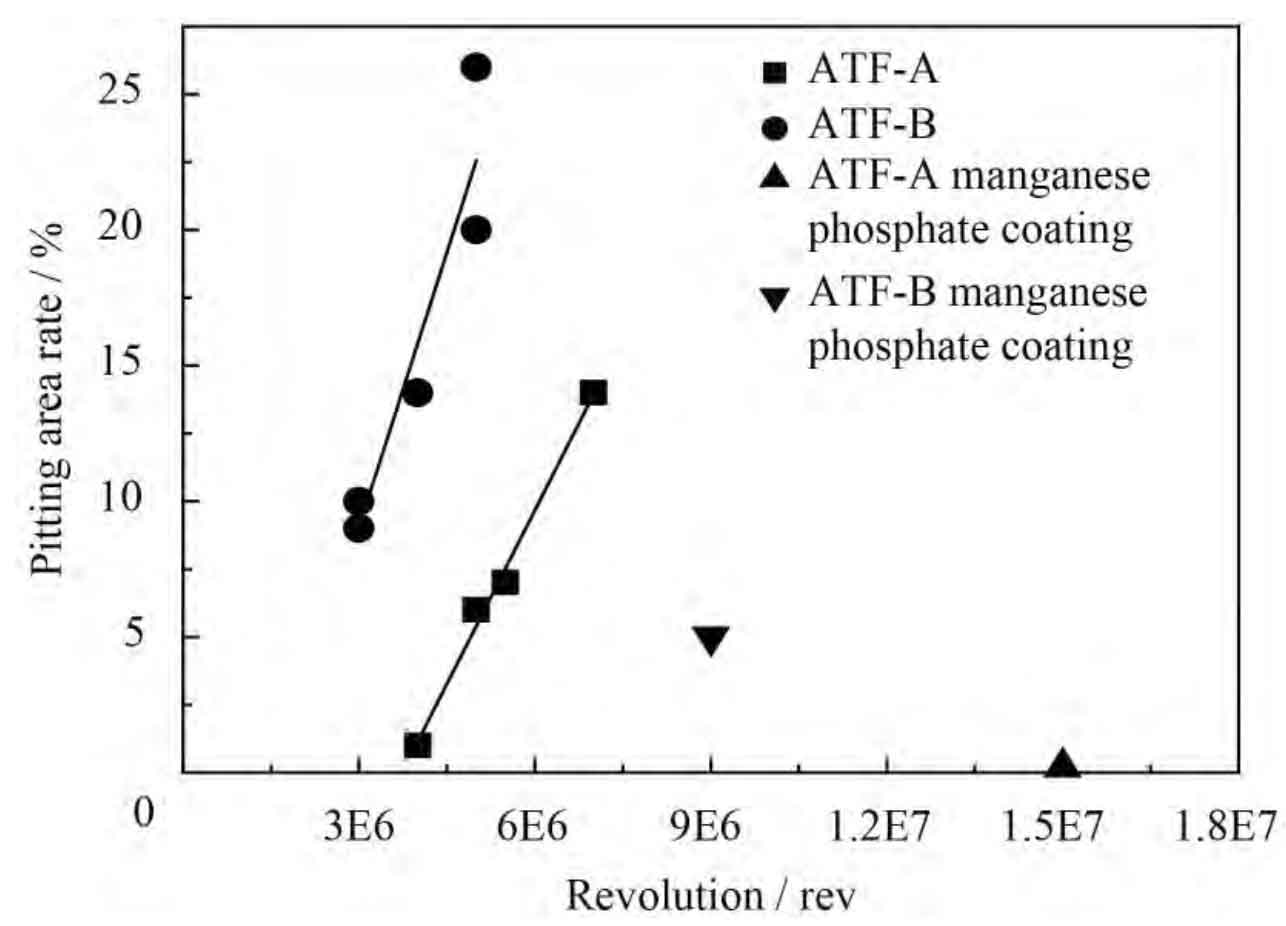
The commonly used working temperature of ATF in transmission is usually between 80 ~ 110 ℃. The fatigue pitting rate of automobile helical gear when the contact stress of automobile helical gear is 1 730 MPa is measured under the condition of working oil temperature of 80 ℃. The results are shown in Figure 2. The fatigue pitting surface area rate of automobile helical gear pair a is less than that of automobile helical gear pair B.
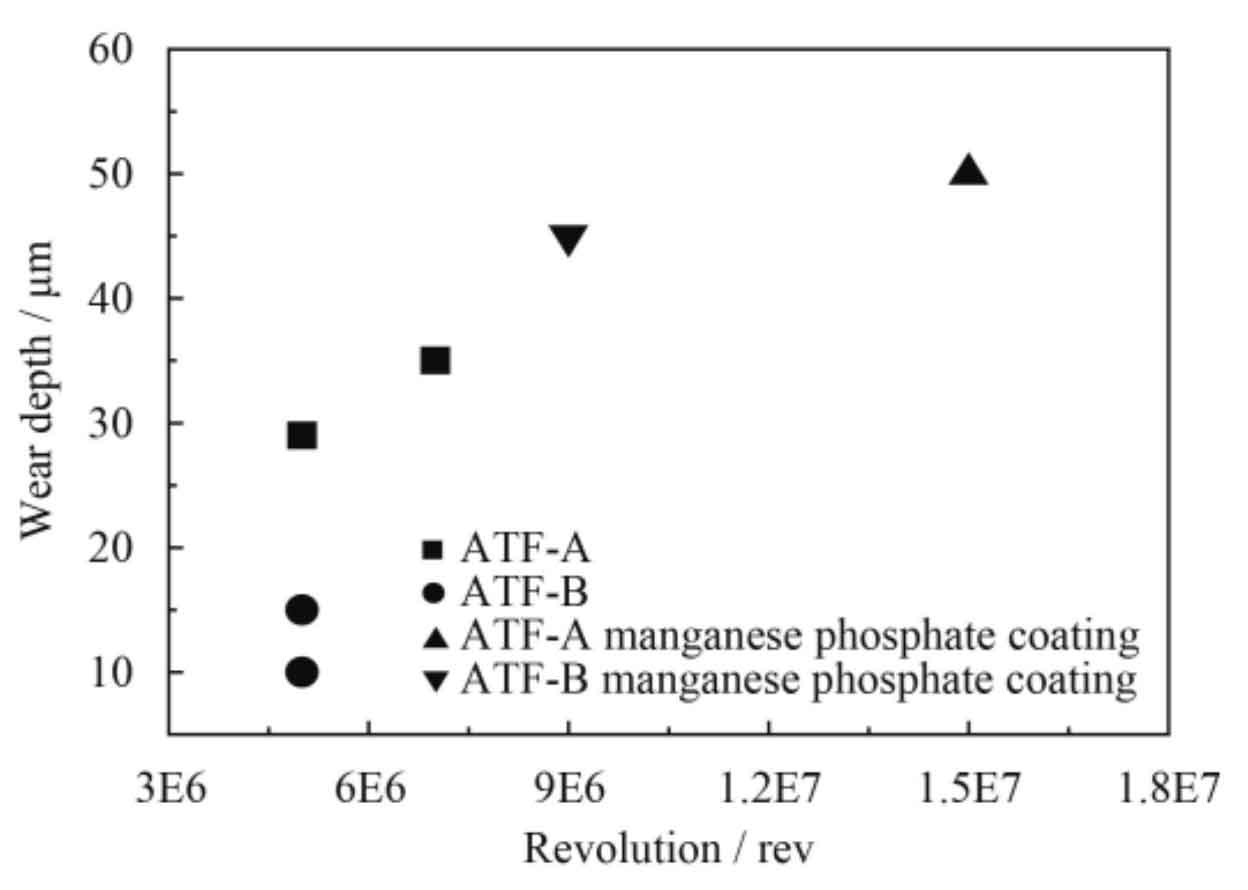
Figure 3 shows the wear amount at the bottom of the automobile helical gear. The driving pinion of the automobile helical gear pair a is much larger than the driving pinion of the automobile helical gear pair B. The experimental results show that the wear amount of automotive helical gear is inversely proportional to the pitting rate.