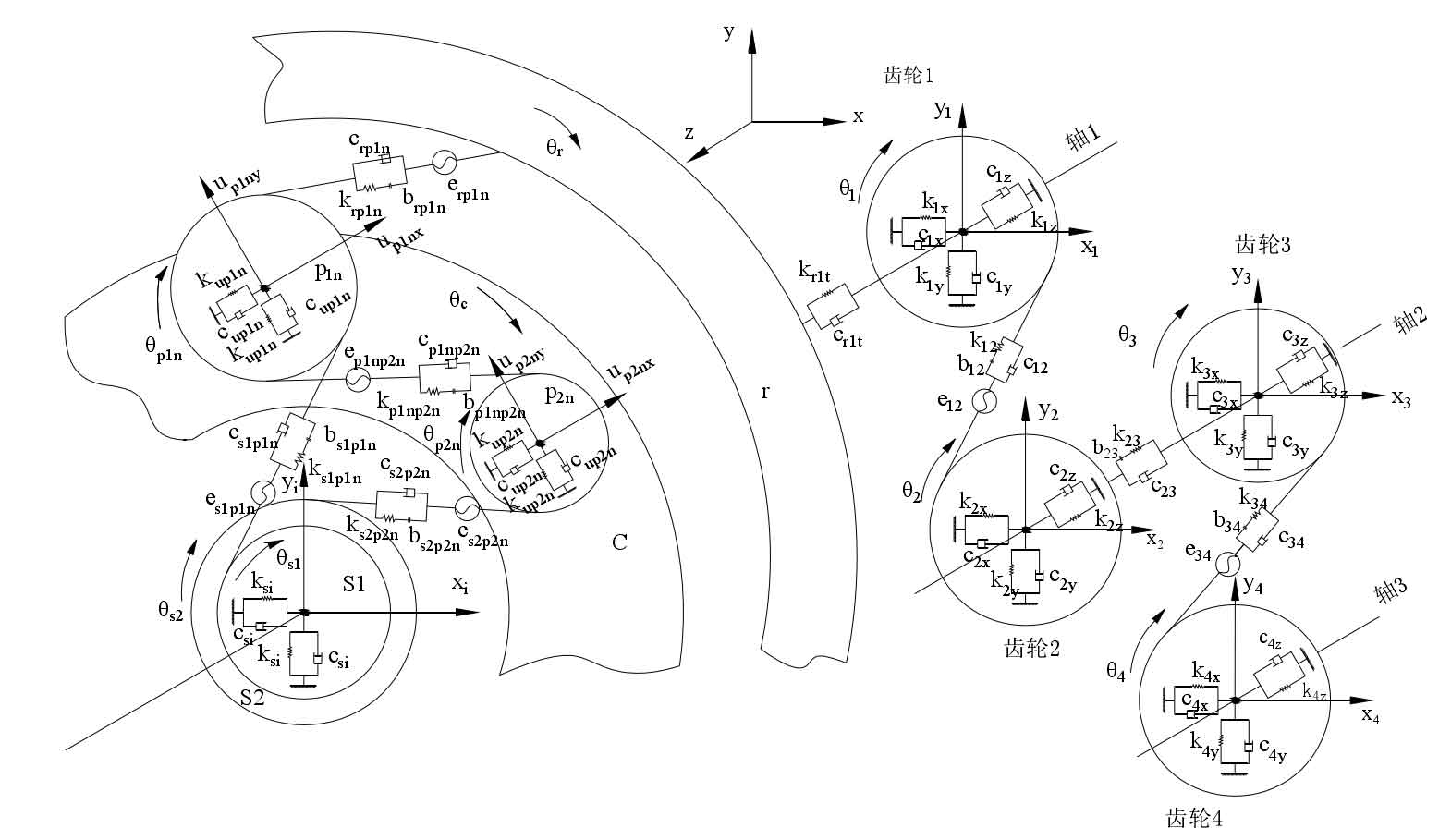
Using the lumped parameter method, fully consider the nonlinear factors in the gear transmission system, such as time-varying meshing stiffness, tooth side clearance and comprehensive meshing error, and establish the transverse torsional dynamic model of the whole gear transmission system of hybrid electric vehicle, as shown in the figure. In order to simplify the calculation, the system friction will not be considered. For the composite planetary gear mechanism, only the torsional deformation of each gear around its own axis and the radial deformation in two orthogonal directions in the plane perpendicular to the axis will be considered, the axial deformation along its axis will not be considered, and it is considered that the stiffness and damping of radial deformation are consistent. For the parallel shaft gear mechanism, the torsional deformation and radial deformation should be considered, as well as the axial deformation along its axis. It is considered that the stiffness and damping of radial deformation and axial deformation are consistent. In addition, the following assumptions are made:
(1) All gears in the system are involute helical gears. All gears are simplified into cylinders. The connection between teeth is connected by spring damping system, which is the meshing stiffness and damping coefficient of meshing pair; The meshing force between all gears acts on the meshing plane of the gear teeth;
(2) All large planetary gears have the same mass and moment of inertia, and all asteroid gears have the same mass and moment of inertia; The meshing stiffness, backlash and comprehensive meshing error of the same category are the same.
As shown in the figure, C, S1, S2, p1n, p2n, R, gear 1, gear 2, gear 3 and gear 4 represent planet carrier, small sun gear, large sun gear, large planet gear, asteroid gear (n represents the nth planet gear), ring gear, output gear, second reduction gear, second reduction pinion and differential. S1p1n, s2p2n, p1np2n, rp1n represent the meshing pair of small sun gear S1 and big planet gear p1n, the meshing pair of big sun gear S2 and asteroid gear p2n, the meshing pair of asteroid gear p2n and big planet gear p1n, the meshing pair of big planet gear p1n and ring gear R, and Kat represents the torsional stiffness of the central member (a = C, S1, S2, R). Cat represents the torsional damping of the central member (a = C, S1, S2, R). KJ represents the comprehensive stiffness of the gear meshing pair, CJ represents the meshing damping of the gear meshing pair, BJ represents half of the tooth side clearance, and EJ represents the comprehensive meshing error (J = s1p1n, s2p2n, p1np2n, rp1n). Mi,, II (I = C, S1, S2, p1n, p2n, R) represent the mass and moment of inertia of planet carrier C, small sun gear S1, large sun gear S2, large planet gear p1n, asteroid gear p2n and ring gear R respectively. RP (P = C, S1, S2, p1n, p2n, R) represents the base circle radius of small sun gear S1, large sun gear S2, large planet gear p1n, asteroid gear p2n and ring gear R, and RC is the calculated radius of planet carrier. θ c、 θ s1、 θ s2、 θ R represents the angular displacement of planet carrier C, small sun gear S1, large sun gear S2 and ring gear R. θ p1nc、 θ P2nc represents the angular displacement of the large planetary gear and the asteroid gear relative to the planet carrier. As defined below θ p1nc= θ p1n- θ c, θ p2nc= θ p2n- θ c, θ p1n,、 θ P2n represents the absolute angular displacement of p1n and p2n respectively. XC and YC represent the lateral displacement and longitudinal displacement of planet carrier C, XR and yr represent the lateral displacement and longitudinal displacement of ring gear R, XC and YC represent the lateral displacement and longitudinal displacement of small sun gear S1, XS2 and YS2 represent the lateral displacement and longitudinal displacement of small sun gear S2, up1nx and up1ny represent the lateral displacement and longitudinal displacement of large planet gear p1n, up2nx and up2ny represent the lateral displacement and longitudinal displacement of large planet gear p2n, KC, Kr, KS1, KS2, KP1 KP2 represents the support stiffness of planet carrier, ring gear, small sun gear, big sun gear, big planet gear and asteroid gear, and CC, Cr, CS1, CS2, CP1 and CP2 represent the support damping of planet carrier, ring gear, small sun gear, big sun gear, big planet gear and asteroid gear. K12 and K34 represent the comprehensive stiffness of the gear meshing pair, C12 and C34 represent the meshing damping of the gear meshing pair, EAB represents the comprehensive meshing error of the gear meshing pair, Kax, Kay, Kaz and Kat represent the transverse, longitudinal, tangential and torsional stiffness of the driving gear respectively, kbx, kby, KBZ and kBT represent the transverse, longitudinal, tangential and torsional stiffness of the driven gear respectively, and CAX, cay, caz and cat represent the transverse, longitudinal and torsional stiffness of the driving gear respectively Tangential and torsional support damping CBX, CBY, CBZ and CBT respectively represent the transverse, longitudinal, tangential and torsional support damping of the driven gear, Xa, ya, ZA θ A represents the transverse displacement, longitudinal displacement, tangential displacement and rotational angular displacement of the driving gear, XB, Yb, ZB θ B represents the lateral displacement, longitudinal displacement, tangential displacement and rotational angular displacement of the driven gear respectively, β B is the helix angle of the base circle, RA and Rb represent the radius of the base circle of driving gears 1 and 3 and driven gears 2 and 4. A represents driving gears 1 and 3, and B represents driven gears 2 and 4.