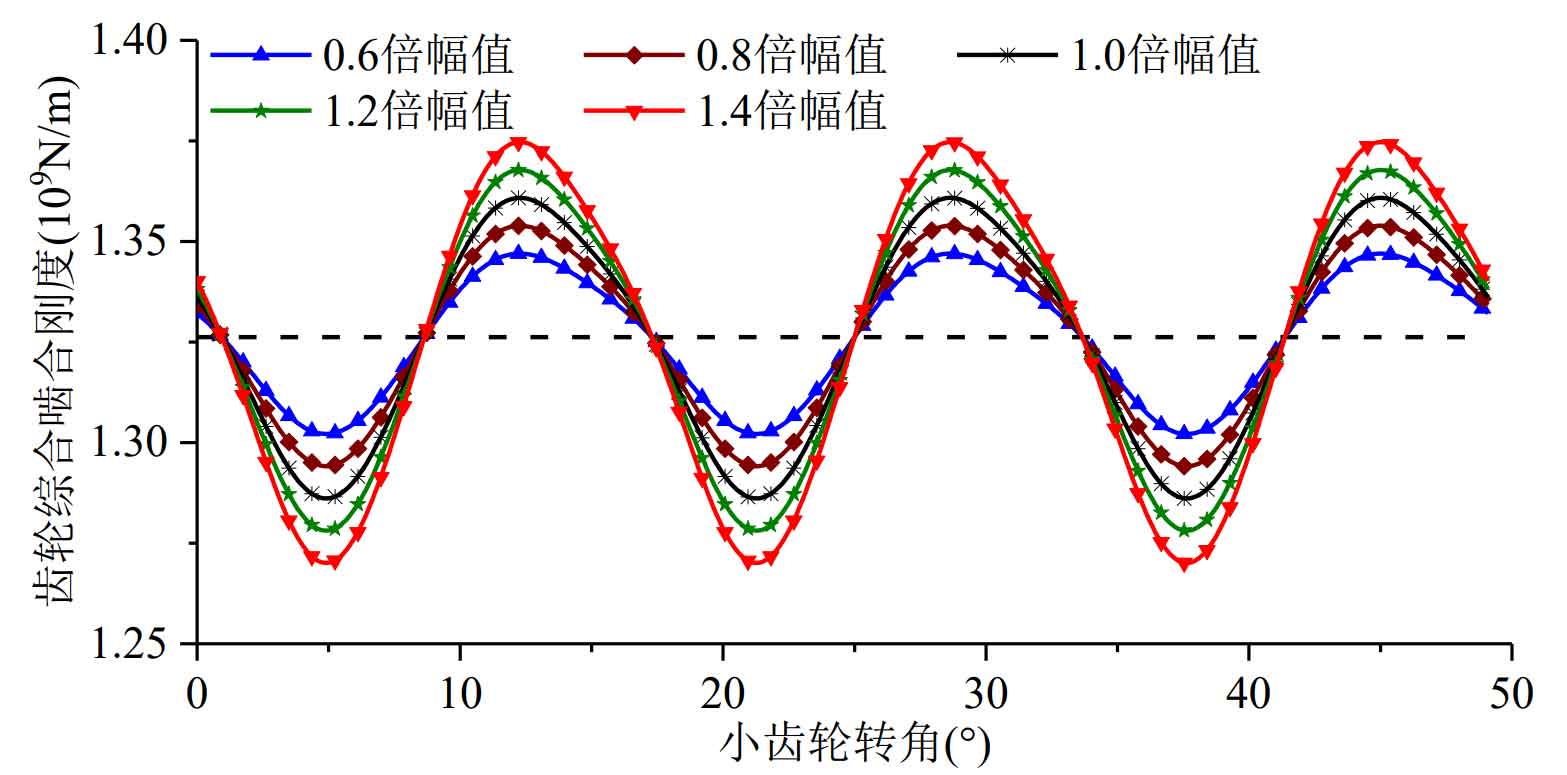
In order to study the influence of the time-varying meshing stiffness amplitude of gears on the vibration characteristics of the system, five different time-varying meshing stiffness amplitudes (the mean value and period of meshing stiffness are unchanged, as shown in Figure 1) are taken as the system excitation based on the calculated time-varying meshing stiffness curve. After the solution, the root mean square value of the vibration acceleration in the direction of the meshing line of the system is obtained, and the vibration speed diagram of the system is made as shown in Figure 2.
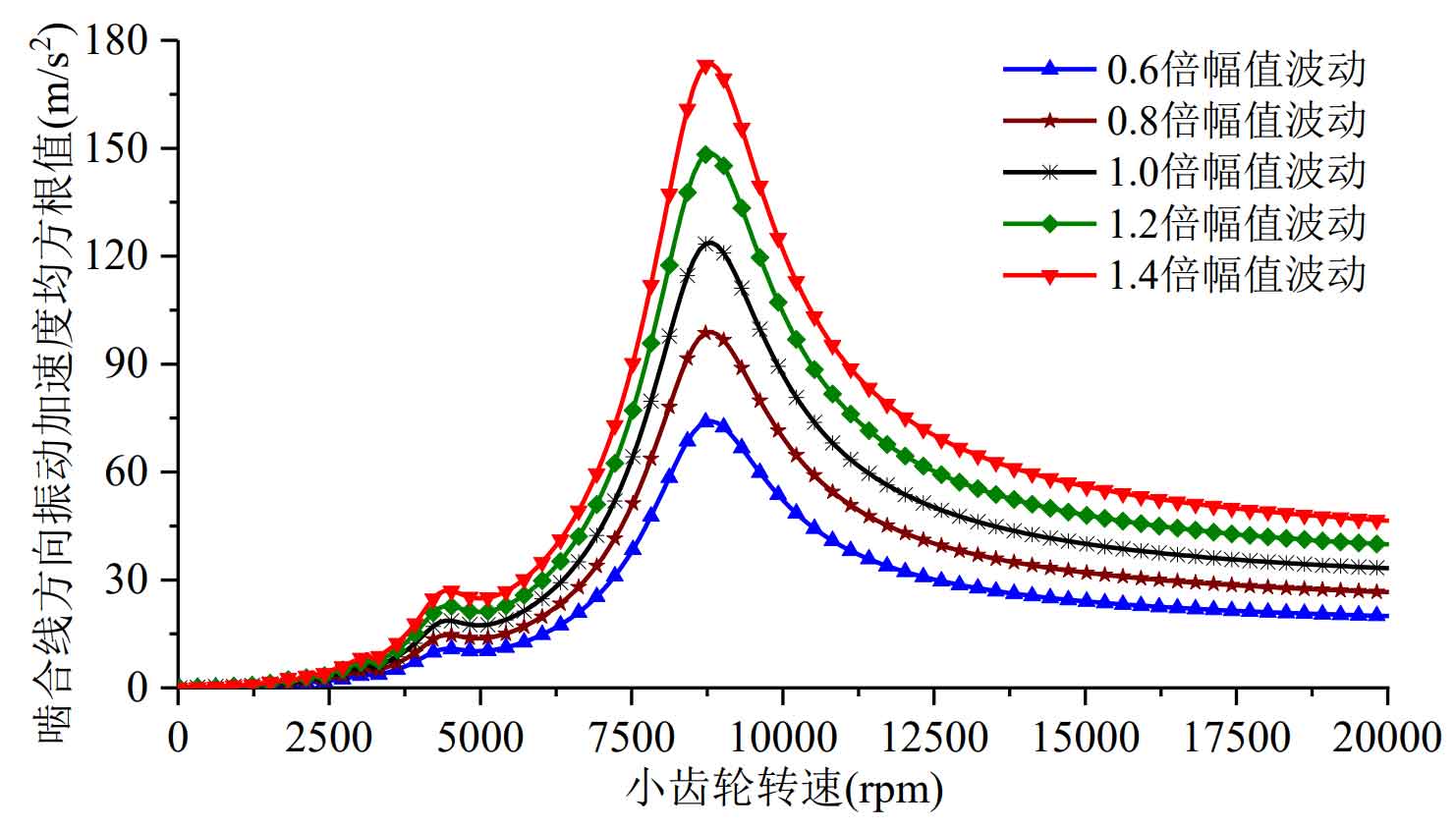
It can be seen from Figure 2 that the larger the time-varying meshing stiffness amplitude is, the larger the root mean square value of gear relative vibration acceleration is when the mean value of gear meshing stiffness is unchanged; The amplitude change of time-varying meshing stiffness does not cause obvious change of system resonance speed; Moreover, near the resonance speed of the system, the increase of time-varying meshing stiffness amplitude will increase the change rate of the root mean square value of the relative vibration acceleration of the system relative to the speed. As mentioned earlier, this will lead to the deterioration of the system stability when the gear speed reaches the resonance speed.
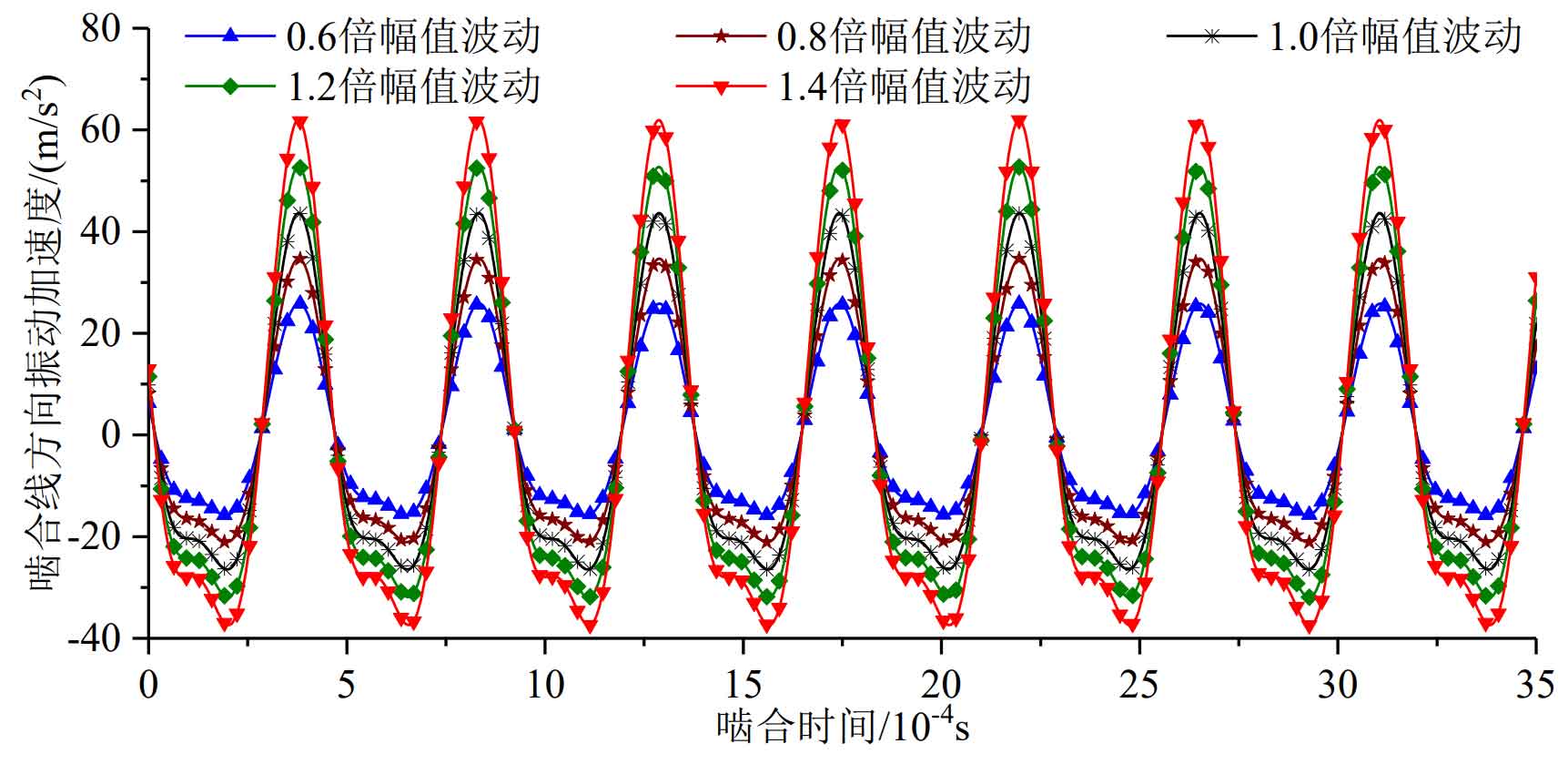
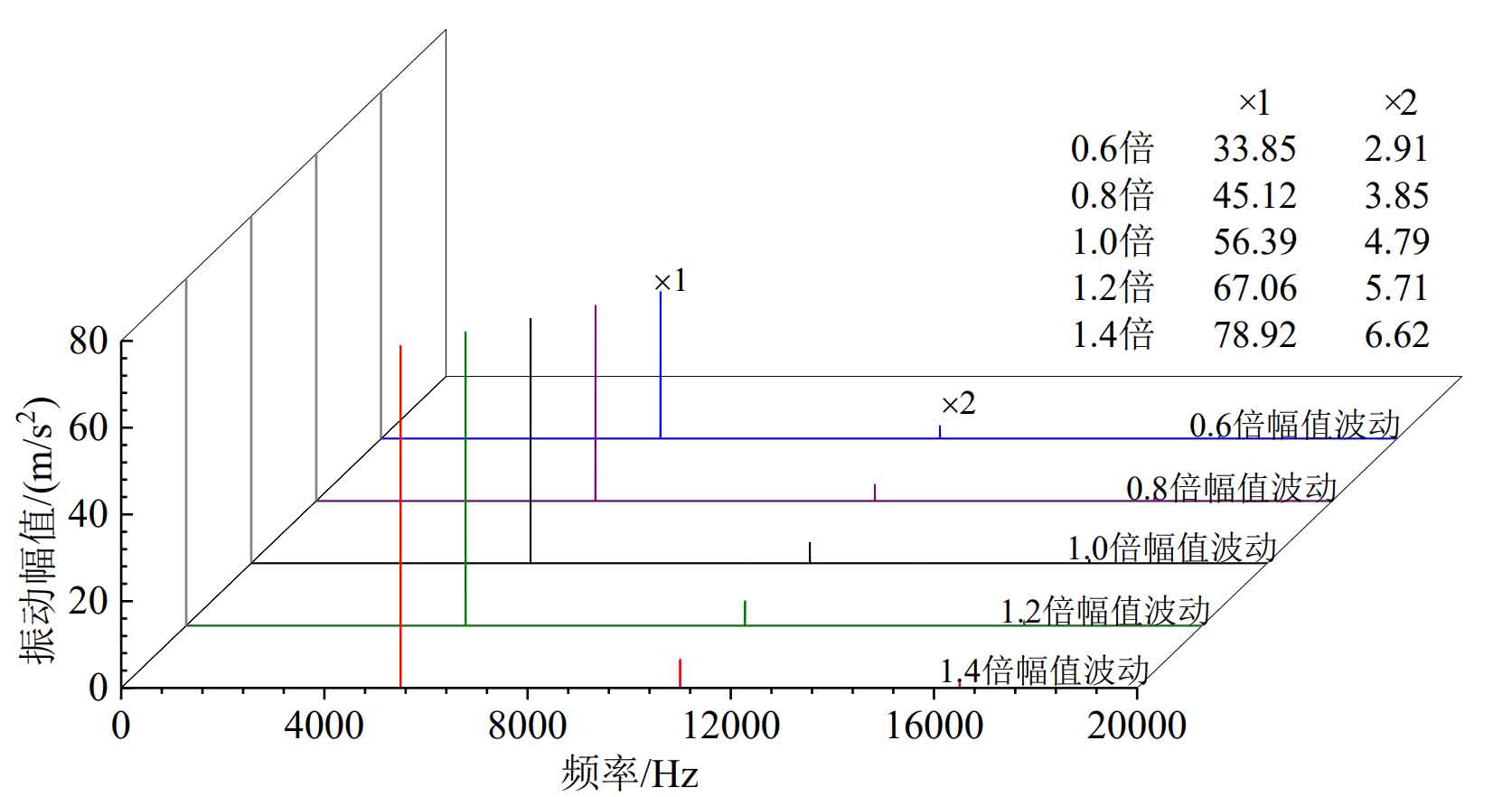
Figure 3 and Figure 5 are the time domain diagrams of the meshing line direction vibration under five different time-varying meshing stiffness amplitudes at 9000rpm and 15000rpm respectively, and their frequency domain diagrams are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 6.
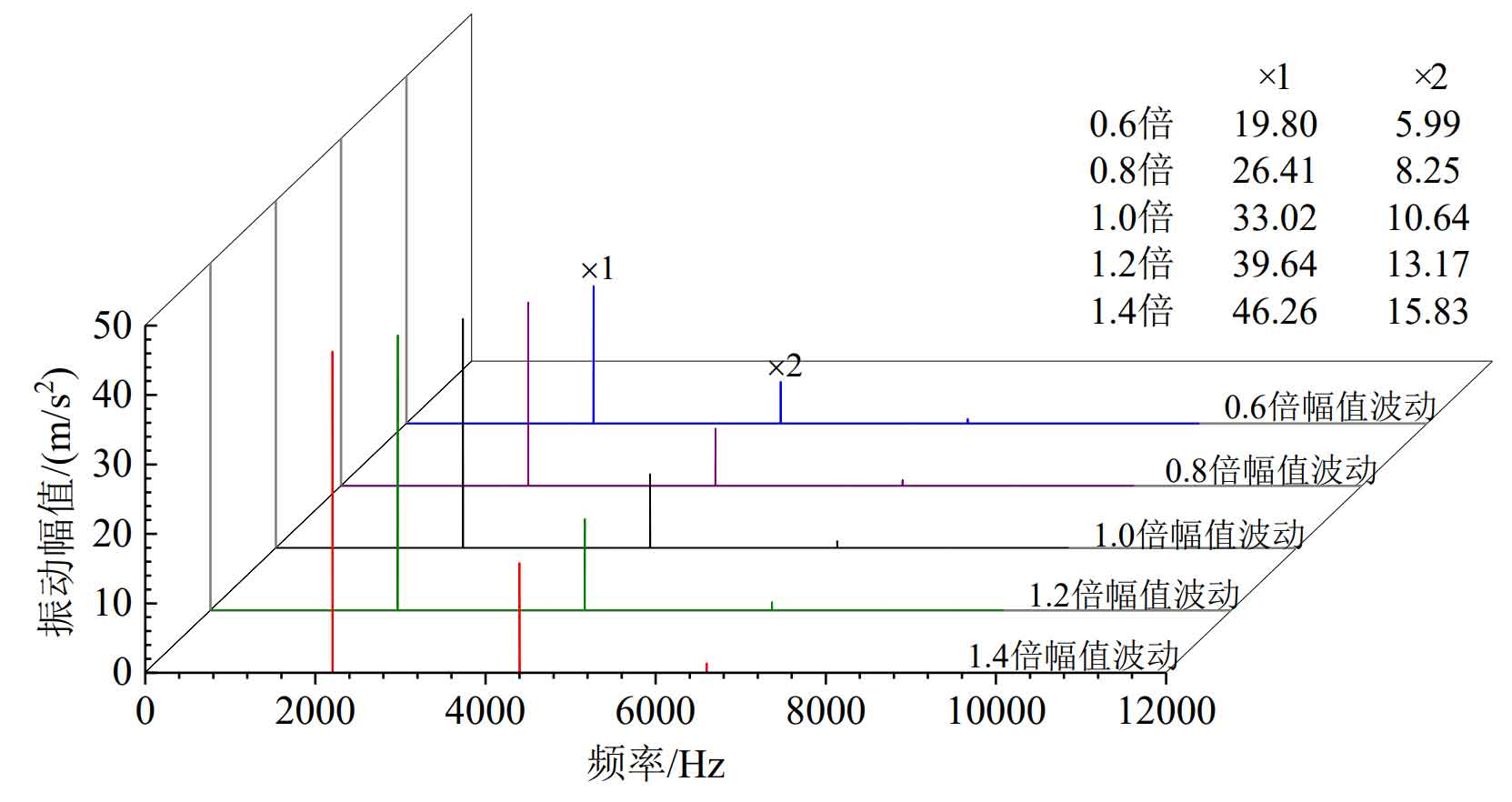
It can be seen from Figure 3 that the greater the amplitude of time-varying meshing stiffness, the greater the fluctuation of relative vibration acceleration in the direction of system meshing line. Figure 4 shows that the greater the amplitude of time-varying meshing stiffness, the greater the amplitude of each order of vibration response of the system.
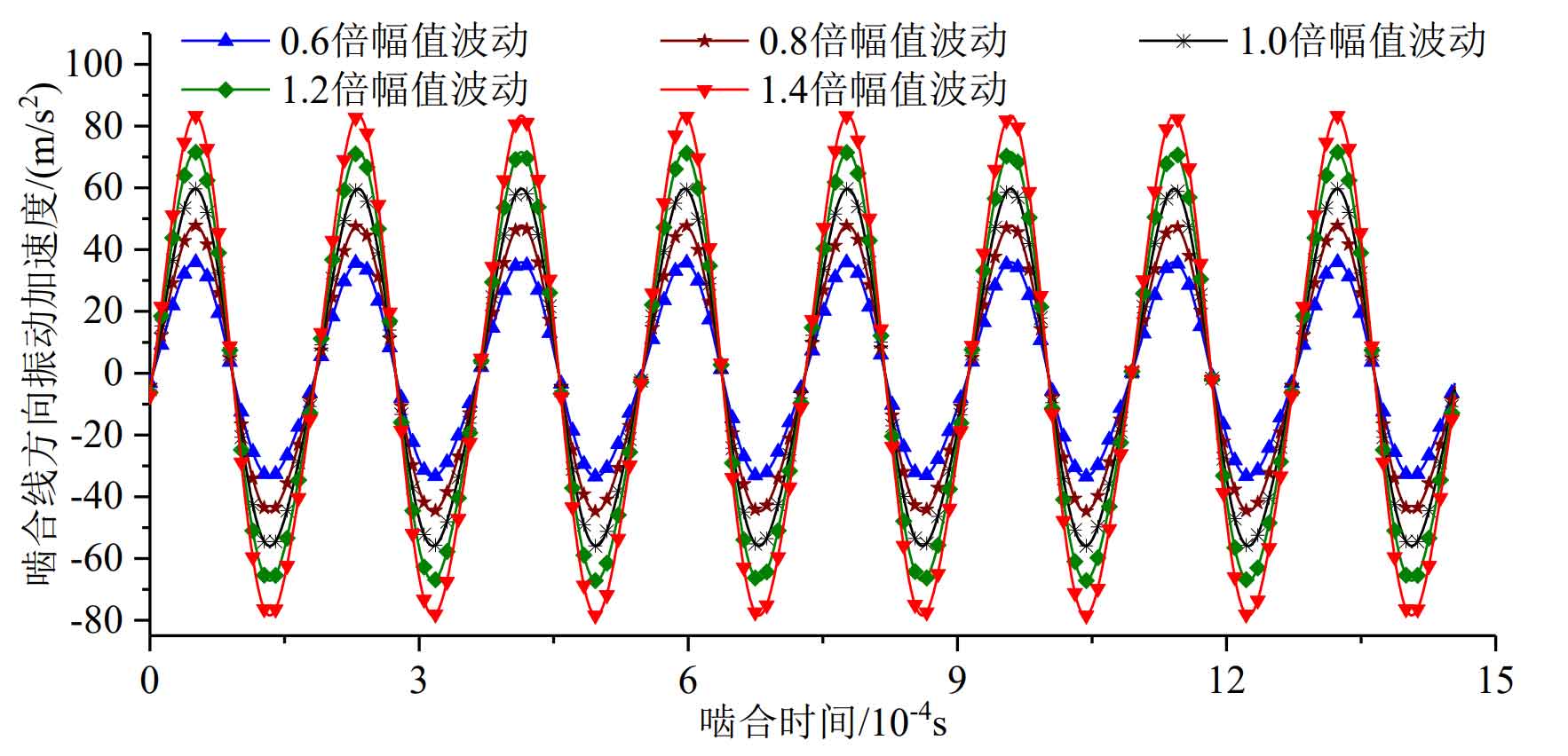
Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the system vibration response results at 15000 rpm under different time-varying meshing stiffness amplitudes. It can be seen from the figure that the larger the time-varying meshing stiffness amplitude is, the greater the relative vibration acceleration fluctuation in the direction of the system meshing line is, which is consistent with the analysis results.