Miner’s linear cumulative damage rule believes that under the repeated action of a given stress level, the damage and stress cycle have a linear cumulative relationship. When the damage accumulates to a certain critical value, it will cause damage, namely:
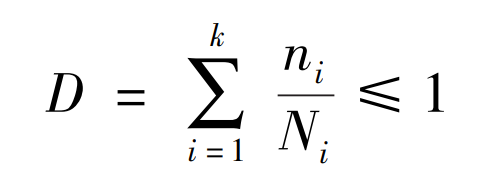
Where, ni represents the number of working cycles under the action of symmetrical cyclic stress level; Ni represents the corresponding failure life (number of cycles); D represents the total damage in a typical load cycle.
According to Miner’s cumulative fatigue damage theory, the fatigue life of the component is T=1/D, that is, the component will be damaged if the typical load cycle is performed T times.
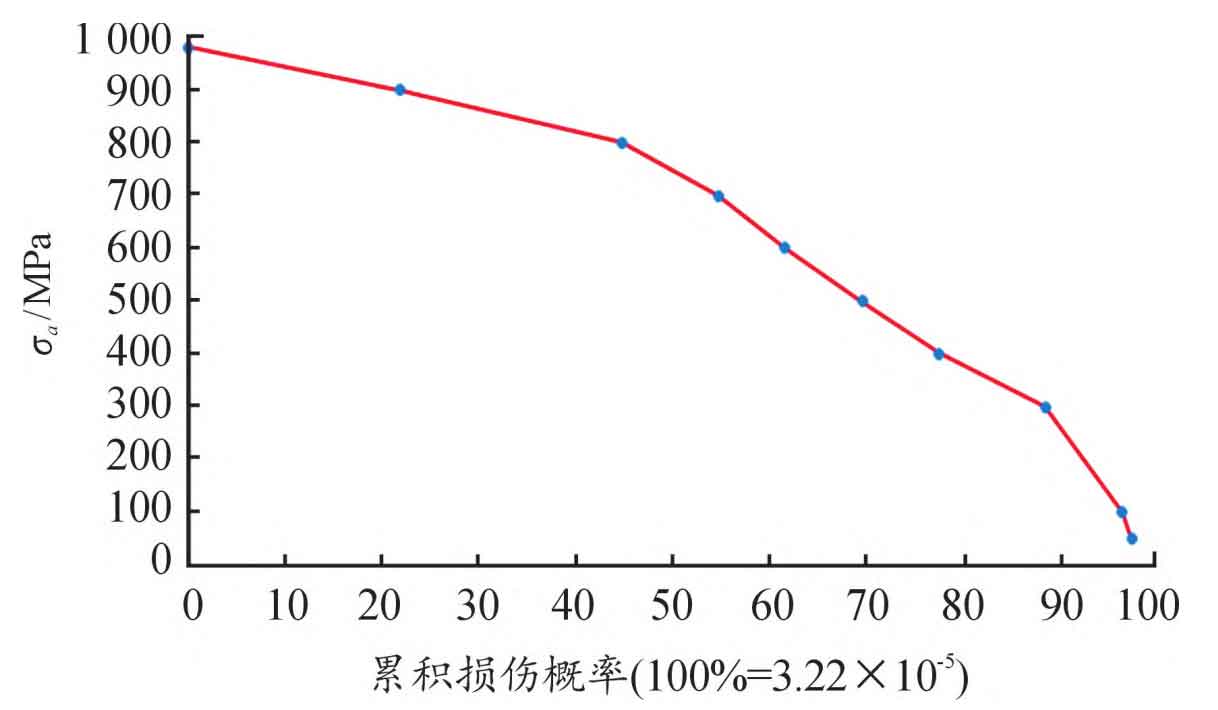
Based on the modified P-S-N curve, the fatigue damage under different stress amplitudes is calculated respectively. According to Miner’s linear cumulative fatigue damage theory, the damage of the transmission driving high-speed helical gear under a cyclic driving condition (UDDS) is calculated D=3.22 × 10-5, as shown in the figure. According to the fatigue life formula, the contact fatigue life of transmission helical gear is T=3.1 × 104, that is, after 3.1 × After 104 UDDS cycles, the helical gear has reached contact fatigue failure, and the mileage life of pure electric vehicle is 370000km.
