The coincidence ratio of the straight bevel gear pair is generally greater than 1.0. When the straight bevel gear is meshed, many pairs of teeth will mesh at the same time, resulting in the distribution of load between the teeth of the meshing gear, so the load distribution ratio cannot be ignored. At present, there is no report on its calculation method. According to the method of solving the load distribution rate of helical gears, the teeth of straight bevel gears are divided into countless micro gears along the tooth width direction, and the load distribution rate model of straight bevel gears is established by combining the minimum potential energy method.
The total potential energy U of the gear is obtained by superposition of the potential energy Uo of the differential gear, as shown in the formula.
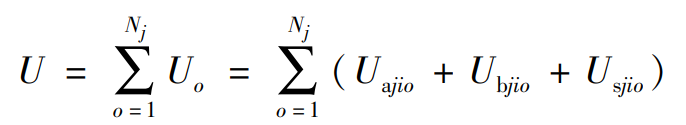
The bending potential energy Ubjio, compression potential energy Uajio and shear potential energy Usjio (i=1,2; j=p, g) of the differential gear can be obtained from the formula respectively.
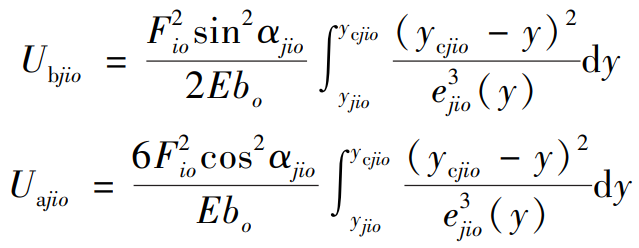
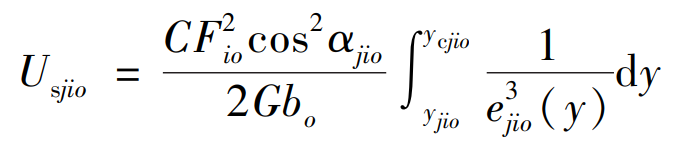
The potential energy Uo of the differential gear can be obtained from the formula.
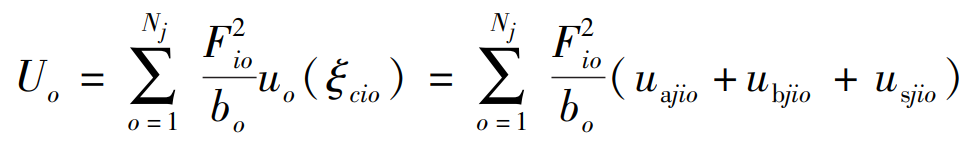
Where: uo( ξ Cio), uajio, ubjio and usjio are the unit potential energy and the bending, compression and shear unit potential energy of the micro-element gear, respectively.
According to the principle of elastic potential energy and Lagrange method, the load distribution rate of straight bevel gear can be obtained as shown in the formula.
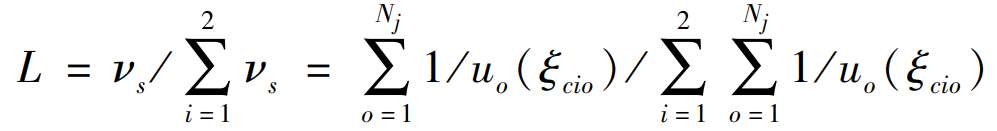
Where, ν S is the inverse unit potential energy of the gear tooth. The load distribution rate model of straight bevel gear with multi-state meshing characteristics is shown in the formula.
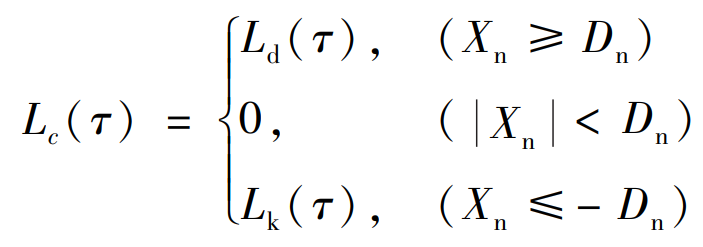
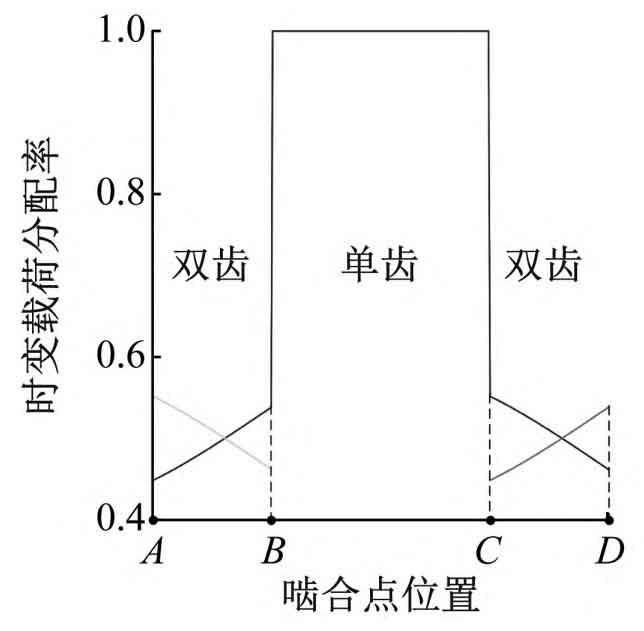
Where, Ld( τ) And Lk( τ) They are respectively the load distribution rate under the tooth surface meshing state and the tooth back contact state. The load distribution rate of the straight bevel gear pair shown in the calculation is shown in the figure. The solid line in the figure represents the load distribution rate of the ith meshing tooth pair, and the dotted line in AB and CD segments represents the load distribution rate of the i-1 and i+1 meshing tooth pair respectively.
