The three-way Dexel modeling engine used is ModuleWorks. In order to establish the simulation, a triangular mesh model is created according to the geometric parameters of hobs and cylindrical gear blanks, and converted into the Dexel model in the engine. In order to reduce the amount of computation, each rack profile on the hob is modeled as an infinitely small thin layer extruded from its rake face. Cylindrical gear blanks are modeled with cylinders. The kinematics model uses process parameters to simulate the relative motion of hobs relative to cylindrical gears. At each time step, the hob uses interpolation method to cut at different track points. The simulation visualization of cylindrical gear hobbing based on three-way Dexel in WCS is shown in Figure 1.

The extraction method of two-dimensional undeformed chip geometric features is shown in Figure 2.
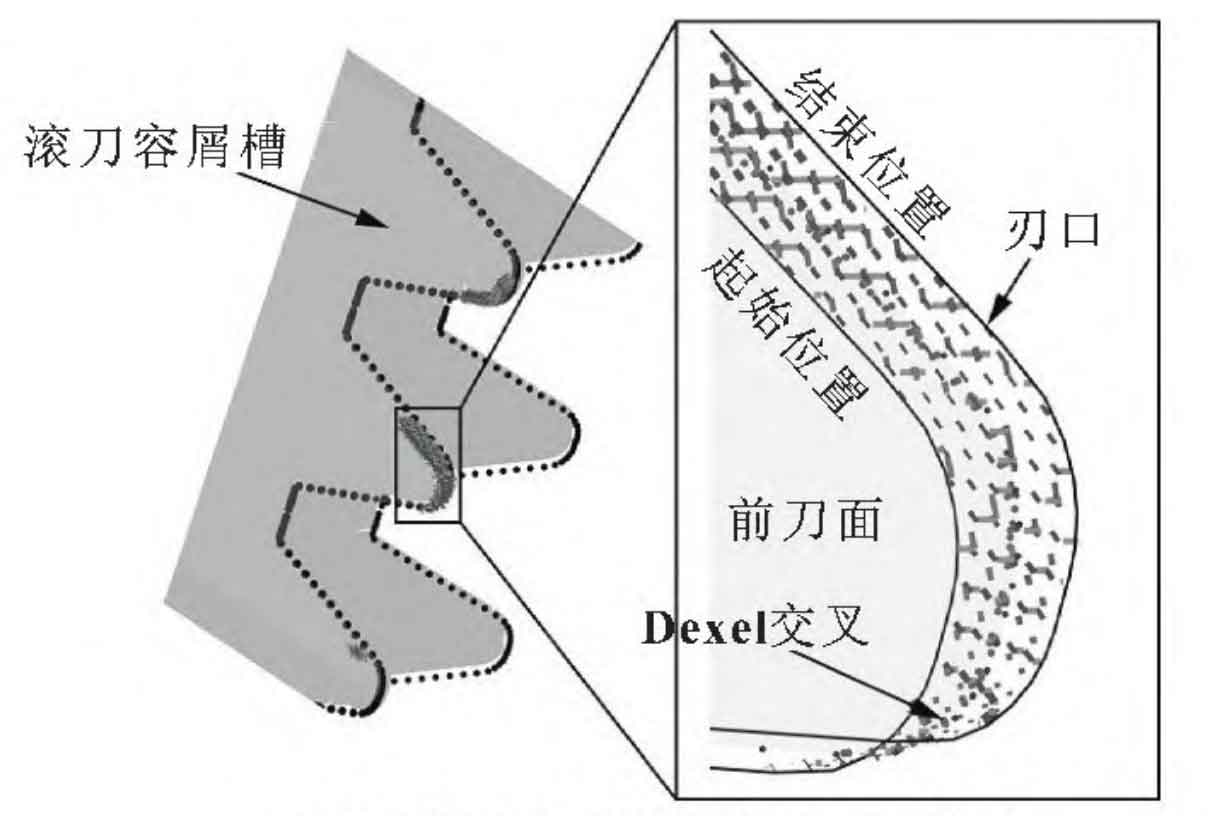
The CWE data extracted by simulation is used to determine the geometric characteristics of undeformed chips, as shown in Figure 2 (a). The Dexel model of 3D undeformed chips is packaged along the contour of XY, YZ and ZX planes. Then, the rake face of the tool intersects these contours to create a 2D point cloud. Delaunay triangulation and alpha shape reconstruction are performed on the point cloud to obtain the instantaneous two-dimensional undeformed chip geometric features of each time step, as shown in Figure 2 (b).
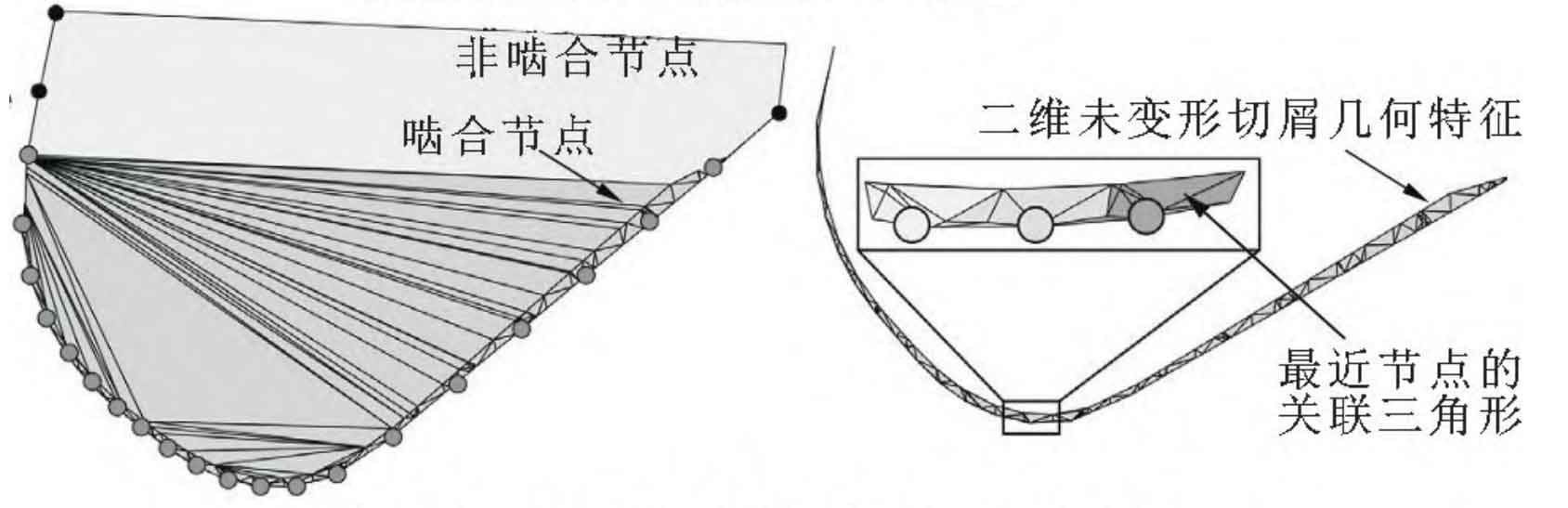
This triangulation also determines the meshing conditions of each discrete node along the cutting edge. Therefore, by extending the CWE calculation to the cylindrical gear hobbing process, the three-dimensional Dexel model can be used to accurately and efficiently calculate the dynamic and undeformed chip geometric characteristics.
