Through experimental verification of the wear resistance of automotive gear forging blanks, it can be seen that different heat treatment processes can cause varying degrees of changes in the wear resistance of automotive gear forging blanks. When using conventional annealing methods to heat treat automotive gear forging blank test samples, the wear volume of the test sample varies inversely with the annealing temperature. As the annealing temperature continues to increase, the wear volume of the test sample can gradually decrease. When the wear volume of the test sample decreases to the minimum range, there is a trend of increasing. When the isothermal annealing method is used to heat treat the automotive gear forging blank test sample, the volume of the test sample decreases significantly, and the wear volume and wear resistance of the test sample vary inversely. As the wear volume of the test sample decreases, the wear resistance of the automotive gear forging blank can be improved. When the wear volume of the test sample increases, the wear resistance of the automotive gear forging billet gradually deteriorates. From the changes in the test samples, it can be seen that using conventional annealing and isothermal annealing methods to heat treat the sample samples respectively, among which the isothermal annealing method has more advantages and is conducive to enhancing the wear resistance of the test samples. The test results of wear resistance of automotive gear forging blanks are shown in the figure.
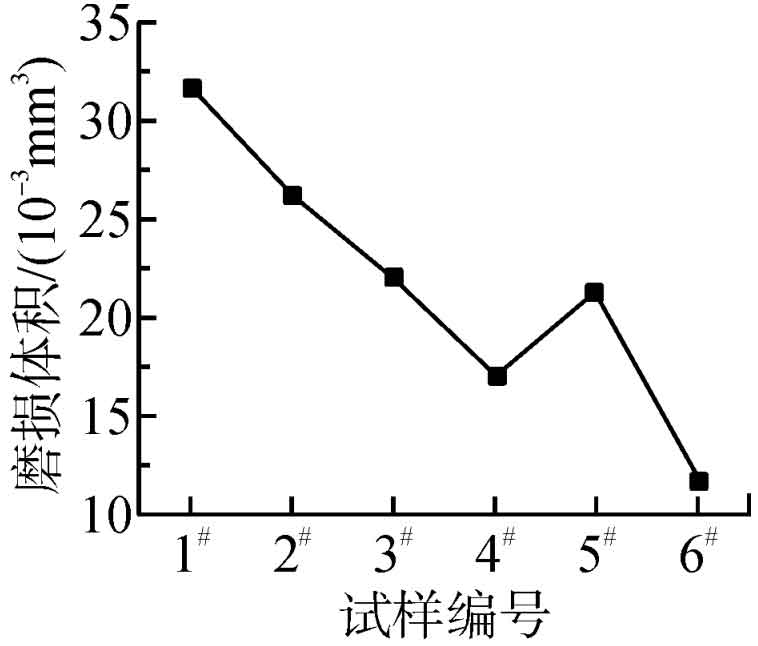
As can be seen from the figure, when the annealing temperature is controlled at 800 ℃, among many test samples, the wear volume of No. 1 is the largest, with a value of 31.8 × 10 ^ – 3 mm ^ 3, this test sample has the worst wear resistance. When the annealing temperature is controlled at 860 ℃, the wear volume value of No. 4 in many test samples is 17.1 × Using a comparative analysis method, the wear volume of No. 4 and No. 1 was reduced by 46% compared to No. 1. When using conventional annealing methods to heat treat the test sample, the wear volume of No. 4 sample is the smallest, but the wear resistance of this sample is the best. When the annealing temperature is controlled at 880 ℃, the wear volume value of No. 4 is 21.5 × The wear volume of No. 4 of 10 ^ – 3mm ^ 3 is 32% smaller than that of No. 1, and its wear resistance shows a downward trend.
When heat treating automotive gear forging blanks, the annealing temperature should be strictly controlled. An appropriate annealing temperature can improve the wear resistance of automotive gear forging blanks to a certain extent. When using conventional annealing methods to heat treat samples, the annealing temperature should be adjusted to 860 ℃. When isothermal annealing method is used to treat automotive gear forging blanks, the wear volume of No. 6 is 11.8 × 10 ^ – 3mm ^ 3, the wear volume of this sample decreased by 63% compared to No. 1 and 31% compared to No. 4. The performance of the test samples treated by isothermal annealing method is significantly better than that of the test samples treated by conventional annealing method.
The samples of Test Nos. 4 and 6 were processed using conventional annealing and isothermal annealing methods, and the apparent appearance of Test Nos. 4 and 6 was analyzed using JSM6510 scanning electron microscope. The surface of No. 4 has many wear marks accompanied by peeling, and the wear phenomenon of this sample is relatively serious. There are a small amount of small wear marks on the surface of No. 6, and this sample has fewer peeling phenomena, and its wear resistance has significantly improved compared to the previous one. In summary, the isothermal annealing process is more suitable for the production and manufacturing of automotive gears, which can significantly improve the wear resistance of automotive gears.
