The hypoid gear is a type of spiral bevel gear used to transmit power between non-intersecting and non-parallel shafts, typically in a 90-degree angle configuration. Hypoid gears are commonly found in automotive differentials, where they are used to transmit power from the driveshaft to the axle shafts in a compact and efficient manner.
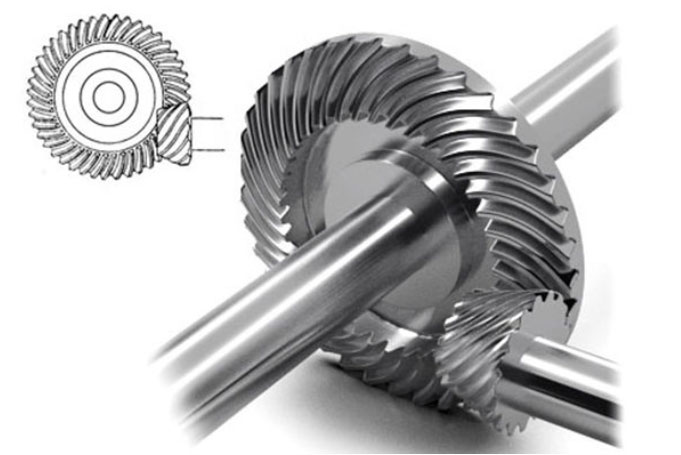
Hypoid gears have several distinguishing characteristics:
- Axis offset: Unlike standard bevel gears, the axes of hypoid gears do not intersect. The pinion (smaller gear) is offset from the center of the larger gear (ring gear), allowing for a larger contact area between the teeth and, consequently, increased load-carrying capacity.
- Tooth geometry: Hypoid gear teeth have a complex geometry, combining elements of spiral bevel gears and worm gears. The teeth are helical and curved, allowing for gradual engagement and reduced noise and vibration during operation.
- Lubrication: Hypoid gears require specialized lubricants due to the sliding contact between the gear teeth. These lubricants typically contain extreme pressure additives to provide adequate protection against wear and ensure a long service life.
Advantages of hypoid gears:
- High torque capacity: Hypoid gears have a larger contact area between the teeth than standard bevel gears, resulting in increased load-carrying capacity and higher torque transmission.
- Smooth operation: The helical and curved tooth geometry allows for gradual engagement, reducing noise and vibration during operation. This makes hypoid gears particularly suitable for automotive applications, where noise and vibration reduction are important factors.
- Compact design: Hypoid gears can transmit power between non-intersecting shafts in a compact and efficient manner, making them an ideal choice for space-constrained applications such as automotive differentials.
- Flexibility: Hypoid gears offer greater flexibility in terms of shaft angles and offsets compared to other types of gears, allowing for more versatile designs.
Disadvantages of hypoid gears:
- Complexity: The complex tooth geometry of hypoid gears makes them more difficult and expensive to manufacture compared to simpler gear types, such as spur or helical gears.
- Lubrication requirements: Hypoid gears require specialized lubricants due to the sliding contact between the teeth, increasing maintenance requirements and costs.
- Efficiency: Due to the sliding contact between the teeth, hypoid gears generally have lower efficiency compared to other gear types, such as helical or spur gears.
Despite these disadvantages, hypoid gears are widely used in automotive applications and other situations where high torque capacity, smooth operation, and compact design are crucial.
Pages: 1 2
