Gear hobbing is indeed an essential process in the field of precision gear manufacturing. It is a highly efficient and versatile machining method used to produce gears with excellent precision, accuracy, and surface finish. Gear hobbing is widely employed in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, robotics, and machinery.
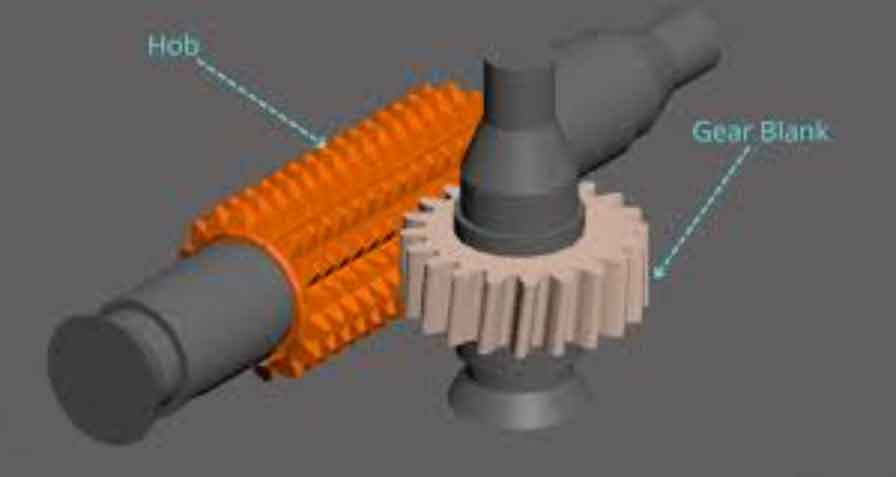
The gear hobbing process involves the use of a specialized cutting tool called a hob. The hob is a cylindrical-shaped tool with helical cutting teeth that progressively engage with the workpiece, removing material to create the desired gear shape. The hob is mounted on a hobbing machine, which is specifically designed for this purpose.
Here are the key steps involved in the gear hobbing process:
- Workpiece Mounting: The workpiece, typically a blank cylindrical gear, is securely mounted on the hobbing machine. It is positioned and aligned properly to ensure accurate gear cutting.
- Hob and Workpiece Alignment: The hob and the workpiece must be precisely aligned to ensure proper engagement of the hob’s teeth with the workpiece. This alignment is achieved by adjusting the machine’s settings.
- Cutting Operation: The hobbing machine starts rotating the workpiece while the hob is fed into it. The rotational motion of the workpiece and the cutting action of the hob create the desired gear tooth profile. The cutting is done progressively as the workpiece rotates, resulting in multiple gear teeth being formed.
- Indexing: Once a complete revolution of the workpiece is completed, an indexing mechanism in the hobbing machine moves the workpiece by a predetermined amount. This ensures that the hob cuts the next set of teeth accurately.
- Cutting Fluid Application: During the cutting process, a cutting fluid, such as oil or emulsion, is applied to lubricate and cool the cutting area. This helps in reducing friction, dissipating heat, and prolonging tool life.
- Finishing and Inspection: After the gear hobbing process is complete, the gear is carefully inspected for dimensional accuracy, tooth profile, surface finish, and other quality parameters. Any necessary finishing operations, such as deburring or chamfering, may be performed at this stage.
Gear hobbing offers several advantages for precision gear manufacturing:
- High Precision: Gear hobbing enables the production of gears with excellent dimensional accuracy, ensuring proper meshing and smooth operation.
- Versatility: The hobbing process can be used to manufacture various types of gears, including spur gears, helical gears, worm gears, and splines.
- Efficiency: Gear hobbing is a relatively fast and efficient method for producing gears in large quantities. The continuous cutting action of the hobbing process allows for high productivity.
- Cost-effectiveness: Once the hob is manufactured, the gear hobbing process can be cost-effective for large-scale production runs due to its efficiency and repeatability.
Despite its advantages, gear hobbing does have some limitations. It is primarily suitable for medium to large-sized gears due to the size constraints of the hobbing machines. Additionally, the initial setup and tooling costs can be relatively high for small production runs or specialized gear designs.
Overall, gear hobbing is an essential process in precision gear manufacturing, providing high-quality gears with precise tooth profiles, ensuring smooth and efficient power transmission in various applications.
