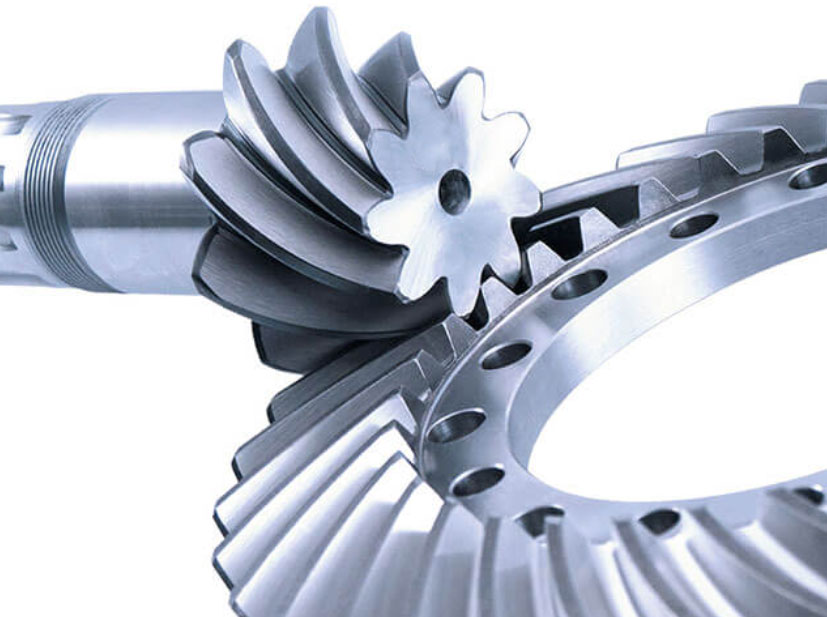
The manufacturing process of spiral bevel gears involves several steps to create precise gear tooth profiles and ensure the gears’ functionality and performance. Advanced machining and gear cutting techniques are used to produce high-quality spiral bevel gears with tight tolerances. Here’s an overview of the typical manufacturing process of spiral bevel gears:
1. Gear Design:
The process begins with the design of the spiral bevel gears. Engineers use computer-aided design (CAD) software to create 3D models of the gears, specifying the gear geometry, helix angle, number of teeth, and other critical parameters based on the application requirements.
2. Gear Blank Preparation:
The first step in manufacturing is to prepare the gear blank, which is the initial piece of material from which the gear will be formed. Gear blanks can be made from various materials, such as alloy steel, stainless steel, or bronze.
3. Rough Machining:
The gear blank is rough machined to achieve the general shape of the gear. This process involves removing excess material to form the gear’s basic structure. CNC machining or other precision machining techniques are used for this step.
4. Gear Cutting – Hypoid Gear Generators:
The next crucial step is gear cutting, where specialized machines known as hypoid gear generators are used. These machines use cutting tools called gear cutters or gear hob cutters to form the tooth profiles. The hypoid gear generator is capable of precisely cutting the spiral bevel gears’ helical tooth profile.
5. Gear Grinding:
After gear cutting, the spiral bevel gears undergo gear grinding to achieve the final tooth profile with high accuracy. Gear grinding removes any remaining imperfections from the tooth surfaces, resulting in smooth and precise tooth profiles. This process is essential for ensuring proper tooth engagement and low noise levels during gear operation.
6. Heat Treatment:
The gears are subjected to heat treatment processes such as carburizing, quenching, and tempering to improve their hardness, wear resistance, and durability. Heat treatment ensures that the gears can withstand the mechanical stresses encountered during operation.
7. Finishing and Inspection:
The gears undergo finishing processes, such as deburring and polishing, to remove any remaining burrs or imperfections. After finishing, the gears are inspected using various measurement techniques to verify that they meet the specified tolerances and quality standards.
8. Surface Coating (Optional):
Depending on the application requirements, spiral bevel gears may undergo surface coating or plating for additional protection against wear, corrosion, or to enhance lubrication properties.
9. Assembly:
The spiral bevel gears are assembled into gearboxes or gear systems, ensuring proper alignment and backlash adjustment for optimal performance.
10. Quality Control:
Throughout the manufacturing process, strict quality control measures are applied to ensure that the gears meet the specified requirements and perform as intended.
By following this comprehensive manufacturing process, engineers can produce high-quality spiral bevel gears with precise tooth profiles and excellent performance characteristics. These gears find application in various industries where precise motion control, efficient power transmission, and reliability are essential.
