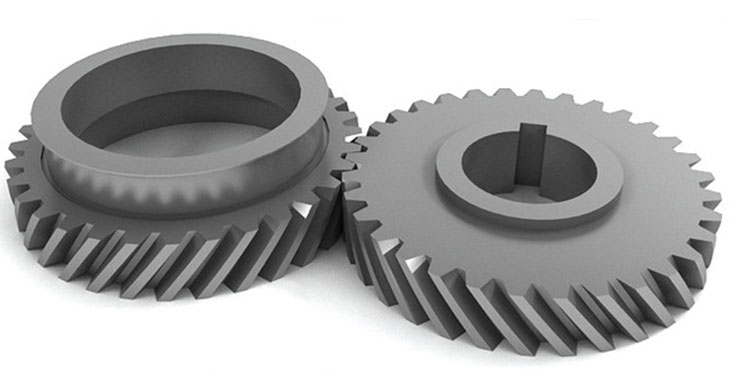
Helical gears and spur gears are two common types of gears used in various mechanical systems. While both gears serve the same fundamental purpose of power transmission between rotating shafts, they differ in design, tooth engagement, performance characteristics, and applications. Here’s a comprehensive comparison between helical gears and spur gears:
1. Design and Tooth Engagement:
- Helical Gears:
- Helical gears have inclined teeth that form a helix shape along the gear’s circumference. The helix angle causes the gear teeth to engage gradually, resulting in smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears.
- The helical shape allows for a larger contact area between gear teeth during meshing, leading to improved load distribution and reduced stress concentration on individual teeth.
- Spur Gears:
- Spur gears have straight teeth that are parallel to the gear axis. They engage suddenly when they come into contact, which can result in impact and noise during meshing.
- Spur gears have a smaller contact area between gear teeth during meshing compared to helical gears, which can lead to higher stress on individual teeth.
2. Noise and Vibration:
- Helical Gears:
- Helical gears provide quieter operation due to their gradual tooth engagement, reduced impact, and smoother meshing. The helical tooth shape helps in minimizing gear noise and vibration.
- The inclined teeth of helical gears also contribute to lower backlash, which further reduces noise during gear reversals.
- Spur Gears:
- Spur gears tend to produce more noise and vibration compared to helical gears due to their sudden tooth engagement. The straight teeth can create impact and shock loads during meshing, leading to increased noise levels.
3. Efficiency:
- Helical Gears:
- Helical gears generally offer higher efficiency compared to spur gears. Their smooth tooth engagement reduces sliding friction, leading to less energy loss during power transmission.
- Spur Gears:
- Spur gears can be less efficient than helical gears due to their higher sliding friction during meshing. The sudden tooth engagement results in more sliding between gear teeth, leading to increased energy losses.
4. Load-Carrying Capacity:
- Helical Gears:
- The helix angle and larger contact area in helical gears allow them to carry higher loads compared to spur gears. Helical gears are often preferred in applications that require high load-carrying capacity.
- Spur Gears:
- Spur gears are suitable for applications with moderate load requirements. They may not be as capable of carrying heavy loads as helical gears due to their smaller contact area.
5. Backlash:
- Helical Gears:
- Helical gears have lower backlash compared to spur gears. The inclined teeth help in minimizing the play between gear teeth, resulting in better precision and repeatability.
- Spur Gears:
- Spur gears can have higher backlash compared to helical gears due to their straight teeth design. Backlash can affect gear accuracy and motion control.
6. Applications:
- Helical Gears:
- Helical gears are commonly used in applications that require smooth operation, low noise, high precision, and heavy load-carrying capacity. They are found in automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, marine propulsion systems, and various other mechanical systems.
- Spur Gears:
- Spur gears are suitable for applications where noise and vibration are less critical, and moderate load requirements are sufficient. They are commonly used in clocks, simple machinery, and certain power transmission systems.
In summary, helical gears excel in applications where smooth and quiet operation, high efficiency, precision, and heavy load-carrying capacity are essential. On the other hand, spur gears are more straightforward and cost-effective, making them suitable for applications with less demanding requirements. The choice between helical gears and spur gears depends on the specific needs and operating conditions of the mechanical system in which they are used.
