This study establishes a mathematical framework for optimizing the transmission accuracy of worm gear-driven precision turntables by integrating multi-body system dynamics with error sensitivity analysis. By quantifying critical error sources and their propagation mechanisms, we propose a systematic approach to enhance manufacturing precision while balancing economic feasibility.
1. Structural Dynamics of Worm Gear Turntables
The worm gear turntable system comprises four subsystems: sliding platform, worm shaft assembly, worm wheel assembly, and rotary worktable. The kinematic chain follows:
$$ \text{Sliding Platform} \rightarrow \text{Worm Shaft} \rightarrow \text{Worm Wheel} \rightarrow \text{Worktable} \rightarrow \text{Load} $$
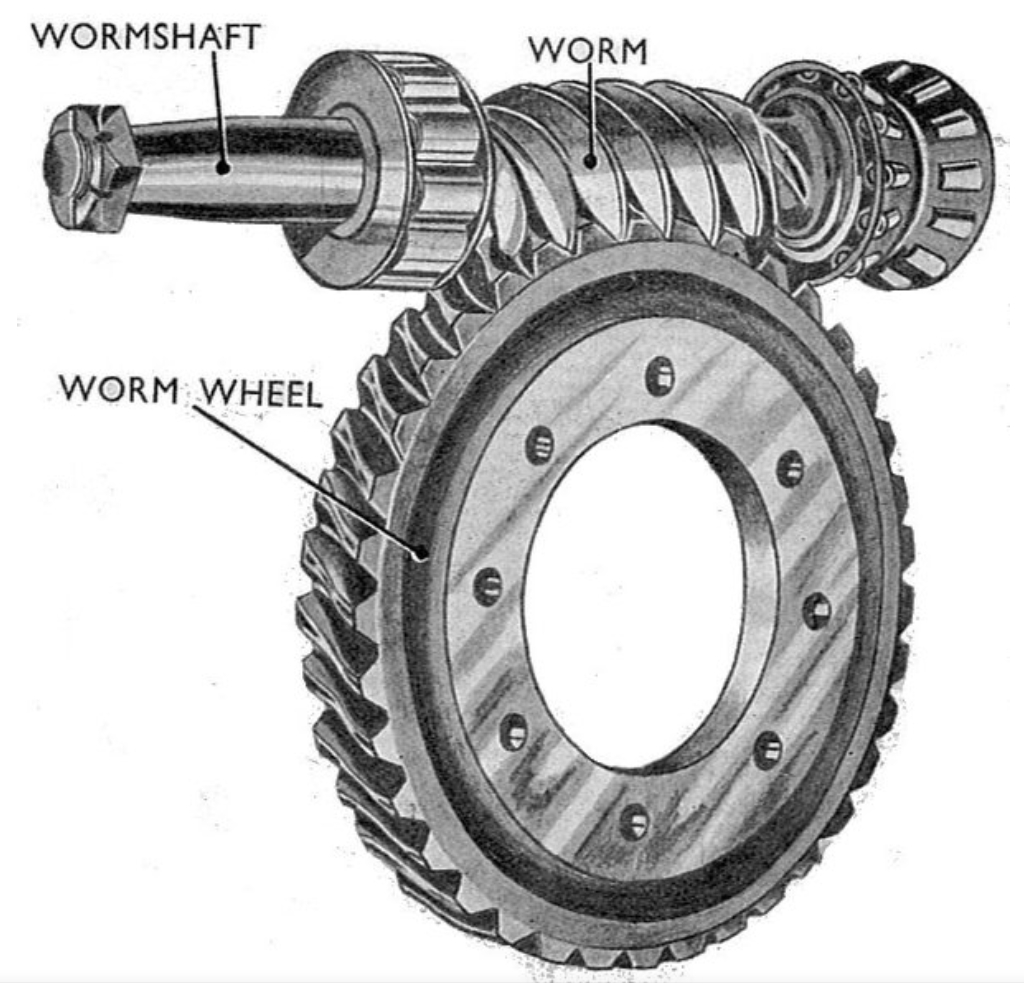
2. Multi-Body Error Propagation Model
Coordinate transformation matrices between adjacent bodies (Ki and Kj) account for positional and angular errors:
$$ \mathbf{P}_i = \mathbf{T}_{ij}^P \cdot \mathbf{T}_{ij}^{PE} \cdot \mathbf{T}_{ij}^S \cdot \mathbf{T}_{ij}^{SE} \cdot \mathbf{P}_j $$
Where:
- $\mathbf{T}_{ij}^P$: Ideal position transformation
- $\mathbf{T}_{ij}^{PE}$: Position error matrix
- $\mathbf{T}_{ij}^S$: Ideal motion transformation
- $\mathbf{T}_{ij}^{SE}$: Motion error matrix
3. Error Sensitivity Quantification
The total positioning error vector is derived as:
$$ \mu = \begin{bmatrix} \mu_x \\ \mu_y \\ \mu_z \end{bmatrix} = \mathbf{P}_{act} – \mathbf{P}_{ideal} $$
Normalized sensitivity coefficients for critical error sources:
$$ \lambda_j = \frac{|\partial f/\partial \theta_j|}{\sum_{k=1}^m |\partial f/\partial \theta_k|} $$
| Error Source | $\mu_x$ Sensitivity | $\mu_y$ Sensitivity | $\mu_z$ Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| $\varepsilon_{x0}(y_1)$ | 0 | 0.552 | 0.015 |
| $\delta_x(z_3)$ | 0.430 | 0.447 | 0.554 |
| $\sigma_x(x_4)$ | 0.430 | 0.447 | 0.554 |
4. Precision Optimization Strategy
Key error control parameters for worm gear systems:
$$ \Delta\theta_{total} = \sum_{i=1}^n \frac{\partial f}{\partial \theta_i} \Delta\theta_i $$
| Error Component | Baseline (” ) | Optimized (” ) |
|---|---|---|
| Axial Perpendicularity | 5.0 | 2.9 |
| Rotational Error | 8.0 | 3.9 |
5. Experimental Validation
Laser interferometry tests demonstrated:
$$ \text{Positioning Accuracy: } 3.9″ \pm 0.5″ $$
$$ \text{Repeatability: } 3.0″ \pm 0.3″ $$
6. Conclusion
The proposed multi-body error model effectively identifies critical sensitivity parameters in worm gear systems, enabling precision improvements exceeding 40%. This methodology provides a theoretical foundation for high-accuracy turntable design while maintaining cost efficiency through targeted error source control.
