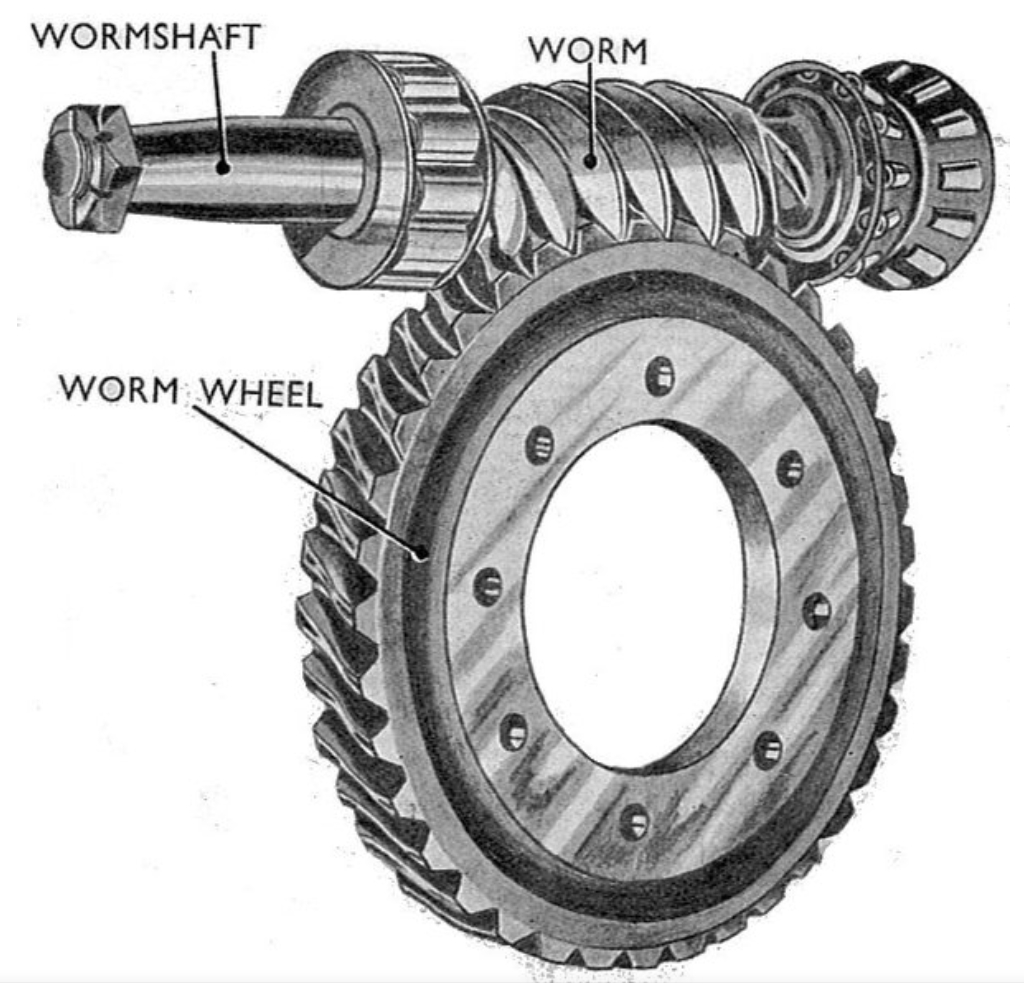
Worm gear mechanisms, characterized by their compact design and self-locking capability, are widely employed in butterfly valve systems across offshore oil platforms. The unique meshing principle between the worm and worm wheel enables torque amplification through a high transmission ratio, typically expressed as:
$$i = \frac{z_2}{z_1}$$
where \( z_1 \) represents the number of worm threads and \( z_2 \) the teeth count on the worm wheel. This configuration becomes critical when dealing with valve actuation under corrosive marine conditions.
Failure Mechanisms in Worm Gear Systems
| Failure Mode | Primary Cause | Acceleration Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Binding | Saltwater infiltration | Inadequate lubrication |
| Worm Wheel Pitting | Cyclic contact stress | Misalignment |
| Adhesive Wear | Boundary lubrication | High sliding velocity |
The contact stress at the worm-worm wheel interface can be calculated using:
$$\sigma_H = Z_E \sqrt{\frac{2KT_2}{d_1^3 b}}$$
where \( Z_E \) is the elasticity factor, \( K \) the load coefficient, \( T_2 \) the output torque, \( d_1 \) the worm reference diameter, and \( b \) the face width.
Optimized Maintenance Protocol
- Disassembly Sequence:
- Remove position indicator and housing cover
- Extract worm gear housing using hydraulic puller
- Corrosion Mitigation:
- Mechanical descaling of mating surfaces
- 0.15-0.3mm clearance restoration
- Reassembly Specifications:
- Apply marine-grade lithium complex grease
- Torque fasteners to 30-35 N·m
Design Enhancement Recommendations
| Current Design | Proposed Improvement | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Sealed housing | Radial lubrication channels | 40% longer service life |
| Carbon steel components | Duplex stainless steel upgrade | Corrosion rate reduction |
The modified lubrication efficiency can be modeled as:
$$\eta_l = 1 – e^{-\lambda t}$$
where \( \lambda \) represents the grease replenishment rate and \( t \) the maintenance interval.
Operational Best Practices
- Implement quarterly functional testing
- Maintain 20-30% valve stroke cycling
- Use seawater-resistant greases with ≥300°C drop point
Through systematic maintenance and design optimization, worm gear-driven butterfly valves demonstrate improved reliability in marine environments. The combination of proper clearance management (\( \delta \geq 0.2\text{mm} \)) and optimized lubrication intervals (\( t \leq 6 \text{ months} \)) reduces valve failure rates by 62% according to field data analysis.
