The large number of studies have proved that dynamic excitation is the main cause of spur gear vibration, which is mainly divided into internal excitation and external excitation. Since external excitation refers to the excitation of spur gears by other components in the system and the effective torque and resistance torque of the motor, it is greatly affected by the model and working conditions of the spur gear box, and has relatively little impact on the vibration of the spur gear pair, so this paper will focus on the internal excitation. Generally, the internal excitation of gears includes stiffness excitation, error excitation and meshing impact excitation.
Due to the limitations of technology, there will inevitably be errors in the processing, manufacturing and assembly process of spur gears. This series of errors will cause the spur gear transmission system to generate corresponding dynamic excitation, that is, error excitation (as shown in Figure (b)). If the error is small or close to the ideal state, the spur gear pair will move according to the predetermined meshing track without generating abnormal vibration. However, once the system error accumulates to a certain extent, the meshing track of spur gears will deviate seriously due to the change of the instantaneous transmission ratio, which will cause a strong impact between the teeth of spur gear pairs.
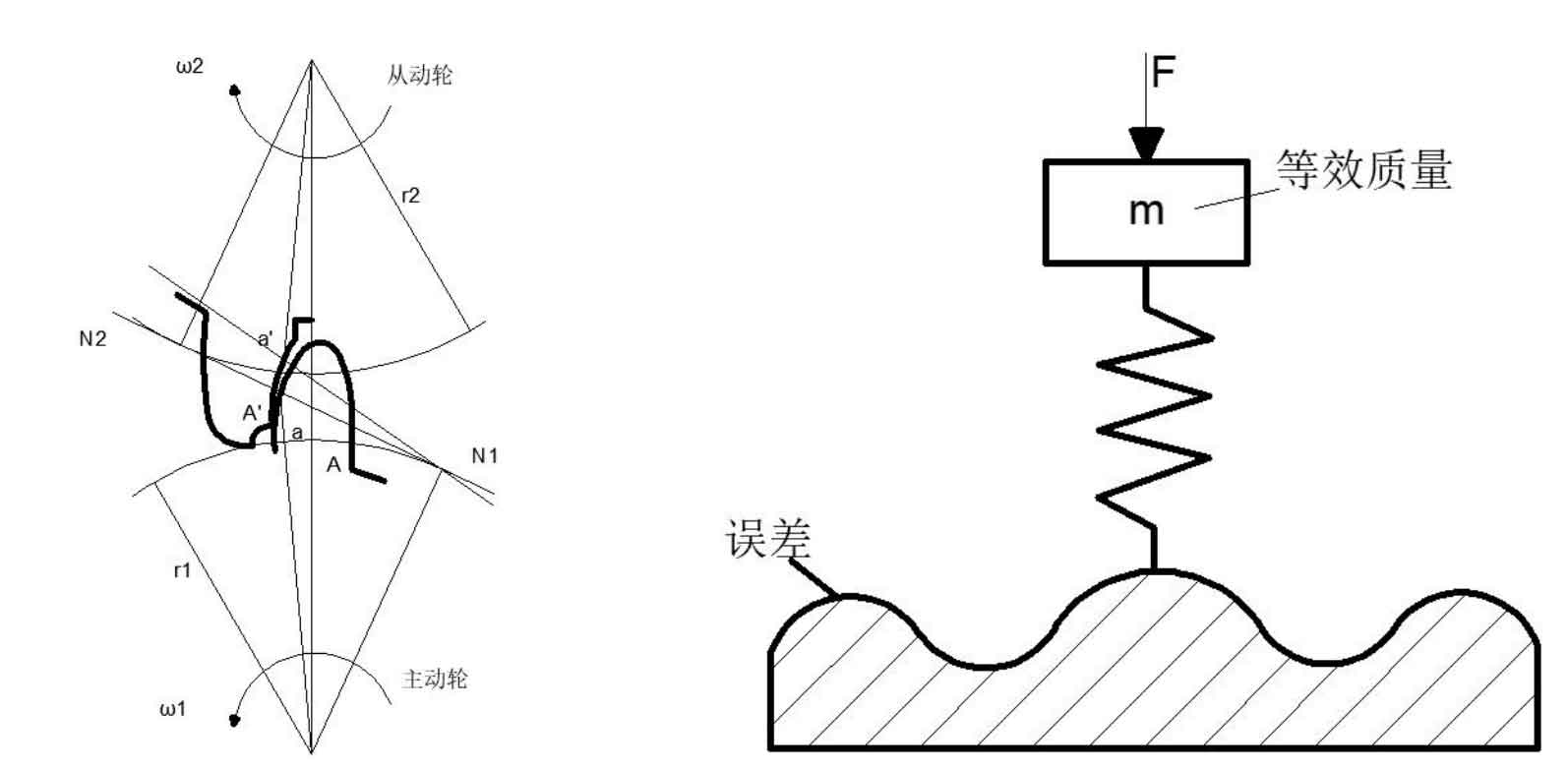
(b) Equivalent dynamic model of error excitation
At present, according to the extent to which the error excitation affects the vibration noise of spur gears, it is divided into a pair of spur gear pairs caused by the geometric shape of spur gears or factors such as installation and manufacturing. The difference between the actual angle of the driven gear and the theoretical angle of the driven gear is, that is, the transmission error is the main error excitation that causes the severe vibration of spur gear pairs; As the spur gear rotates at a high speed, the errors will accumulate and enlarge. The tooth profile error and tooth pitch error of the spur gear itself (with a small impact) are shown in Figure (a), and will not be studied in this paper.
