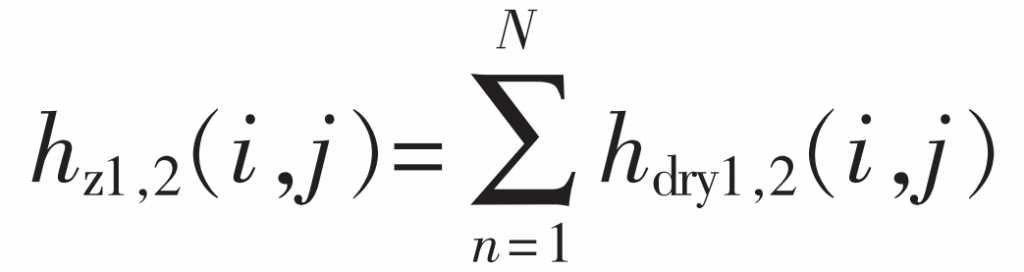During the meshing transmission of helical gear pairs, sliding wear occurs due to the relative sliding of the tooth surfaces. According to the classical Archard tooth surface adhesion wear calculation model, the wear volume of the gear tooth surface under dry contact condition is:
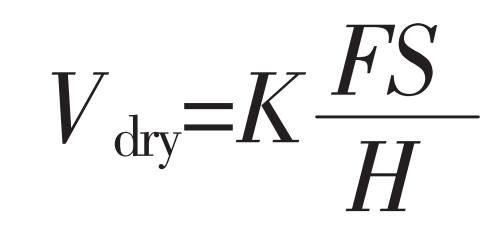
Where: K – non dimensional wear coefficient of helical gear material;
S – Slip distance.
From this, the wear depth of the tooth surface of the driving and driven wheels in a dry contact state after a certain meshing position is obtained:
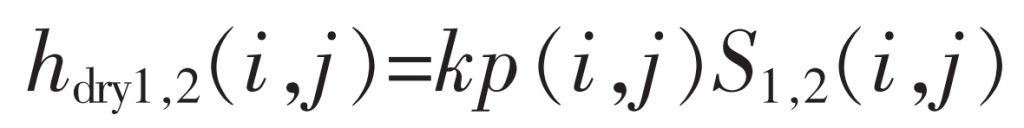
Average contact pressure at helical gear engagement position:
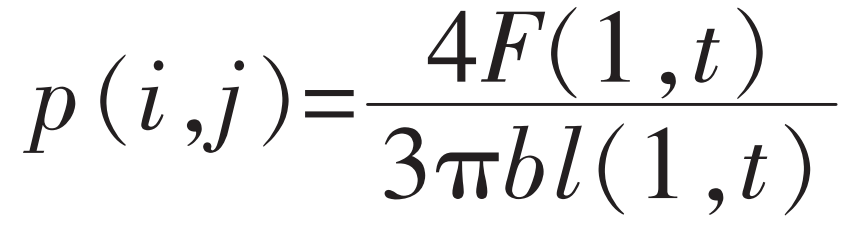
Dimensional wear coefficient:
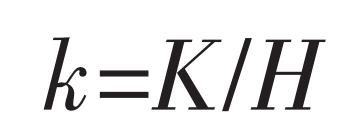
After N times of meshing, the cumulative wear depth of the helical gear tooth surface is: