The essence of the cycle counting method is to study the number of the occurrence of the basic damage element of the load from the perspective of fatigue damage, and establish a relationship between the counting process of the load and the fatigue characteristics of the material. At present, the rain-flow counting method is a random load cycle counting method that is generally considered to conform to the fatigue damage law by scholars at home and abroad, and has been widely used in engineering practice. The rain flow counting process is generally realized by computer program, which can be divided into two steps: data compression and cycle number extraction.
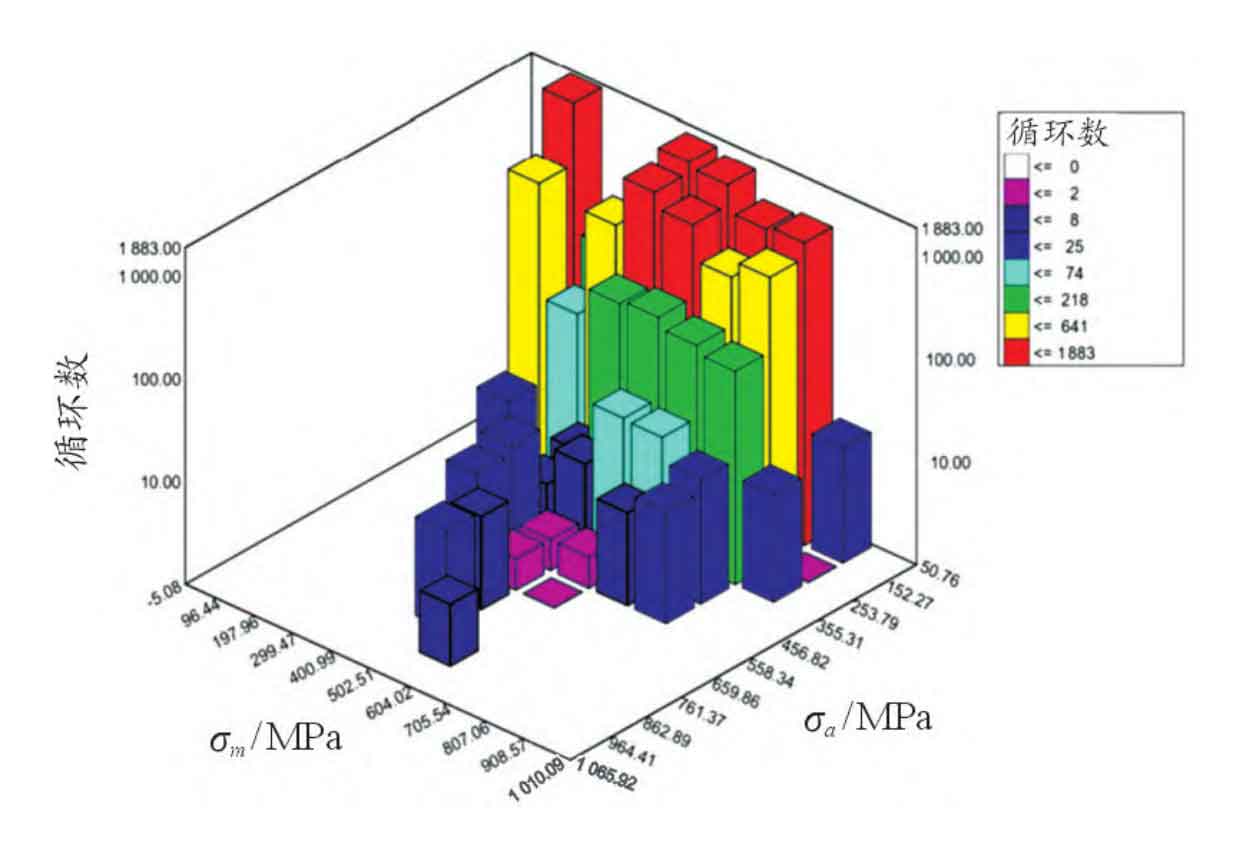
According to the principle of rain-flow counting method, the algorithm mainly counts the load cycles for the continuous load history, while the stress on a single tooth of helical gear is not continuous after one cycle of operation. Therefore, the contact stress spectrum of helical gears is extracted and reconstructed through data processing. The total time of helical gear rotation for one cycle is a function of rotational speed, as well as the meshing period and number of teeth of a single gear tooth. Based on this relationship, the load data of helical gear can be extracted and reorganized, so that the stress-time curve of a single gear tooth can become a continuous load history, and the rain flow counting method can be used for cycle counting. Finally, the relationship between the mean value and frequency of the contact stress amplitude of the driving gear is obtained, as shown in the figure. Statistical analysis of the counting results and K-S hypothesis test show that the mean value of load follows normal distribution, and the load amplitude follows Weibull distribution. The mean value and standard deviation of the mean distribution of contact stress of helical gears are 508MPa and 82.3MPa respectively.
