Tooth width is usually regarded as an effective measure to improve gear strength, but in the actual design process, when changing the tooth width, the parameters such as the quality of the gear system, the moment of inertia and the gear fit eccentricity will also change, and the change of tooth width is restricted by many factors. It is difficult to estimate the impact of the change of tooth width on the dynamic characteristics of the gear based on experience alone. Taking the gear tooth width of the camshaft with weak strength in the driving fuel injection pump as a variable, taking into account the changes of other relevant parameters such as the quality under the actual conditions and normal design conditions, the dynamic characteristics of the gear are studied when the tooth width is 20, 21, 22, 23, 24 and 25 mm respectively.
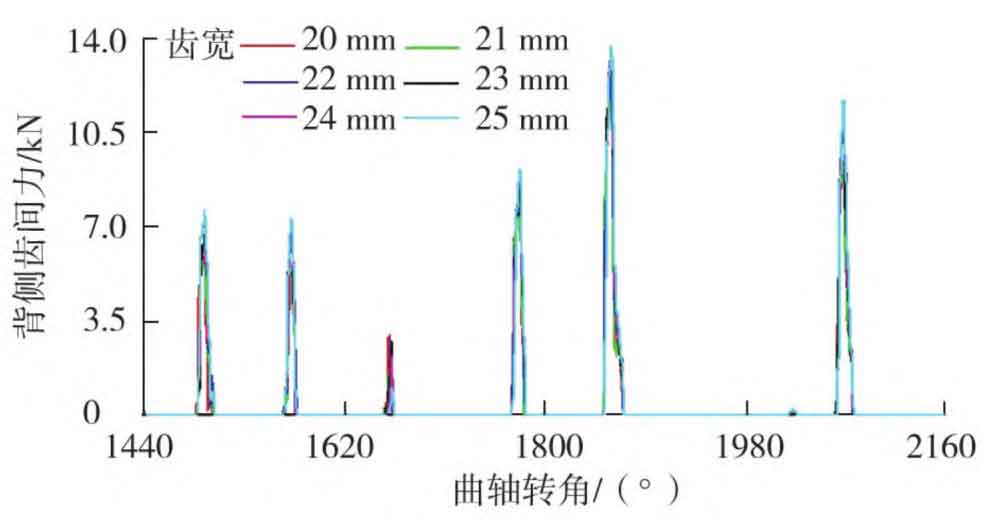
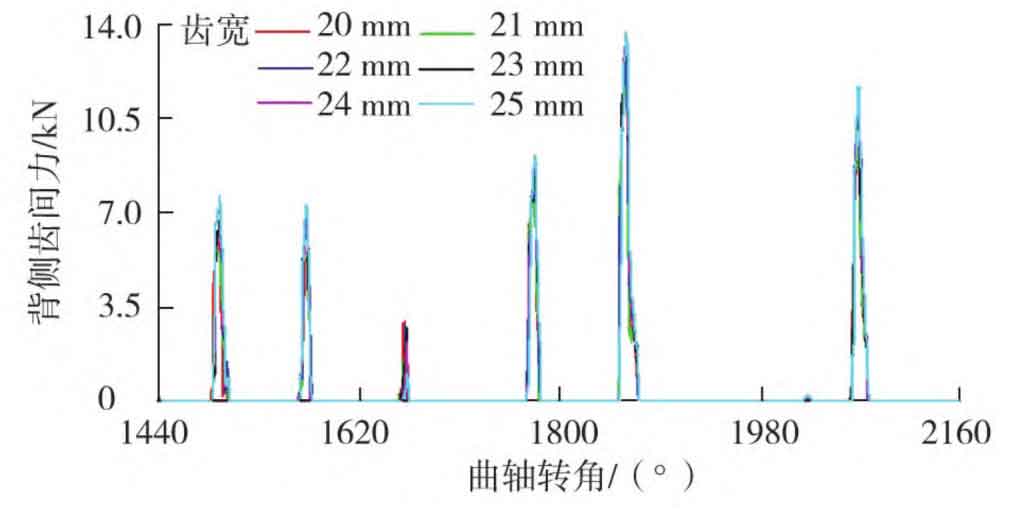
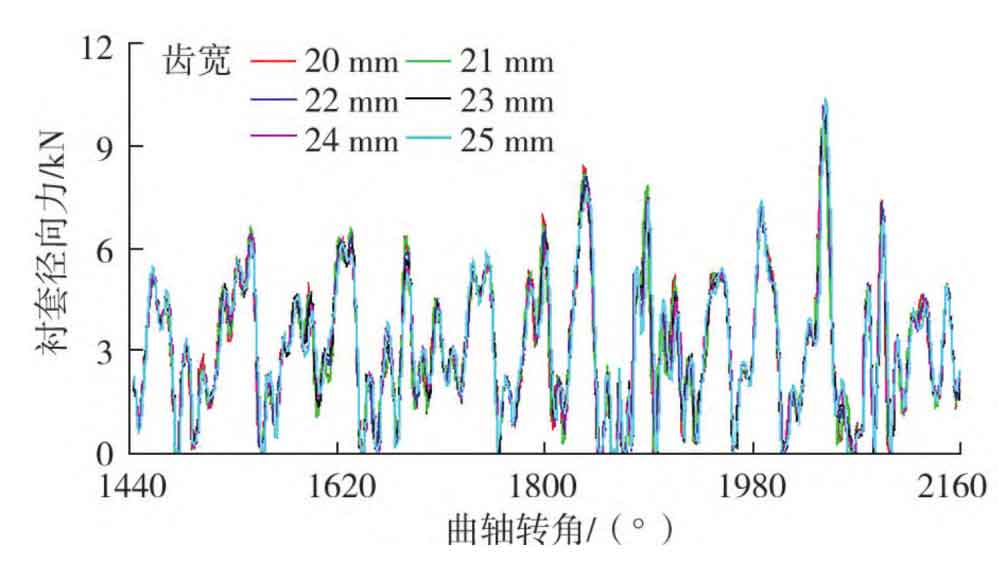
The inter-tooth force at the driving side, the inter-tooth force at the back side and the radial force of the bushing at different tooth widths are shown in Figures 1-3.
It can be seen from Figures 1 to 3 that when the tooth width is 20, 21, 22, 23, 24 and 25 mm respectively, the maximum inter-tooth force at the driving side is 18103 7、18 367. 2、18 481. 2、18 386. 1、18 459. 6、18 573. 4N, the maximum back interdental force is 12488 0、 12 379. 1、12 961. 5、13 357. 1、13 472. 8、13 762. 1N, the maximum bushing radial force is 9782 7、9 715. 5、10 052. 8、10 104. 0、10 217. 9、10 387. 7 N; With the increase of tooth width, the inter-tooth force at the driving side and the inter-tooth force at the back side of the gear will increase as a whole; With the increase of tooth width, the radial force of the bushing shows an increasing trend, but the change range is small, indicating that the influence of tooth width on the radial force of the bushing is small.
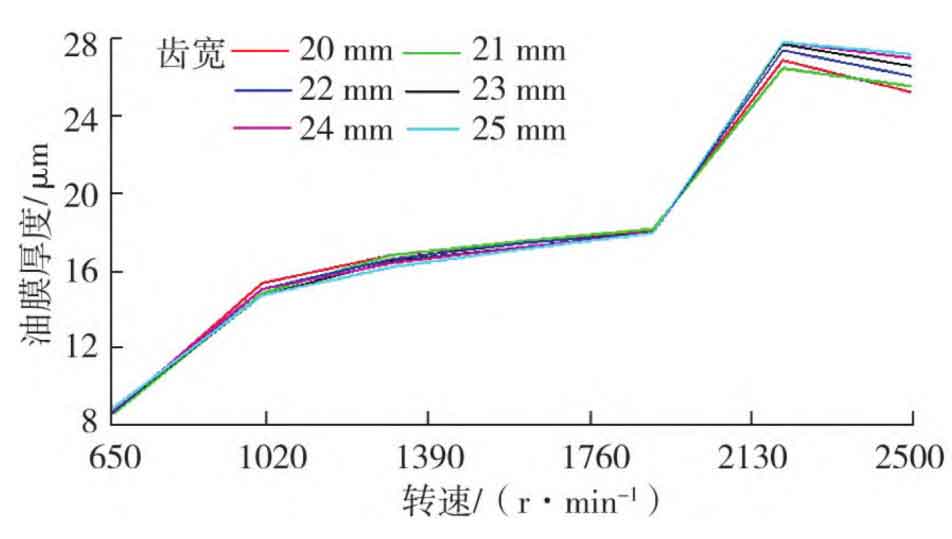
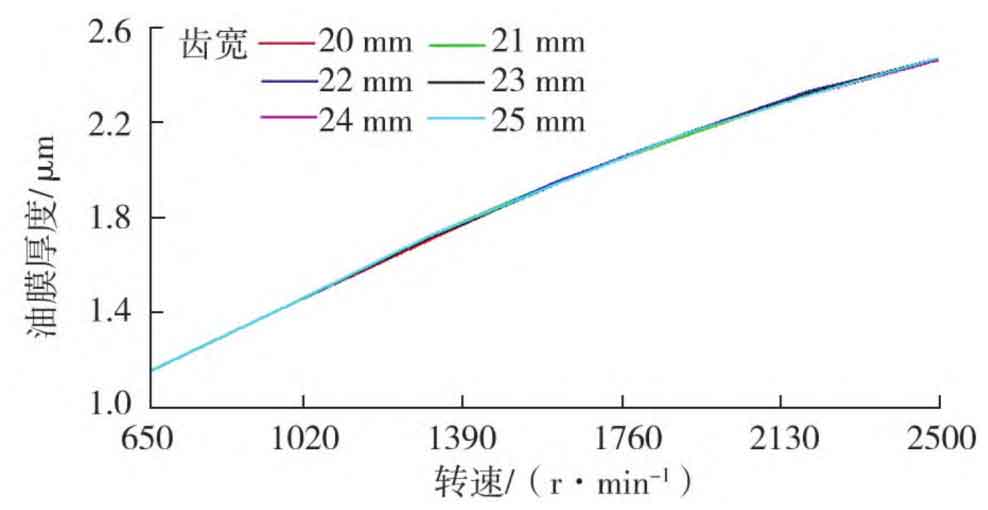
The oil film thickness of camshaft gear bushing and injection pump idler gear bushing with different tooth widths are shown in Figures 4 and 5. It can be seen from Figures 4 and 5 that the increase of tooth width affects the oil film thickness of the bushing where the gear is located, and the change of the oil film thickness of the bushing is more obvious when the engine speed is higher; The increase of tooth width has little effect on the oil film thickness of the bushing around it, which can be ignored.
As the tooth width increases, the gear mass and moment of inertia increase, and the impact effect between gears increases. At this time, the influence of tooth width on strength cannot be judged only by the force between teeth, but the strength should be calculated by considering various changes. Use Kisssoft software to analyze the change of basic parameters of gear and the force between teeth, calculate the bending fatigue strength of crankshaft gear and camshaft gear root and the contact fatigue strength of tooth surface, and obtain the bending fatigue safety factor of crankshaft gear root α 1. Bending fatigue safety factor of camshaft gear root α 2. Contact fatigue safety factor of crankshaft gear tooth surface β 1. Contact fatigue safety factor of camshaft gear tooth surface β 2, as shown in Table 1.
| Tooth width/mm | α1 | α2 | β1 | β2 |
| 20 | 1.12 | 0.99 | 1.18 | 1.19 |
| 21 | 1.15 | 1.02 | 1.20 | 1.21 |
| 22 | 1.18 | 1.05 | 1.22 | 1.24 |
| 23 | 1.23 | 1.10 | 1.25 | 1.27 |
| 24 | 1.27 | 1.13 | 1.28 | 1.29 |
| 25 | 1.30 | 1.17 | 1.31 | 1.32 |
It can be seen from Table 1 that on the premise that the mass and moment of inertia increase with the tooth width synchronously, increasing the tooth width has an impact on the gear safety factor, but the impact is small. If the tooth width increases by 5mm, the gear strength safety factor will increase by less than 0.2. Further analyze the strength calculation results under the premise of strictly limiting the increase of gear mass, as shown in Table 2.
| Tooth width/mm | α1 | α2 | β1 | β2 |
| 20 | 1.12 | 1.18 | 1.18 | 1.19 |
| 21 | 1.21 | 1.26 | 1.20 | 1.27 |
| 22 | 1.31 | 1.34 | 1.22 | 1.35 |
| 23 | 1.40 | 1.42 | 1.25 | 1.43 |
| 24 | 1.49 | 1.49 | 1.28 | 1.51 |
| 25 | 1.58 | 1.57 | 1.31 | 1.58 |