In the process of EDM, the electrode will have a certain amount of burning loss, which will change the electrode tooth parameters before and after machining. In order to simplify the problem, the following premises and assumptions are proposed:
(1) The electrode burning loss in the rough machining stage does not affect the tooth profile accuracy of the die.
(2) The burning loss rate of each point on the electrode tooth profile is the same in the middle and finishing stages.
(3) At the end of rough machining, replace the finishing electrode to start finishing, and all points on the electrode tooth profile have entered the machining state.
The influence of electrode burning loss on electrode tooth shape parameters from the beginning to the end of finish machining will be analyzed.
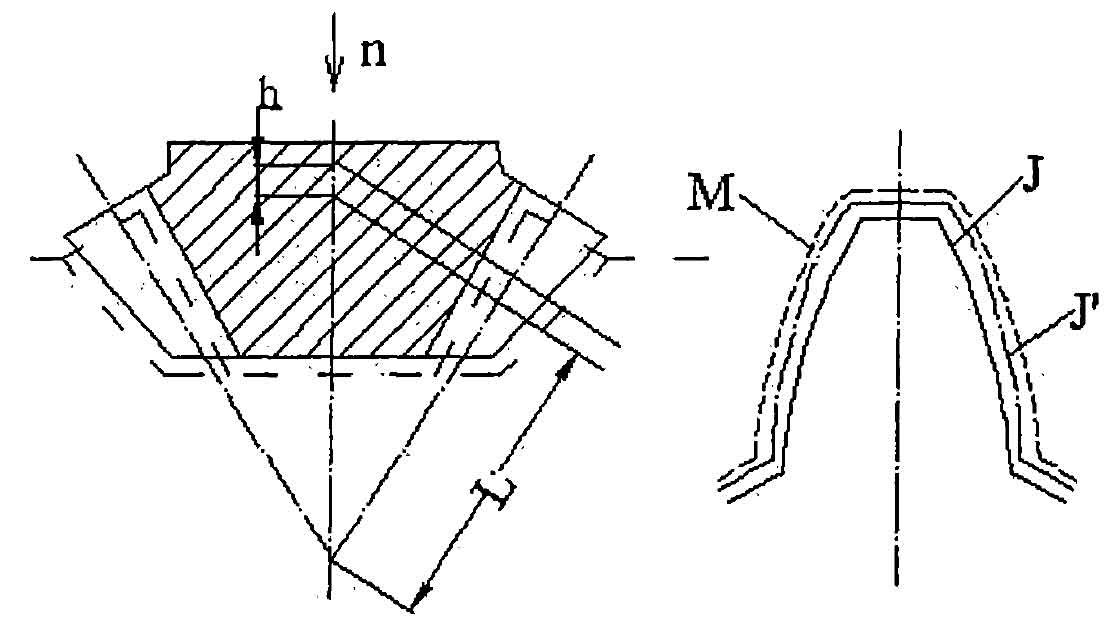
Fig. 1 shows the equivalent cavity tooth profile m and the equivalent electrode tooth profile J at the pitch L after a pulse discharge in the process of EDM, which are evenly different by a discharge gap along the normal direction. Thereafter, during the pulse interval, the electrode is sent h distance in the N direction. At this time, the electrode tooth profile at l becomes J ‘. Obviously, the normal distance between J ‘and M is less than that between J and m; Moreover, the closer the point on J ‘to the tooth top, the smaller the normal distance between M. Therefore, the minimum gap near the tooth top reaches the breakdown voltage and is broken down and discharged, and then the points along the tooth root direction are broken down in turn, so that the normal gap between J ‘and M is equal. Thereafter, the electrode feeding and pulse discharge continue alternately, and the above EDM process is repeated. It can be seen that the burning loss of each point on the electrode tooth profile is different. The closer the point to the tooth top, the longer the working time, and the greater the burning loss.
Next, calculate and analyze the electrode tooth shape parameters after burning.
It is assumed that h is fed into the electrode from the beginning of middle processing to the end of finishing processing. The tooth shape parameters of the electrode after burning are shown in Fig. 2.
Among them,
MX, jx1 – equivalent tooth profile of die cavity and electrode at LX at the beginning of finishing;
MK, jk1 – equivalent tooth profile of die cavity and electrode at LK at the beginning of finishing;
ROK, Rox – dividing circle radius of jk1, jx1;
BX1 – any point on jx1;
BK1 – Radial corresponding point of point BX1 on jk1;
φ— Represents the indexing cone angle of the bevel gear.