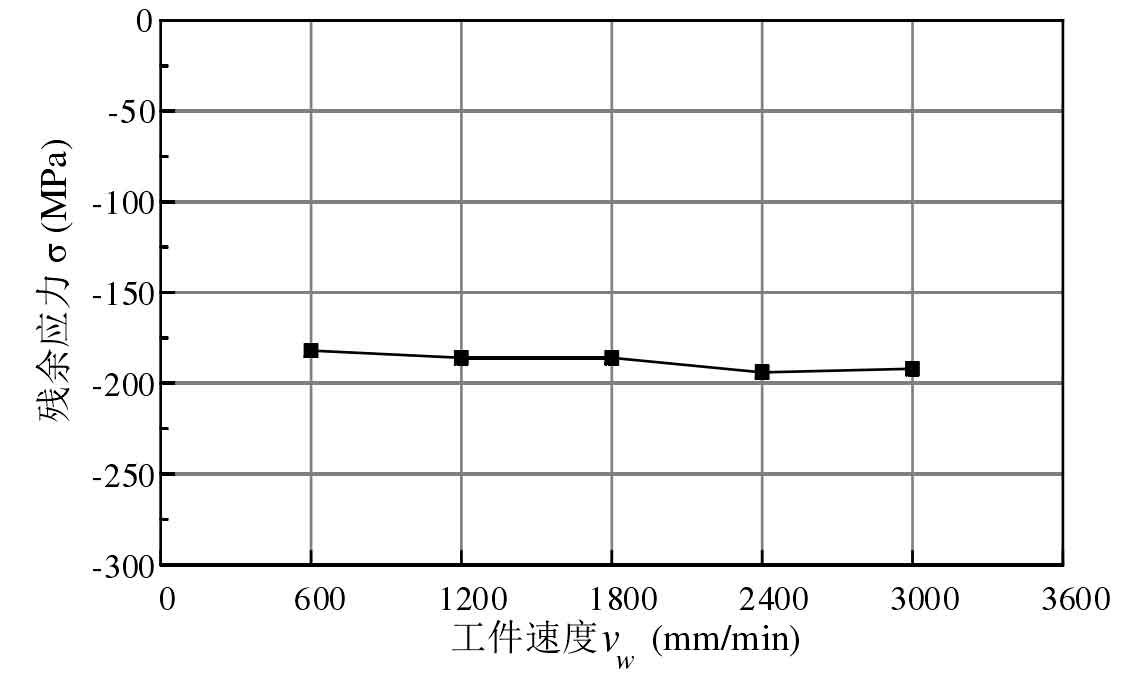
Fixed cylindrical gear steel grinding speed vs = 20.3 M / s, cylindrical gear steel grinding depth AP = 50 μ m. The test is carried out at different workpiece speeds VW, and the influence of workpiece speed on residual stress is shown in the figure.
The figure shows the influence of the change of workpiece speed on the surface residual stress of 30CrMnTi material after grinding. It can be seen that the influence of workpiece speed shadow on residual stress is not significant, but the value of residual compressive stress increases slightly with the increase of workpiece speed. This is because with the increase of workpiece speed, the undeformed chip thickness of single abrasive grain increases, and the grinding force and grinding heat of cylindrical gear steel increase. However, the growth of grinding heat of cylindrical gear steel is limited, and the change of residual tensile stress is small. The residual compressive stress caused by the increase of grinding force of cylindrical gear steel plays a leading role. At the same time, the increase of workpiece speed reduces the contact time between grinding wheel and workpiece and reduces the influence of thermal stress. Therefore, with the increase of workpiece speed, the change of residual stress on the grinding surface of cylindrical gear steel is not significant, and the value of compressive stress increases slightly.