Figure 1 shows the influence curve of the pinion tooth width on the time-varying meshing force of the helical gear pair at different speeds. It can be seen from the figure that the tooth width of the pinion can only make the time-varying meshing force of the helical gear under the low-speed working condition (2000r/min) decrease with its increase, but has little effect on the other working conditions.
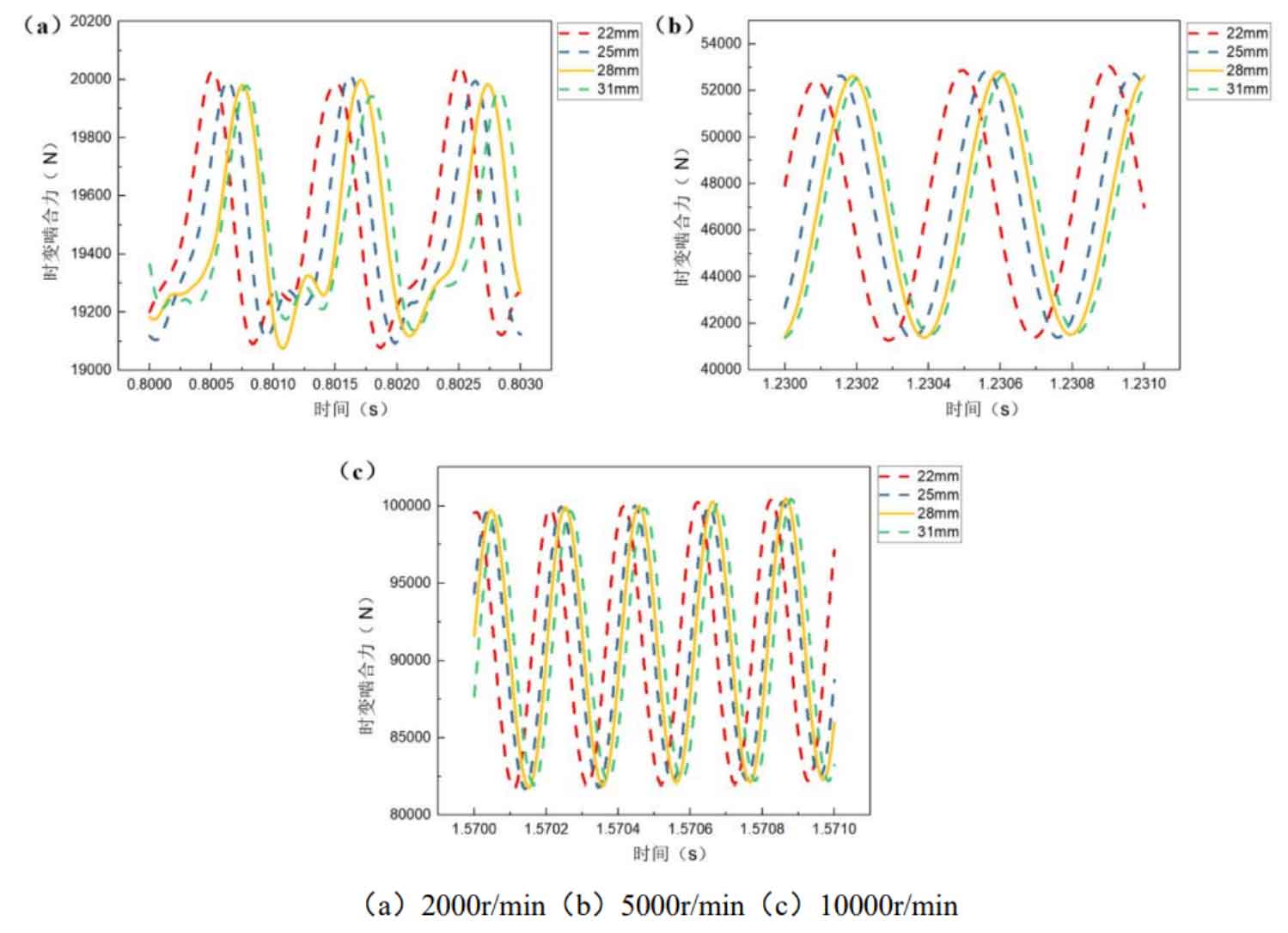
Figure 2 shows the influence curve of the pinion tooth width on the time-varying meshing stiffness of the helical gear pair. It can be found that the time-varying meshing stiffness increases with the increase of the pinion tooth width.
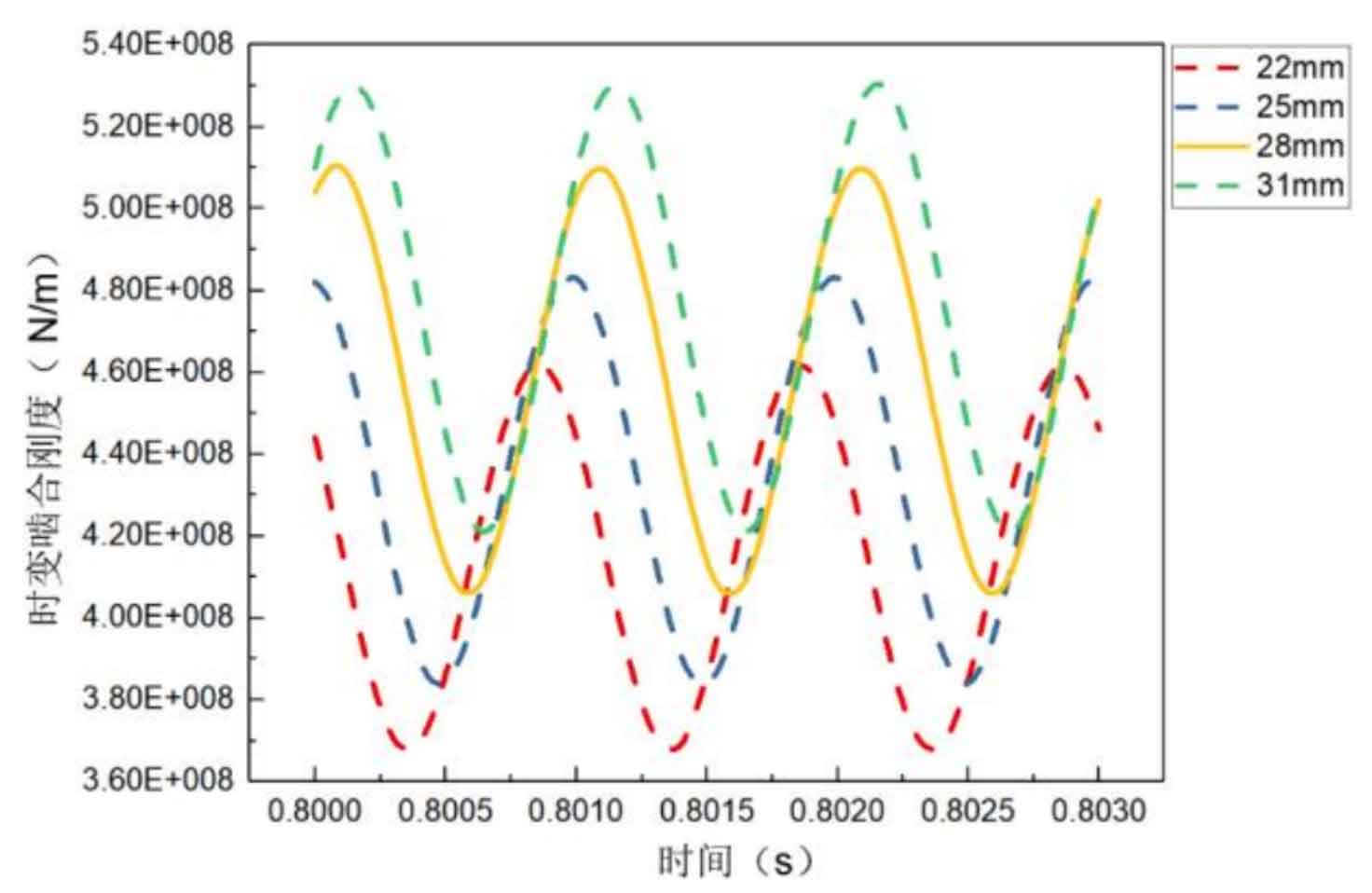
Figure 3 shows the influence curve of the tooth width of the big gear on the time-varying meshing force of the helical gear pair at different speeds. Like the pinion, the tooth width of the big gear only affects the time-varying meshing force of the helical gear at low speeds, and the time-varying meshing force decreases with the increase of the tooth width.
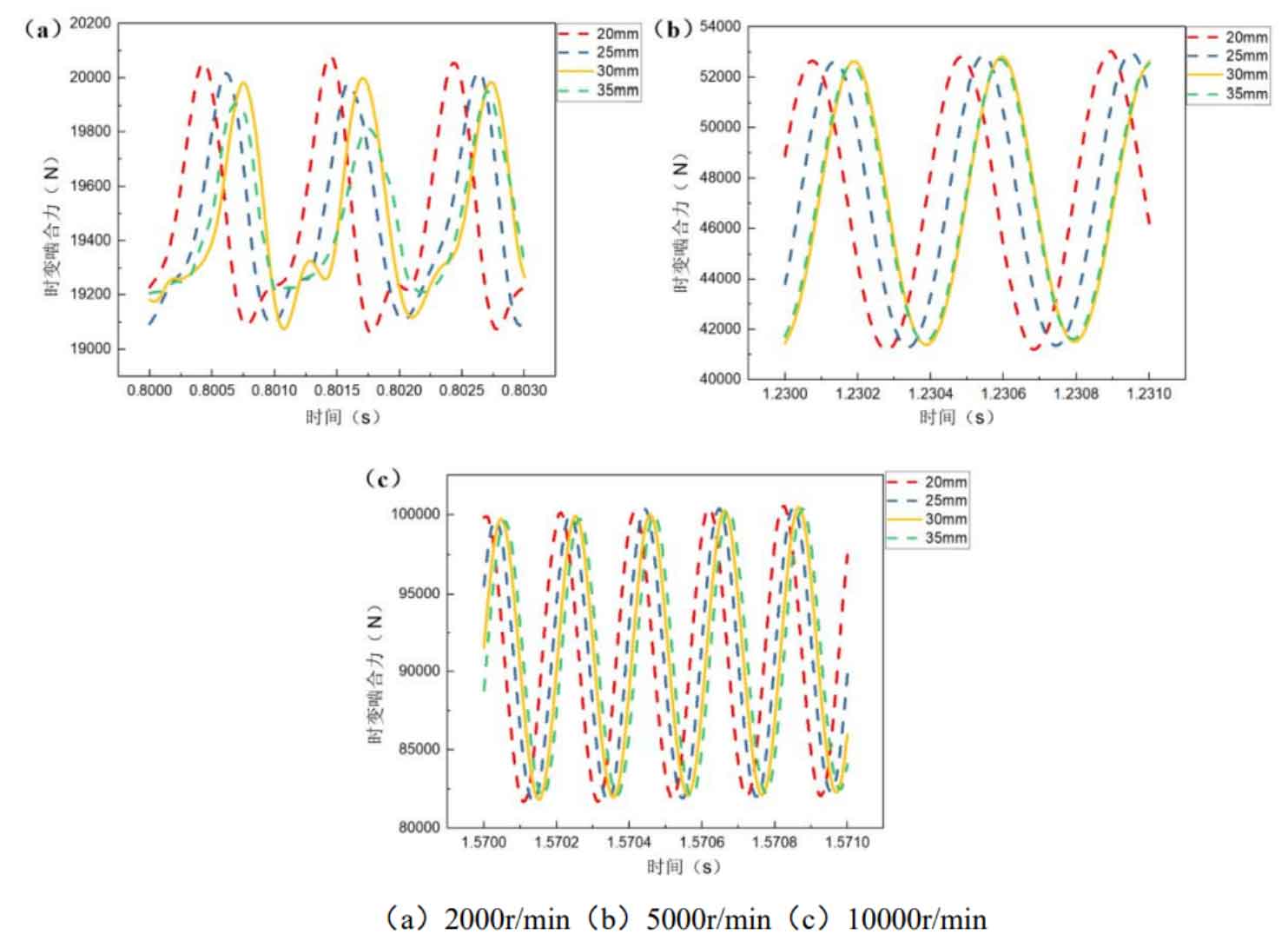
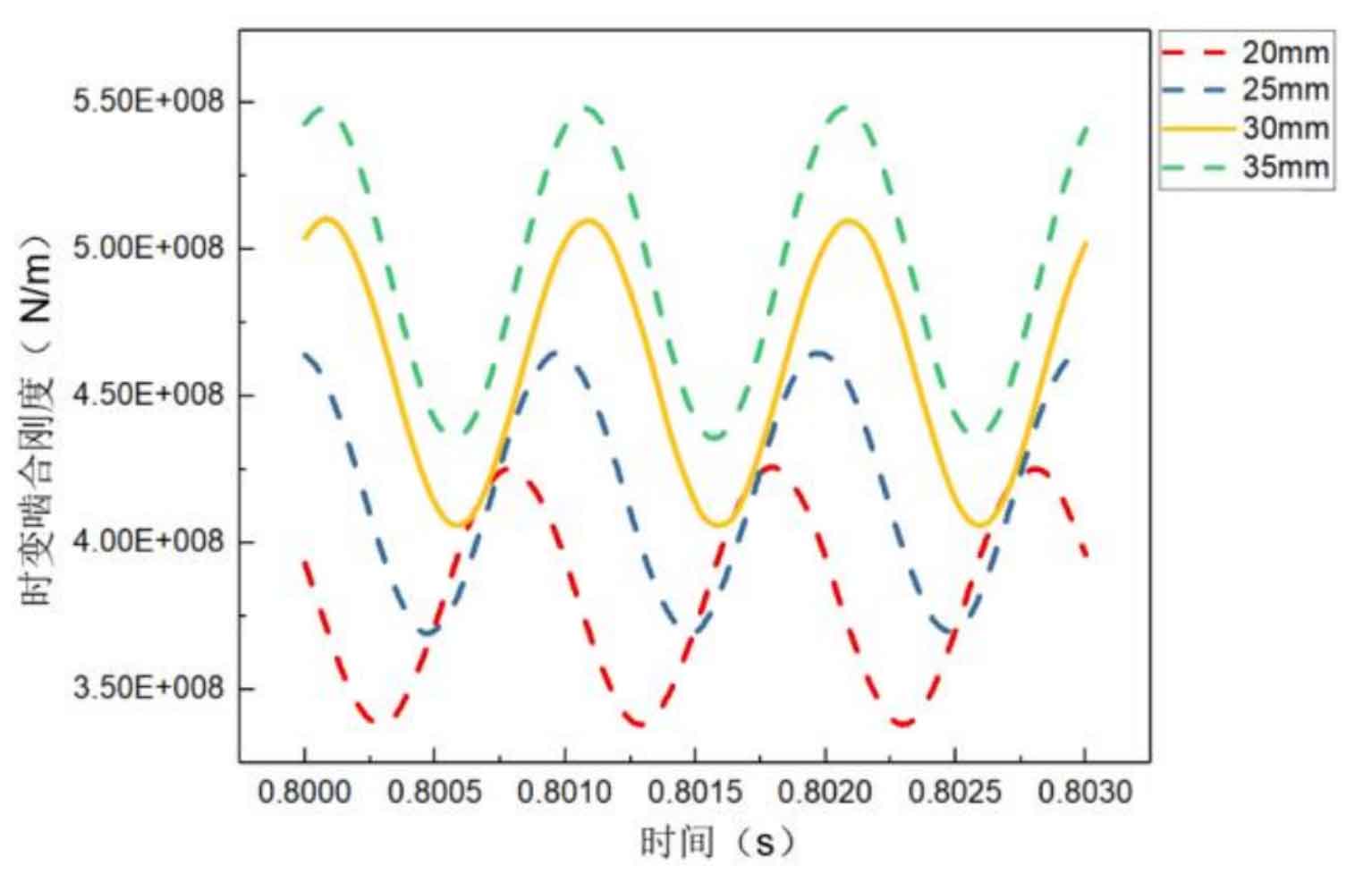
Figure 4 shows the influence curve of the tooth width of the large gear on the time-varying meshing stiffness of the helical gear pair. Like the pinion, the larger the tooth width, the greater the time-varying meshing stiffness.
To sum up, the selection of tooth width of helical gear is not absolute, because large tooth width reduces the time-varying meshing force of the gear, but increases the time-varying meshing stiffness. In addition, because the influence of the tooth width of the helical gear on the time-varying meshing force of the helical gear pair at medium and high speeds is very limited, if the requirements for the use of the helical gear pair at low speeds are not strict, a smaller tooth width can be selected to obtain better vibration and noise performance of the helical gear pair at medium and high speeds.
