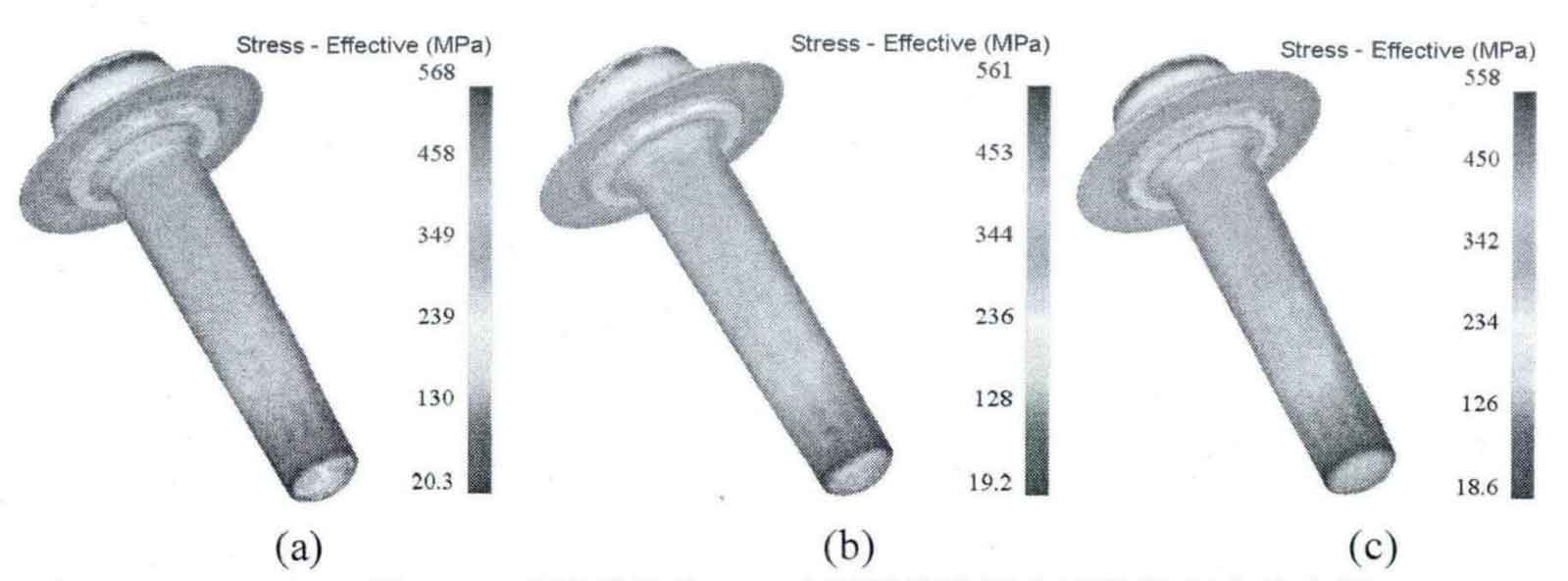
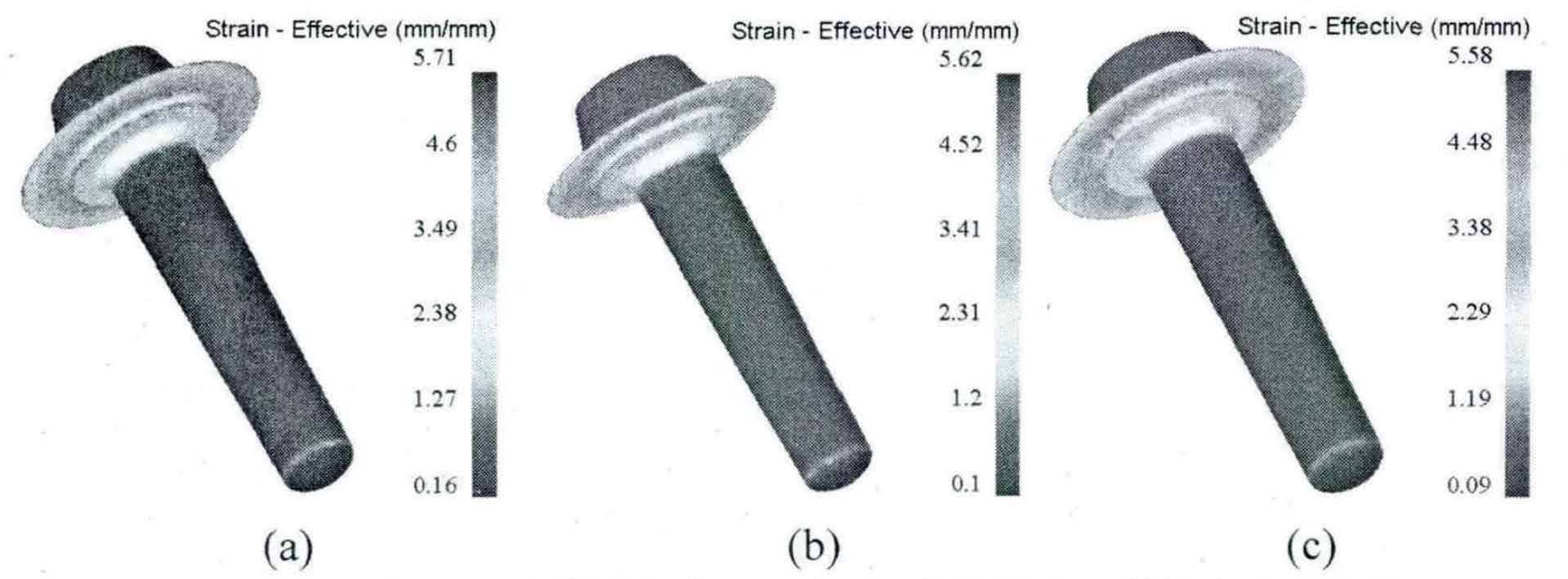
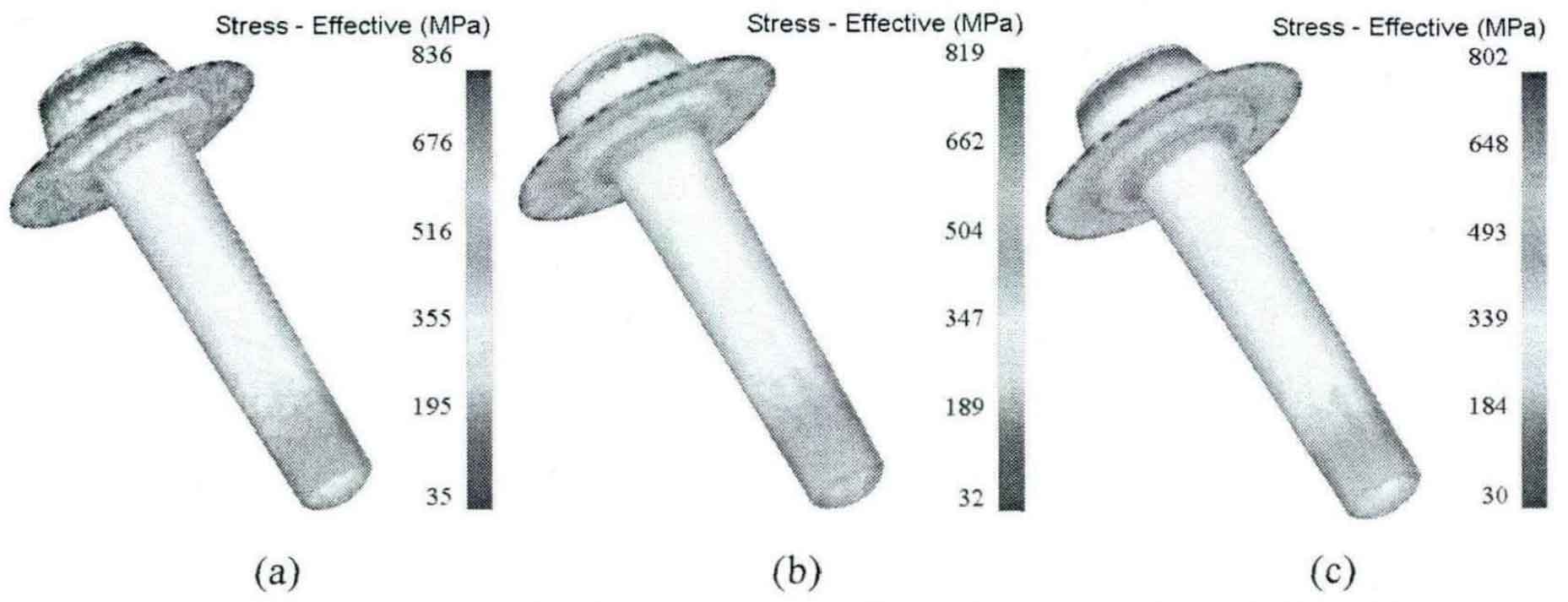
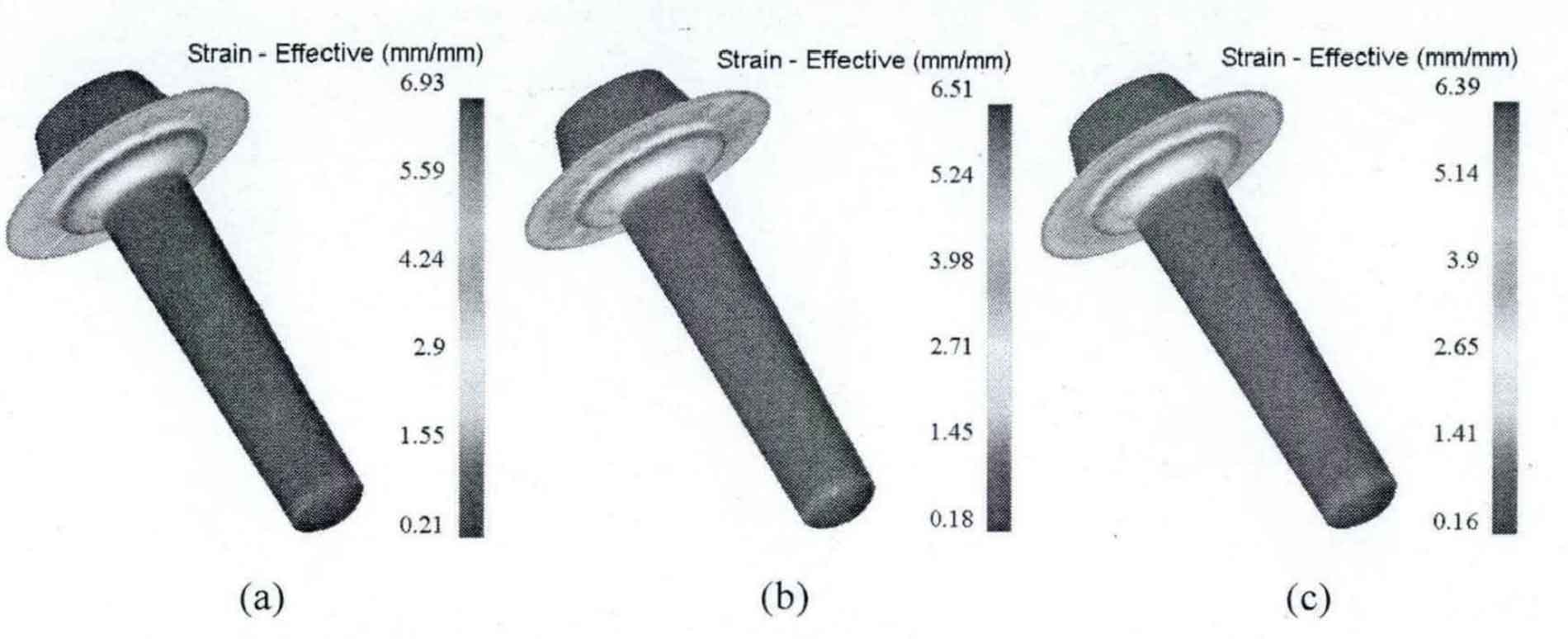
Taking the initial forging temperature as 1000 ° C, 1050 ° C and 1100 ° C respectively, and the friction coefficient as 0.3 and 0.7, the forging process of driving spiral bevel gear blank is numerically simulated, and the effects of initial forging temperature and friction coefficient on forming effect are analyzed.
When the friction coefficient is 0.3 and 0.7 respectively, the equivalent stress and strain distributions under different initial forging temperatures are shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig. 3 and Fig. 4.
The numerical simulation results are shown in the table.
| Scheme | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Temperature (° C) | 1000 | 1000 | 1050 | 1050 | 1100 | 1100 |
| Friction coefficient | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.7 |
| Equivalent stress (MPa) | 568 | 836 | 561 | 819 | 558 | 802 |
| Equivalent strain | 5.71 | 6.93 | 5.62 | 6.51 | 5.58 | 6.39 |
It can be seen from the above chart that the forging process of driving spiral bevel gear blank is the same as that of driven spiral bevel gear. In the range of 1000-1100 ° C, when the friction coefficient is the same, the higher the initial forging temperature, the smaller the stress-strain value during final forging; When the initial forging temperature is the same, the smaller the friction coefficient, the smaller the stress-strain value at the final forging. Among them, the influence of friction coefficient is greater than that of initial forging temperature.