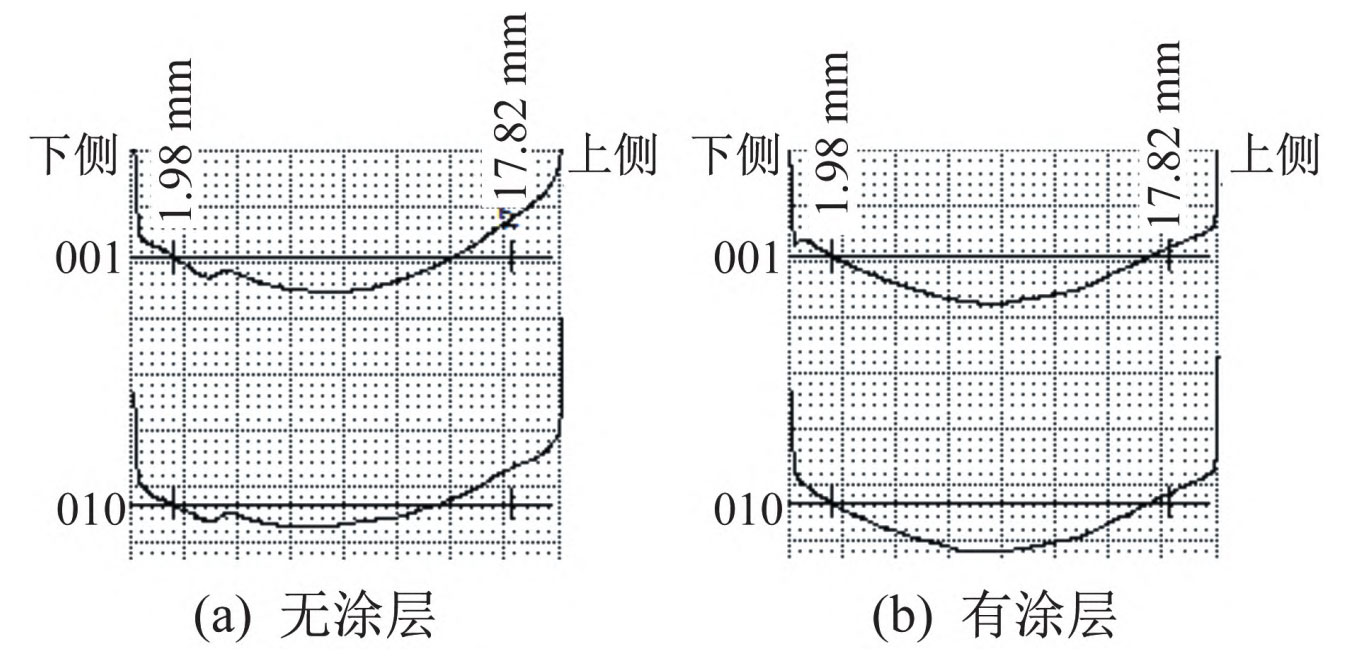
1. Accuracy Testing Results of Helical Gears
The detection results of the tooth alignment accuracy of the helical gear after running in are shown in Figure 1.
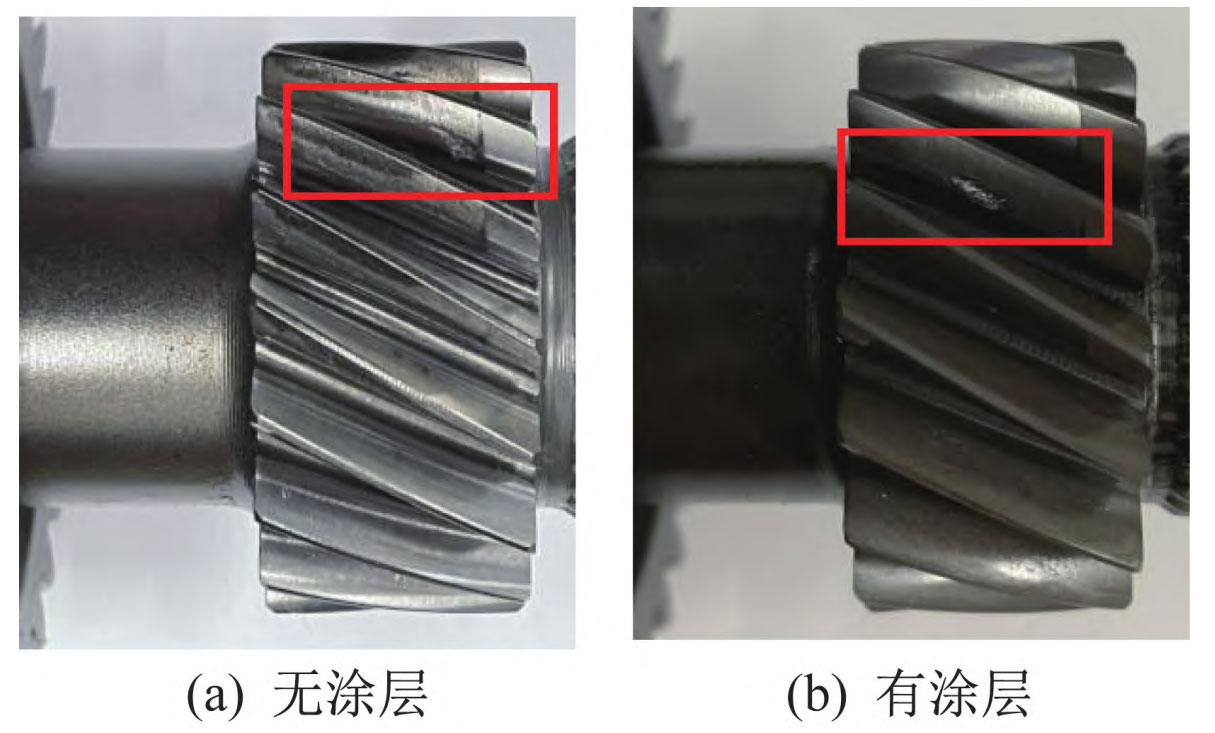
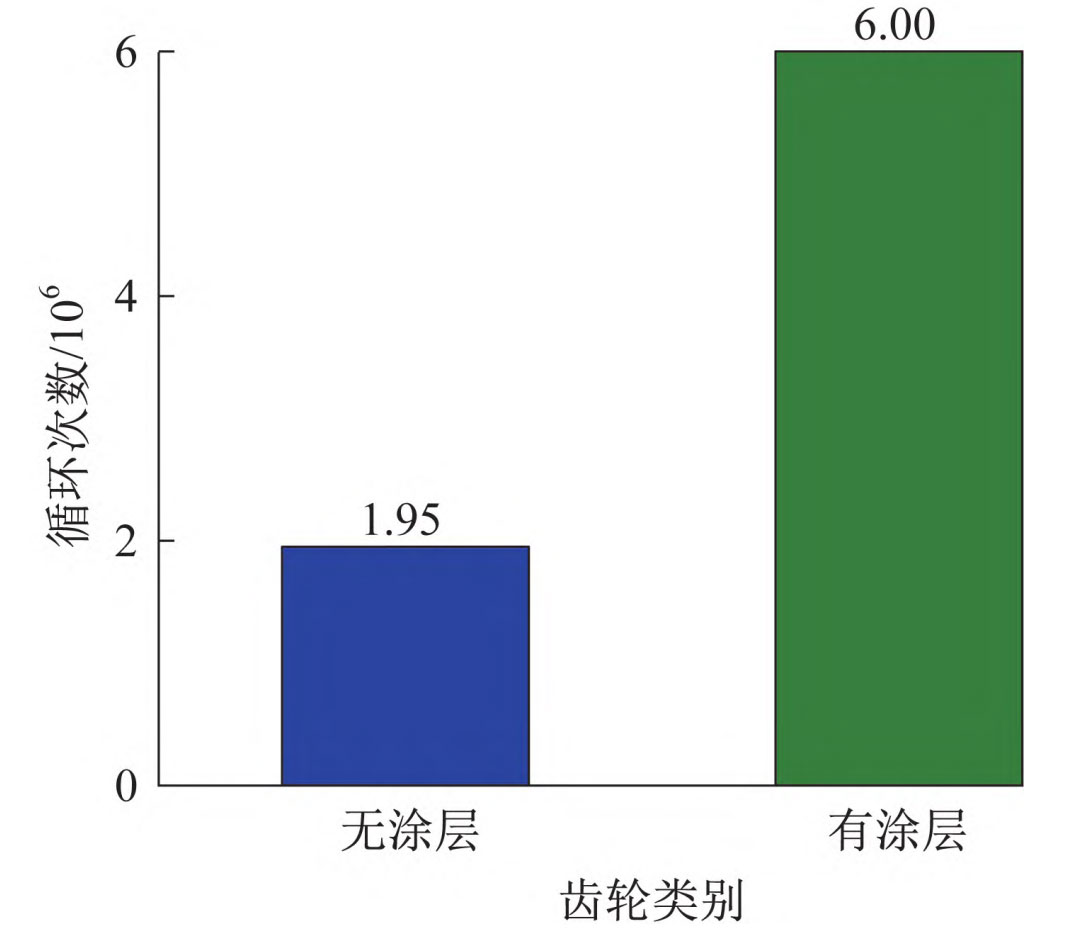
2. Test results of contact fatigue life of helical gears
According to the contact fatigue strength test standard for helical gears, real-time monitoring of vibration acceleration and observation window observation are used. When the area of pitting corrosion on the surface of the gear teeth exceeds 4%, it is determined that the helical gear has failed, and the experiment is stopped. The fatigue endurance cycles of helical gears obtained from the experiment are shown in Figure 2. As shown in the figure, the fatigue durability cycle number of coated helical gears is more than twice that of uncoated helical gears.
The fatigue pitting state of the helical gear tooth surface is shown in Figure 3. From the figure, it can be seen that due to the experimental box being a large-span helical gear box, its supporting stiffness is relatively small, which leads to biased loading of the helical gear during the meshing process. The fatigue pitting position of the uncoated tooth surface occurs at the pitch circle of the helical gear, and is inclined towards the side where the stress concentration is concentrated in the meshing area. Compared with the uncoated helical gear, the pitting position of the coated helical gear is inclined towards the middle of the meshing area.