(1) Selection of long and short modification methods
Long modification refers to the repair and removal of the part from the single tooth meshing point to the highest meshing point or from the lowest meshing point to the meshing point of the helical gear as shown in Figure 1; The starting position of short modification is the same as that of long modification, but the length is half of that of long modification. The wide helical gears with large helix angle, large double engagement, frequent load changes and severe working conditions shall adopt long modification, while those with small straight teeth and helix angle and stable working conditions shall adopt short modification. Obviously, the helical gear pair studied has a large helix angle, a large coincidence degree and acts on the high-speed and heavy load working conditions, so the long modification should be adopted.
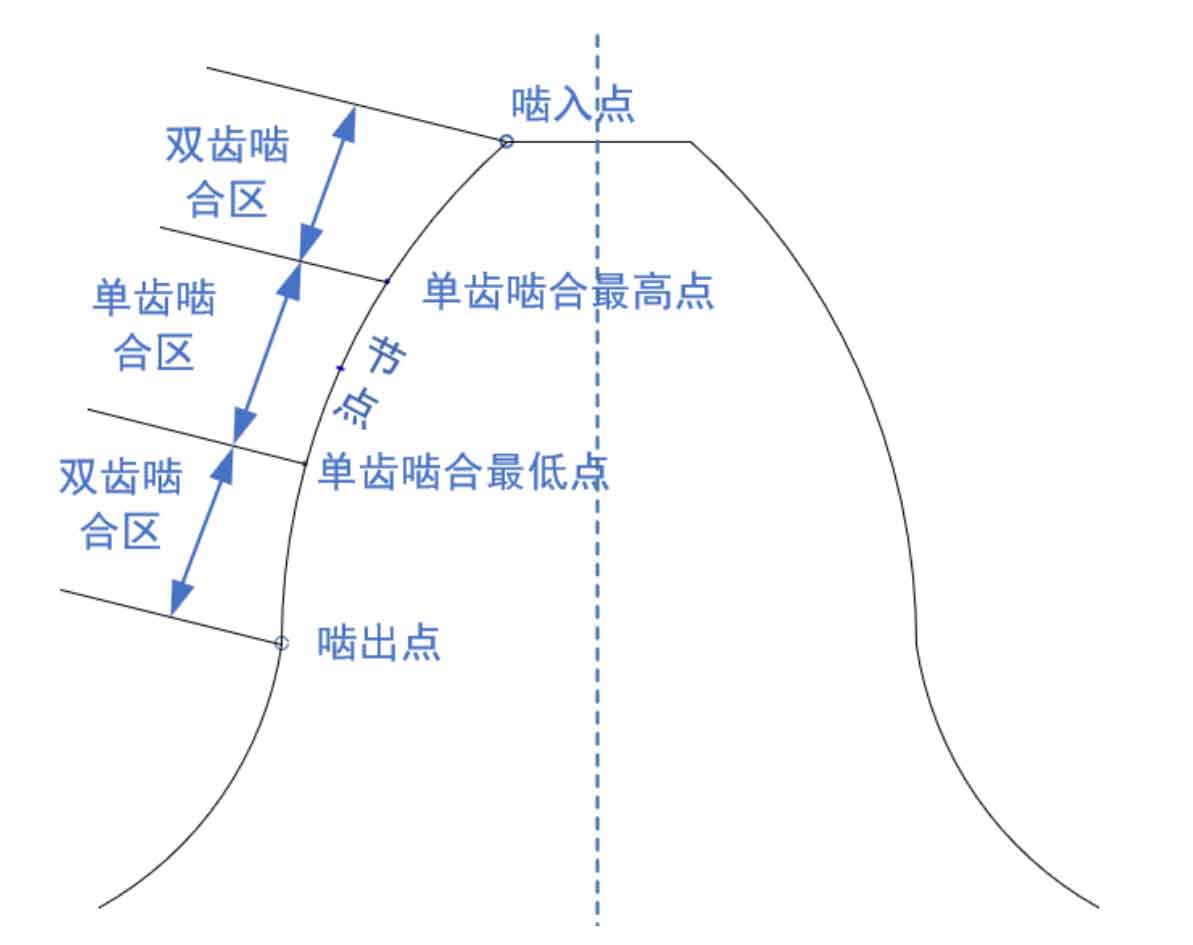
(2) Selection of gear tooth modification position
Usually, the tooth root is the weakest part of the helical gear, so the tooth root strength determines the service life of the helical gear pair. Wu Jiang suggested that if the tooth root modification of the meshing helical gear pair would cause stress concentration and reduce the strength of the helical gear, it is generally not recommended to modify the tooth root. Therefore, except that the tooth profile drum shape modification and tooth direction drum shape modification are unavoidable for the root part of the tooth, other modification methods only consider the tooth top modification.
(3) Selection of Large and Small Modified Gears
The selection of large and small modified helical gears is controversial in the industry. For example, it is recommended to modify the big and small gears at the same time under high-speed and heavy load conditions; It is recommended that only the pinion be modified under any working condition; It is recommended to modify the high-speed large gear of reducer. Therefore, this paper fully considers the three possibilities of simultaneous modification of big and small gears, modification of small gears only, and modification of big gears only, to avoid missing the optimal modification scheme.
(4) Formulation of tooth profile and tooth direction modification scheme
The tooth profile modification can improve the load distribution on the tooth surface, that is, reduce the Hertz contact stress of helical gears, while the tooth profile modification mainly reduces the vibration noise of helical gears, that is, the transmission error. Therefore, the idea of formulating the modification scheme in this paper is to first consider a single way of modification, that is, to screen the scheme with the lowest Hertz contact stress and transmission error as possible through the tooth profile or tooth direction modification as the optimal solution, and then consider the tooth direction composite modification on the basis of the tooth profile optimization modification scheme. In addition, due to the limited space, only the commonly used tooth drum modification is considered here.
(5) Determination of modification quantity and accuracy
Generally, excessive modification will damage the structural strength of helical gear body and affect its service life and transmission performance; If the modification amount is too small, it is possible to make the modification amount close to zero under the effect of processing errors and other factors. At this time, helical gear modification will become meaningless. This means that in the actual project, it is necessary to consider the influence of processing equipment, human factors and various irresistible factors in combination with the analysis of specific working conditions in order to select the appropriate modification parameters. In view of the recommended modification range of Chinese helical gear manual is 0.7 μ m~30 μ M and the modification amount used by Eaton is 3 μ m~30 μ M, and considering that the machining accuracy of domestic imported machine tools has reached the micron level, there is still+3 μ M, so the range of modification is set as 3 μ m~25 μ m. The step size, namely, the correction accuracy, is set to 1 μ m。
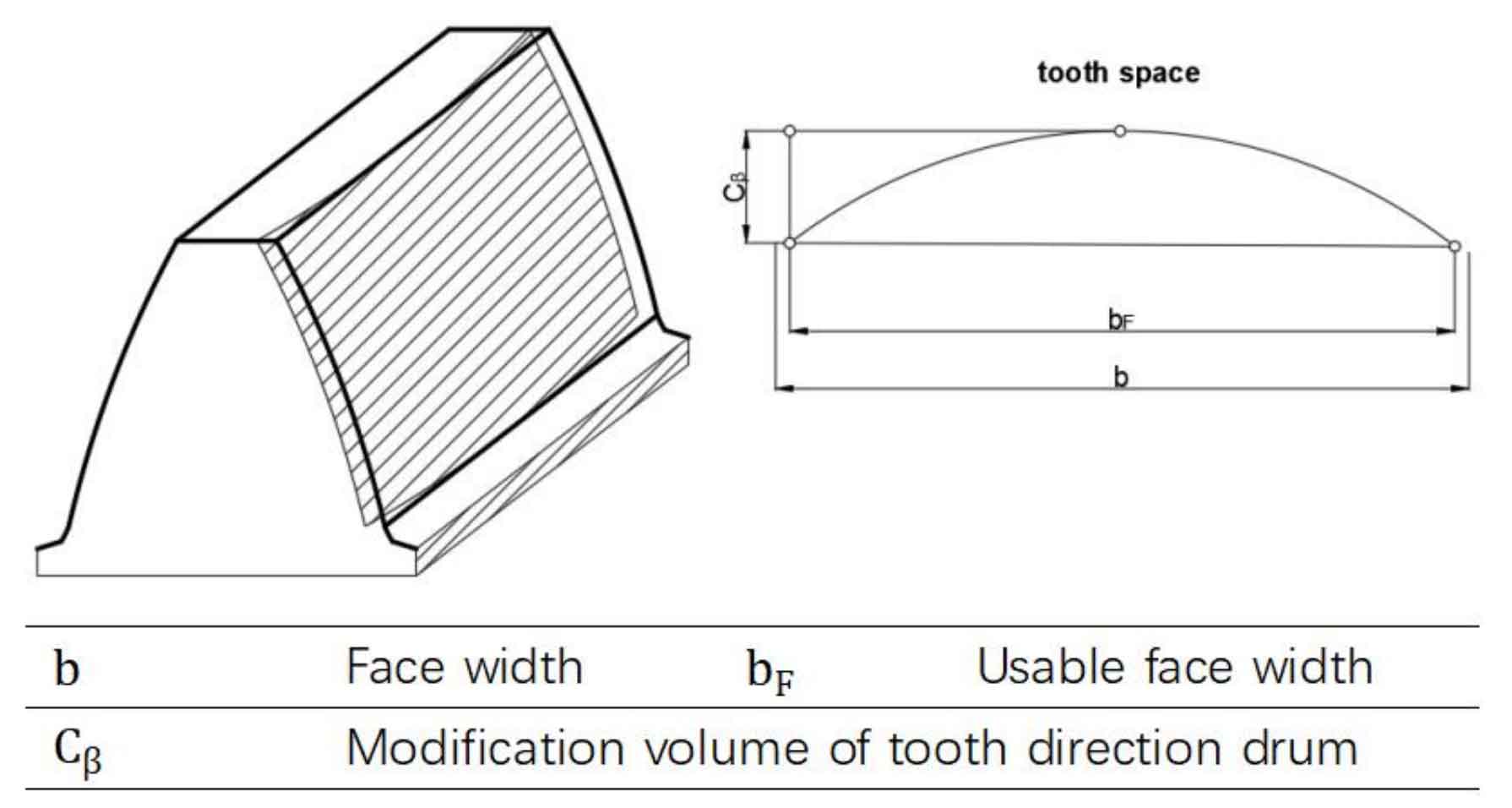
In order to describe some of the specific modification methods involved more intuitively, the shapes, general principles and shapes of different tooth profile modification methods have been given, while the modification principles of tooth drum are shown in Figure 2.
