Gear manufacturing involves various methods, each with its own advantages and limitations. Gear hobbing is one of the most widely used techniques, but it is important to consider its pros and cons in comparison to other gear manufacturing methods. This article provides an overview of gear hobbing and highlights its pros and cons when compared to alternative gear manufacturing methods.
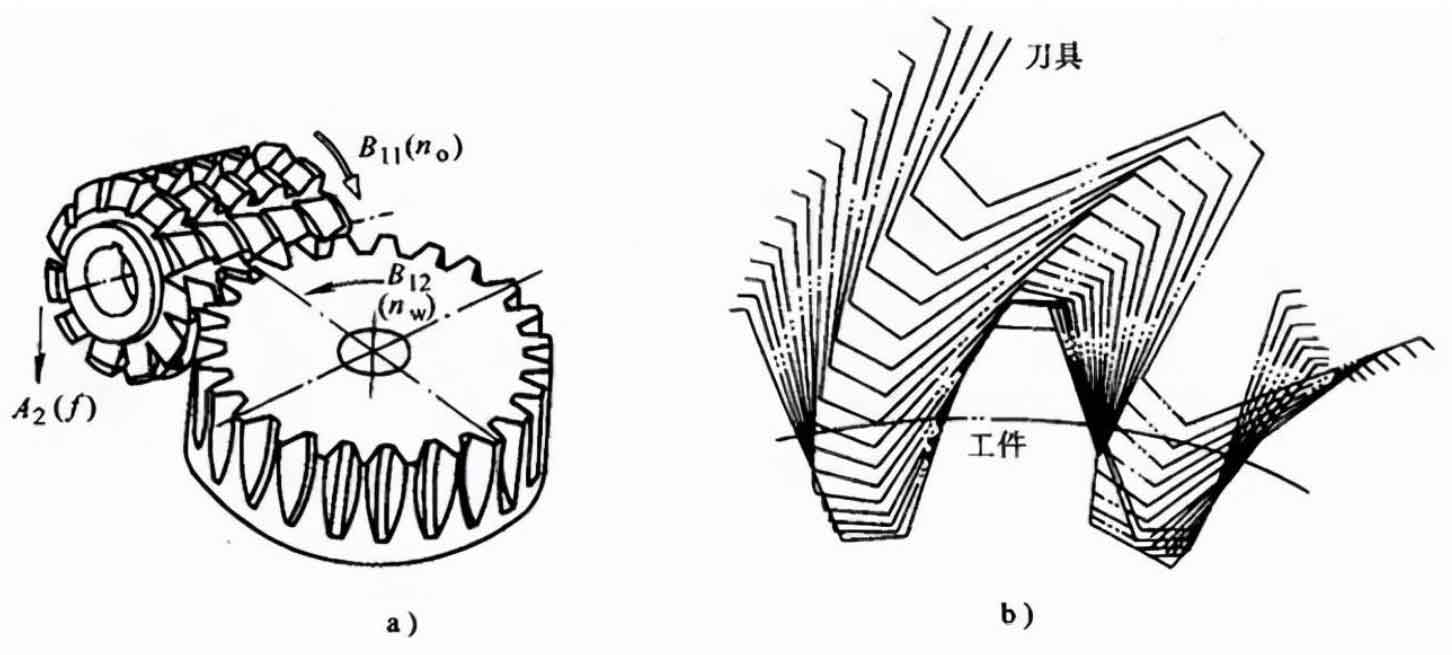
Gear Hobbing:
Gear hobbing is a process that uses a hobbing machine equipped with a hob to cut gear teeth. The hob has a series of cutting edges that gradually shape the gear teeth as the workpiece rotates. Gear hobbing is known for its accuracy, efficiency, and versatility.
Pros of Gear Hobbing:
- Precision: Gear hobbing enables the production of gears with high precision and accurate tooth profiles. This results in smooth gear meshing, optimal load distribution, and reliable power transmission.
- Efficiency: Gear hobbing is an efficient method for mass production of gears. It allows for the simultaneous cutting of multiple gear teeth, reducing machining time and increasing productivity.
- Versatility: Gear hobbing can produce various types of gears, including spur gears, helical gears, and worm gears. It is suitable for both small and large gears, making it a versatile manufacturing method.
Cons of Gear Hobbing:
- Initial Investment: Setting up a gear hobbing operation requires a significant initial investment in hobbing machines, tooling, and skilled operators. This can be a barrier for small-scale manufacturers or those with limited resources.
- Limited Gear Size Range: Gear hobbing has limitations in terms of the gear size range it can handle. Very small or very large gears may require alternative manufacturing methods.
- Complexity for Non-Standard Gears: Gear hobbing is more suited for standard gear designs. Producing non-standard or custom gear profiles may require additional tooling or modifications to the hobbing machine.
Alternative Gear Manufacturing Methods:
- Gear Shaping: Gear shaping is a process where a rotating cutter shapes the gear teeth by removing material from the workpiece. It offers excellent precision and is suitable for various gear types. However, it typically has slower production rates compared to gear hobbing.
- Gear Grinding: Gear grinding is a process that uses abrasive grinding wheels to finish gear teeth to high precision. It is commonly used for high-precision gears or when a superior surface finish is required. However, gear grinding can be time-consuming and costly.
- Gear Milling: Gear milling involves using a milling cutter to remove material and create gear teeth. It offers flexibility and is suitable for small to medium-sized gears. However, gear milling may not achieve the same level of accuracy and efficiency as gear hobbing.
Gear hobbing is a widely used gear manufacturing method known for its precision, efficiency, and versatility. It is suitable for a range of gear types and offers efficient mass production capabilities. However, it does require an initial investment and may have limitations in terms of gear size range and non-standard gear profiles. When considering alternative gear manufacturing methods such as gear shaping, gear grinding, and gear milling, manufacturers should carefully assess their specific requirements in terms of precision, production volume, gear type, and cost considerations. Selecting the most suitable gear manufacturing method will ultimately depend on the specific needs of the application and the desired balance between accuracy, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
