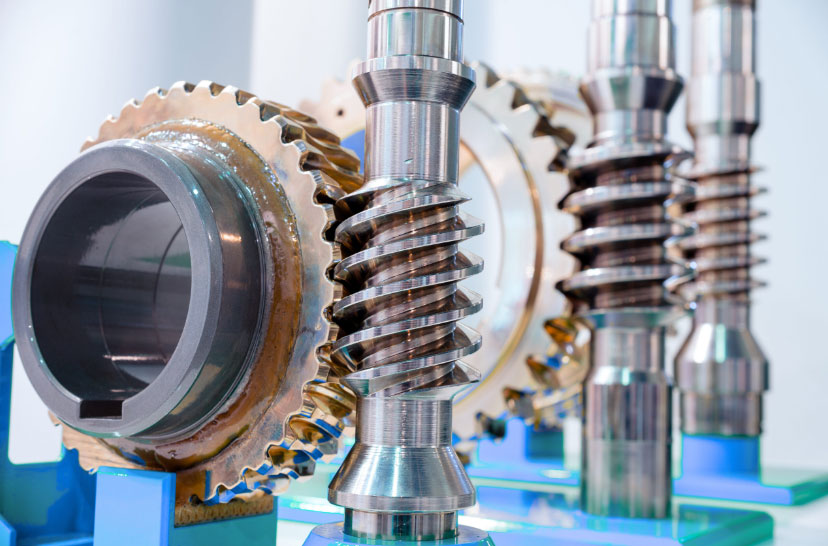
Gear mesh at an angle refers to the interaction between helical gears, which have teeth that are cut at an angle to the gear’s axis. Unlike spur gears that have teeth straight along the gear’s axis, helical gears have a helix angle, which allows for smoother and more gradual tooth engagement. The science behind helical gear interactions involves several important aspects:
- Helix Angle: The helix angle is the angle between the tooth’s helix line and the gear’s axis. It determines the direction and amount of force that is transmitted between the meshing gears. The helix angle reduces the sliding contact between the teeth, resulting in less noise and wear compared to spur gears.
- Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of helical gears is complex due to the helix angle. It is usually designed based on standard tooth profiles like involute or cycloid. The tooth profile influences how the gears transmit motion and torque efficiently.
- Contact Ratio: Helical gears have a higher contact ratio than spur gears. The contact ratio is the ratio of the number of teeth in contact between the meshing gears at any given moment. A higher contact ratio distributes the load more evenly across the gear teeth, reducing wear and increasing the gear’s load-carrying capacity.
- Axial Thrust: Due to the helix angle, helical gears create an axial thrust force along the gear’s axis. This thrust force must be accommodated in the gear design by using thrust bearings or other appropriate means.
- Load Distribution: Helical gears distribute the load along the tooth engagement gradually, reducing the peak loads that occur in spur gears during initial contact. This leads to smoother operation and less vibration.
- Efficiency: Helical gears typically have higher efficiency than spur gears because of their improved load distribution and reduced sliding contact. However, they do have higher axial thrust losses, especially in parallel-axis helical gears.
- Noise and Vibration: Helical gears generate less noise and vibration than spur gears because the teeth engage gradually and smoothly. However, they can still produce axial thrust-related noise, which may require additional design considerations to mitigate.
- Manufacturing and Assembly: The manufacturing of helical gears is more complex than spur gears due to the angled tooth profile. Precision machining and assembly are necessary to ensure proper gear mesh and minimize noise and wear.
Helical gears offer several advantages over spur gears, including smoother operation, higher load-carrying capacity, and reduced noise. Their design and manufacturing complexity require careful consideration, but their benefits make them suitable for various applications, particularly where quiet and efficient power transmission is essential.
