The color capture of the color pickup lens of a CCD industrial camera is mainly based on three primary colors: R, G, and B, enabling the acquisition of colorful images. However, the recognition of automotive gear grinding crack images is independent of image color. The image data with a large proportion of color will not only compress the storage space of the image, but also cause slow progress in subsequent work. Therefore, it is necessary to grayscale the filtered and noise reduced image of grinding cracks in automotive gears to reduce the influence range of multiple optical paths.
Grayscale processing includes grayscale single component method and grayscale threshold subtraction method. Firstly, grayscale single component method is used to perform fusion weight assignment on image data with high color sensitivity, so as to obtain image weights that are not sensitive to the three primary colors R, G, and B. Then, set a gray threshold value using the gray threshold subtraction method, limit the image modules with uneven color distribution and greater difficulty in eliminating to a specified area, and repeatedly perform subtraction calculations on the image data in that area until the color saturation returns to zero. The expression of the grayscale single component method is as follows:
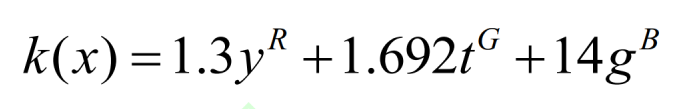
Where: x is the image fusion weight coefficient; Y ^ R, t ^ G, and g ^ B are the lowest weighted sensitivities for the three primary colors.
The silhouette calculation formula is as follows:
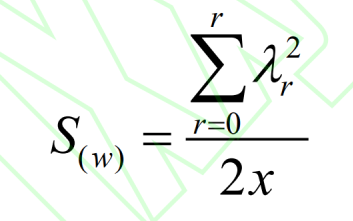
Where: w is the center of the car gear in the silhouette area; λ Is the difference coefficient of image silhouette; Where r is the color saturation. When r=0, the image data silhouette of this area ends, and a grayscale image of the grinding crack of the automotive gear is obtained.
