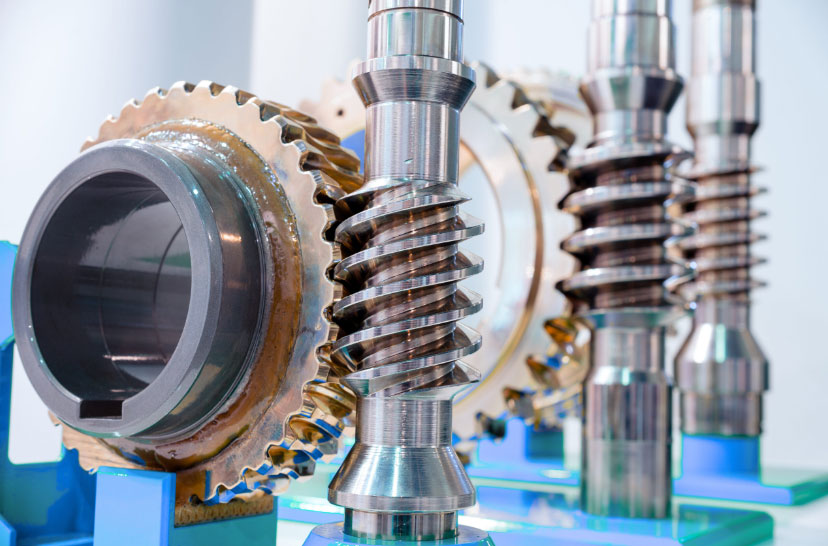
Helical gears are a fundamental type of gear used in various mechanical systems and machines. They belong to the family of cylindrical gears and are widely employed in industries such as automotive, manufacturing, and robotics. Unlike spur gears, which have teeth aligned parallel to the axis of rotation, helical gears have teeth that are cut at an angle to the gear’s axis, resulting in a helix shape.
Here are some key aspects to understand about helical gears:
- Tooth Profile: The teeth of helical gears have a helical shape, which means they are cut at an angle to the gear’s axis, forming a helix. The helix angle is the angle between the tooth and the gear’s axis. The helix angle contributes to smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears.
- Contact Area: Helical gears have a greater tooth engagement with their counterparts compared to spur gears. This extended contact area spreads the load across more teeth, leading to higher load-carrying capacity and improved torque transmission.
- Direction of Rotation: Helical gears can transmit rotational motion between non-parallel shafts. When two helical gears mesh, the teeth gradually engage, which helps reduce noise and vibration during operation.
- Axial Thrust: Due to the helical tooth orientation, helical gears generate axial thrust along the gear axis. This thrust must be accommodated by suitable thrust bearings or by using gear pairs with opposing helix angles.
- Efficiency: Helical gears are generally more efficient than spur gears, especially for high-speed applications, as they experience less sliding friction during engagement.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is crucial for helical gears, as the sliding motion along the helical teeth can generate heat and wear. Adequate lubrication ensures smooth operation and prolongs the gear’s lifespan.
- Manufacturing: Helical gears are more complex to manufacture compared to spur gears due to the angled tooth profile. This process often involves specialized gear-cutting machinery or techniques such as hobbing or shaping.
- Applications: Helical gears are commonly used in automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, gearboxes, and various other power transmission systems.
Despite their advantages, helical gears also have some drawbacks. The axial thrust they generate can cause issues if not properly managed, and they may be more expensive to produce due to the complexity of manufacturing.
Overall, helical gears are an essential gear type used in many mechanical applications, striking a balance between efficiency, smoothness, and load-carrying capacity. Their versatility makes them indispensable in modern engineering and machinery.
