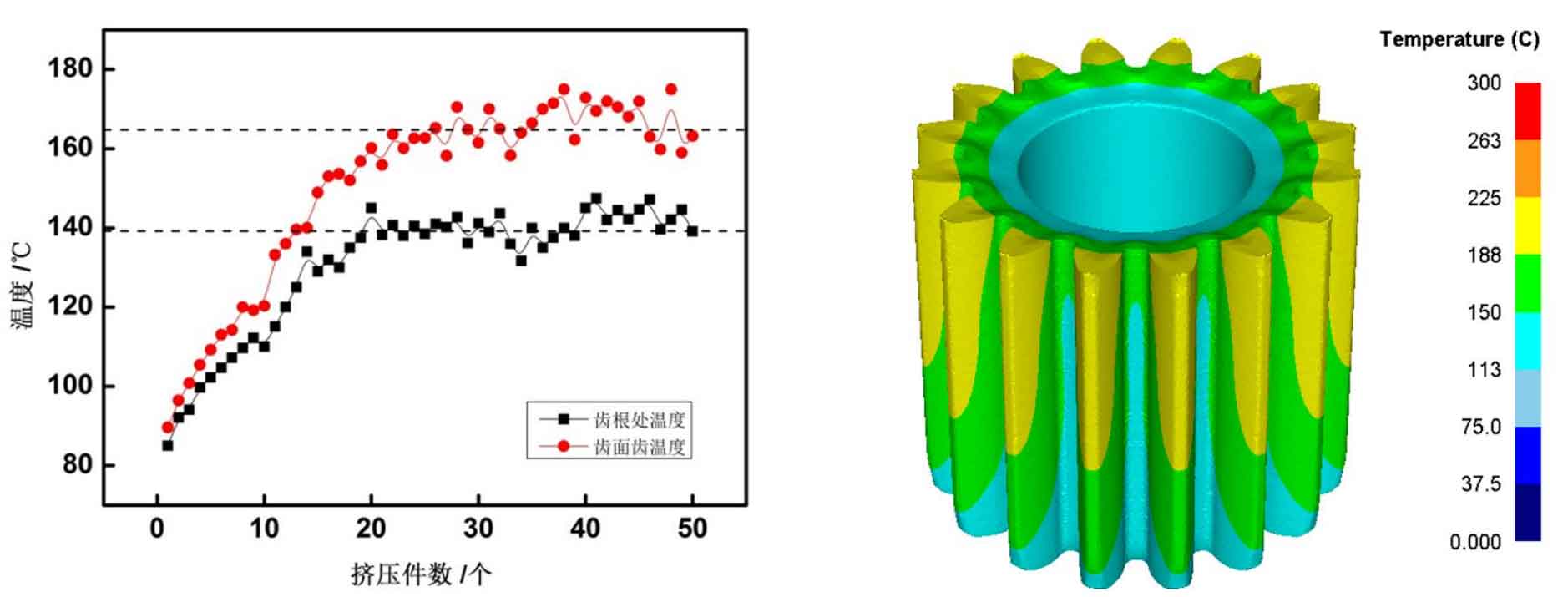
In actual production, the forming of workpiece is accompanied by heat generation, and the temperature of die and workpiece will rise accordingly. The surface temperature of the gear formed by cold extrusion has changed. When the continuous production of cold shaping immediately after cold extrusion is adopted, the temperature directly affects the forming quality and accuracy of the gear after shaping. Figure (a) shows the temperature measurement results of the extruded gear with a non-contact infrared thermometer. The detection points are respectively selected near the tooth surface and tooth root of the middle section of the gear, and the first part is detected from the beginning of extrusion to the 50th part. After extrusion to 20-30 pieces, the temperature detection data tend to be stable, the tooth surface temperature is about 160 ℃, and the tooth root temperature is about 140 ℃. Figure (b) shows the numerical simulation results of the temperature distribution on the gear surface after cold extrusion. It can be seen from the figure that the temperature of the gear parts increases after cold extrusion, the temperature at the lower end of the gear is lower than the upper end, and the temperature at the tooth surface and tooth top is higher than that at the tooth root.
In order to study the influence of deformation heat on gear forming accuracy, numerical simulation is carried out under the condition of turning on and off the heat conduction function. The unilateral shaping amount is 0.15mm, and the shaping method of only shaping the tooth surface is adopted. When heat conduction is turned on, after extrusion, the gear has a temperature field and will be inherited to the next shaping simulation. When heat conduction is turned off, the temperature of blank, die and gear is always room temperature in the numerical simulation of cold extrusion and cold shaping.
The total deviation of tooth profile and helix of formed gear under the conditions of isothermal and deformation heat are compared. It can be seen from the table that the deformation heat has an obvious impact on the gear forming accuracy, and the deformation heat will increase the tooth surface deviation and reduce the accuracy. This is because in the forming process, the blank deformation and deformation heat distribution are uneven, resulting in the uneven temperature distribution of the gear, the thermal expansion coefficient and elastic modulus of the material are different at different temperatures, and the elastic recovery of the gear after forming is also different, which affects the precision of the formed gear.
