There are three kinds of optimal modification schemes for tooth profile drum shape, which are the modification amount of driving wheel 3 μ M. Shape modification of driven wheel 3 μ m. Modification amount of driving wheel 3 μ M. Shape modification of driven wheel 0 μ m. Modification amount of driving wheel 0 μ M. Shape modification of driven wheel 3 μ m。 Figure 1 shows the time-varying meshing force curve of the helical gear pair before and after the optimization and modification of the tooth profile drum shape at different speeds. It can be seen that if the tooth profile drum shape of the driving and driven gear (pinion) or only the driven gear (big gear) is modified, the time-varying meshing force of the helical gear pair will not only significantly reduce, but also the meshing impact phenomenon will disappear. However, if only the driving wheel (pinion) is modified, not only the time-varying meshing force of the gear is not reduced, but also the meshing impact is still serious. Because the modification effect is too poor compared with the other two drum optimization schemes of tooth profile, this scheme is omitted.
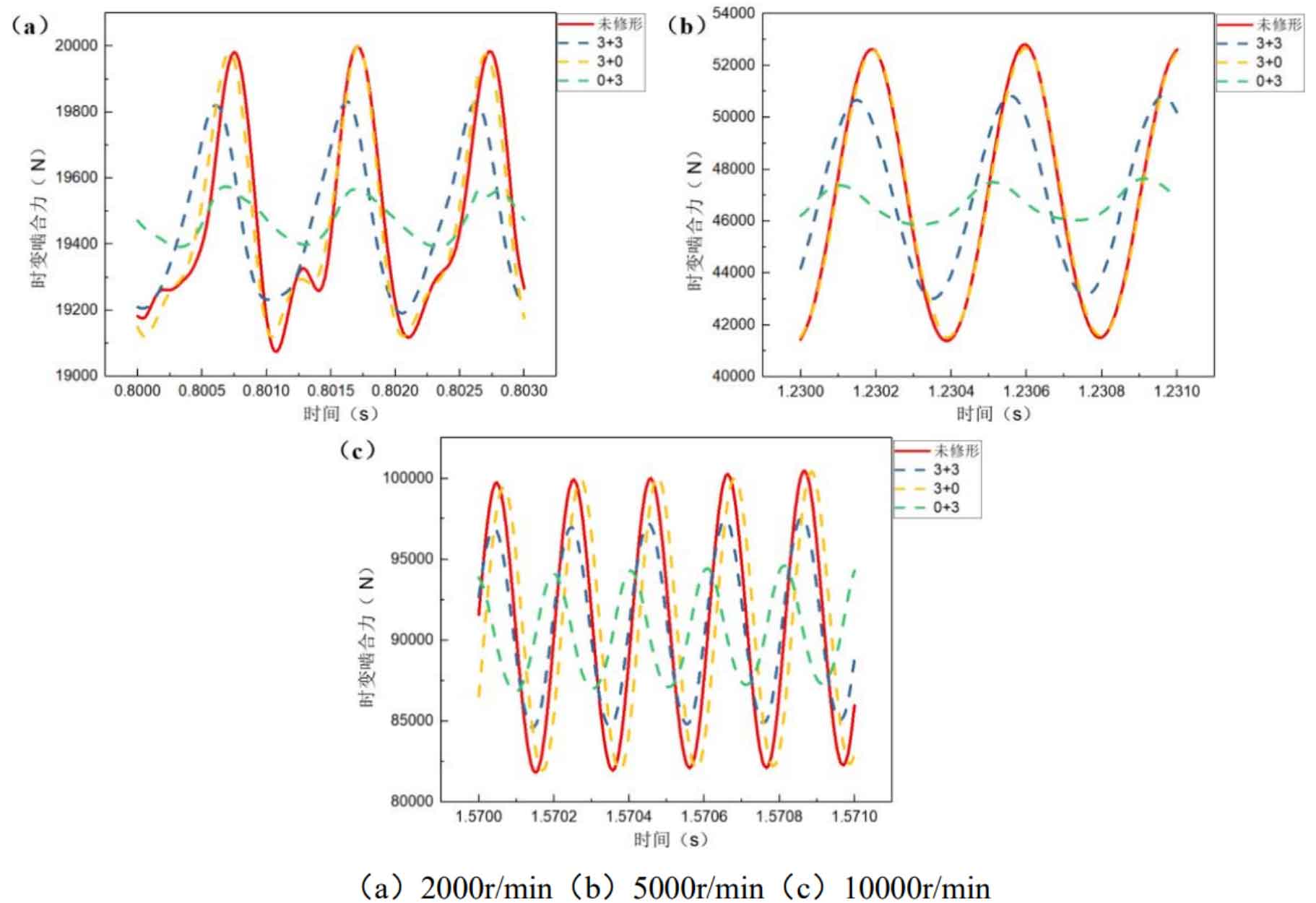
The peak value of the time-varying meshing force of the helical gear pair of the reduction box of an electric vehicle after the optimization and modification of the active and passive gear profile is 19826.629N, 50804.301N and 97544.961N respectively at low speed, medium speed and high speed, which is 172.484N, 1989.976N and 2936.359N lower than that before the modification; However, only after the drum shape of the passive gear tooth profile of the helical gear pair is optimized and modified, the peak value of the time-varying meshing force at low speed, medium speed and high speed is 19573.523N, 47619.484N and 94555.805N respectively, and the degree of decline is as high as 425.59N, 5174.793N and 5925.515N respectively.
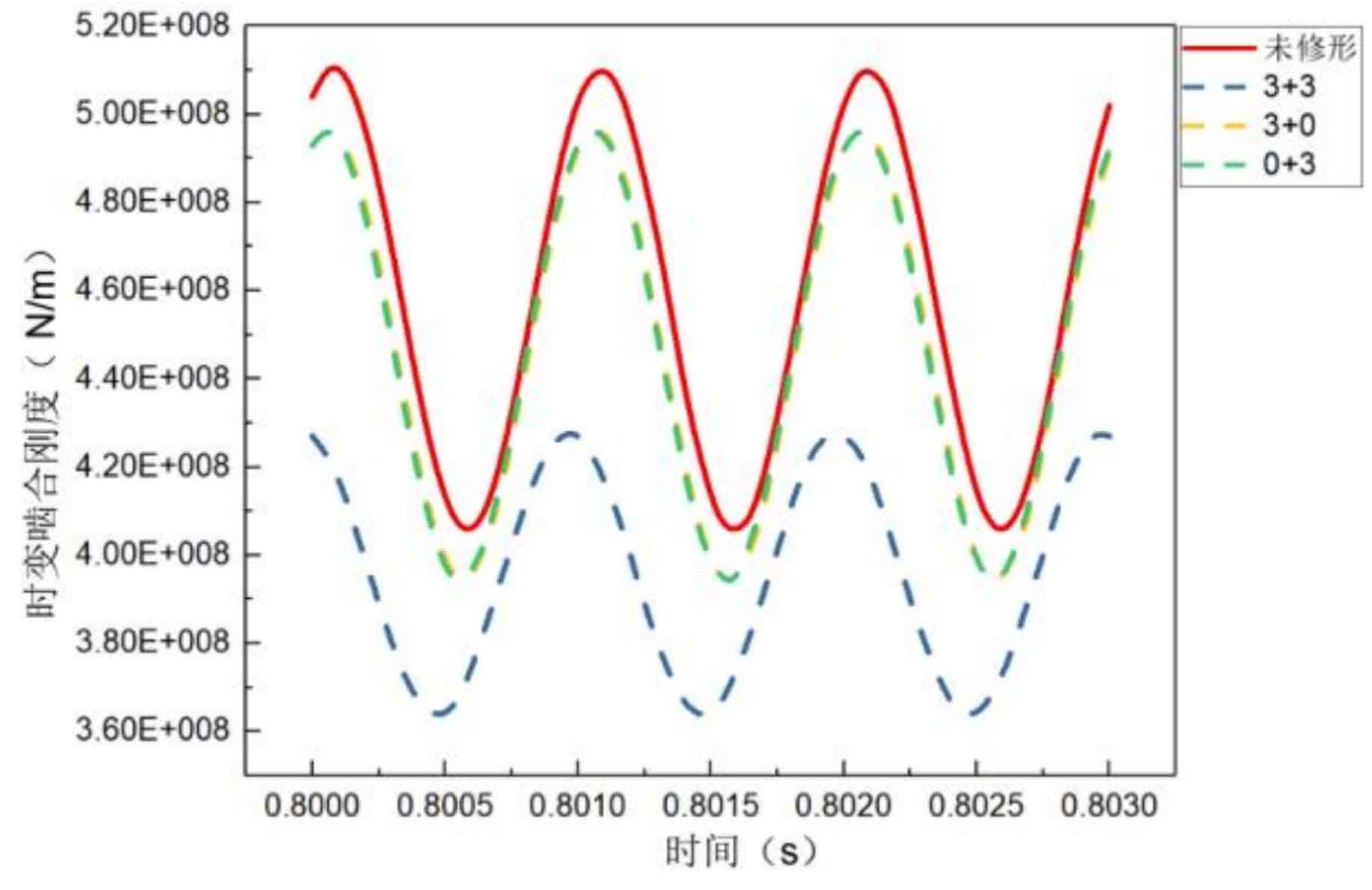
Figure 2 shows the time-varying meshing stiffness curve of the helical gear pair before and after the optimization modification of tooth profile drum. It can be found that the time-varying meshing stiffness is the lowest after the simultaneous tooth profile drum modification of the driving and driven gears (pinion), and the fluctuation range is reduced to 3.64 × 10^8N/m~4.27 × 10 ^ 8N/m, with a peak decrease of 16.3%; However, the time-varying meshing stiffness is the same, and the peak value decreases to 4.96, regardless of the drum shape of the driving gear or the passive gear × 108N/m, with a decrease of 2.7%.
To sum up, the selection of the modified helical gear is very critical for the drum modification method of the tooth profile. If the main purpose is to reduce the stiffness excitation of the helical gear pair, it is recommended that the large and small gears be modified at the same time; If the objective is to reduce the time-varying meshing force of the helical gear pair, eliminate the meshing impact phenomenon, and prevent the gear pair from violent vibration, it is recommended to modify the shape of the large gear or the small gear at the same time. In addition, the drum shape optimization of the tooth profile of the driving gear (pinion) can also reduce the stiffness excitation to a certain extent, but the effect is obviously relatively poor, so it is not recommended.
