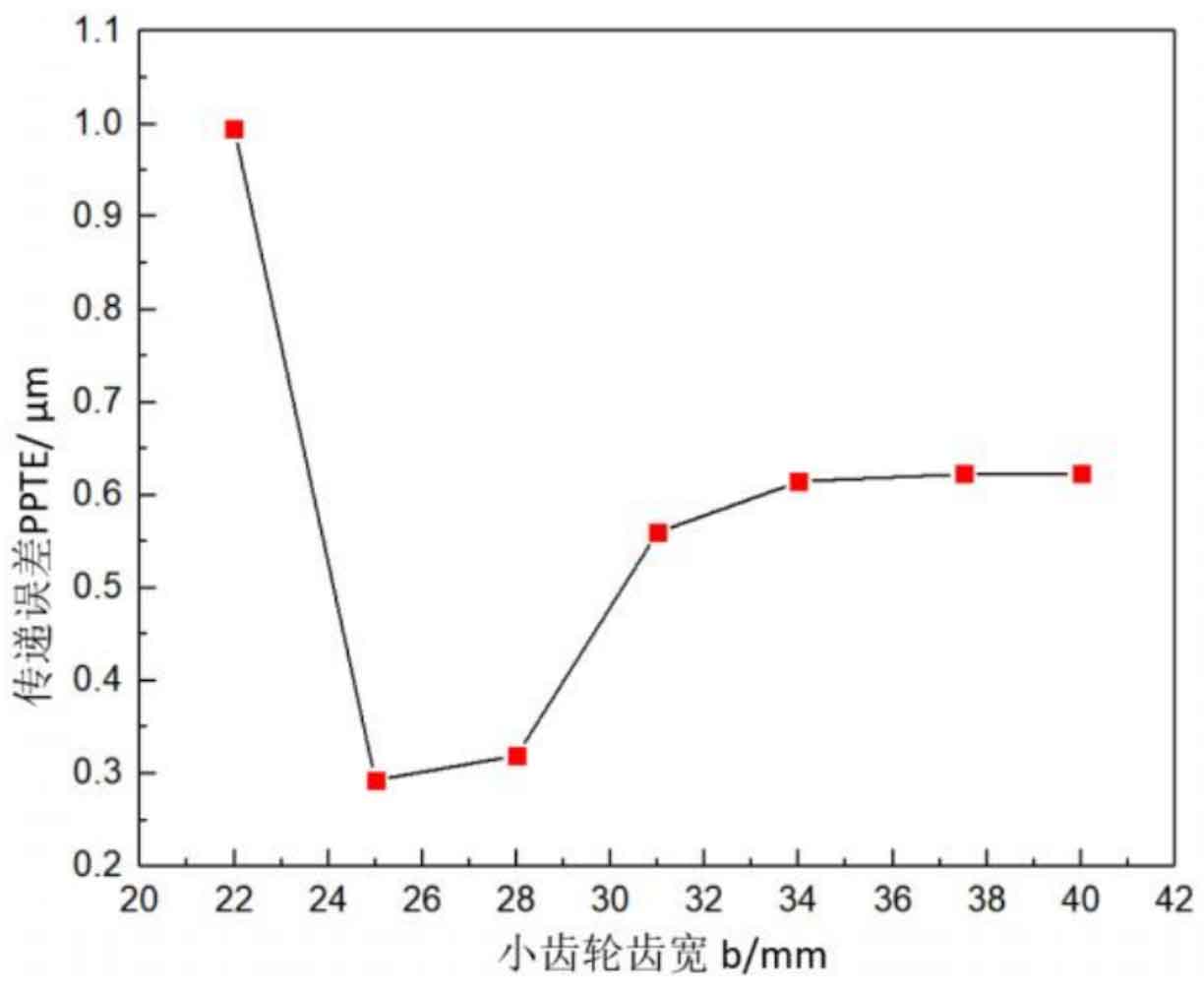
(1) Influence of pinion tooth width on transmission error of helical gear
Figure 1 shows the relation curve between the pinion tooth width and the transmission error h of helical gear. It can be seen that in the range of 22mm~40mm, with the increase of the pinion tooth width, the transmission error first decreases and then increases until it remains unchanged, that is, when the pinion tooth width reaches 34mm, the transmission error h is stable at 0.615 μ m。
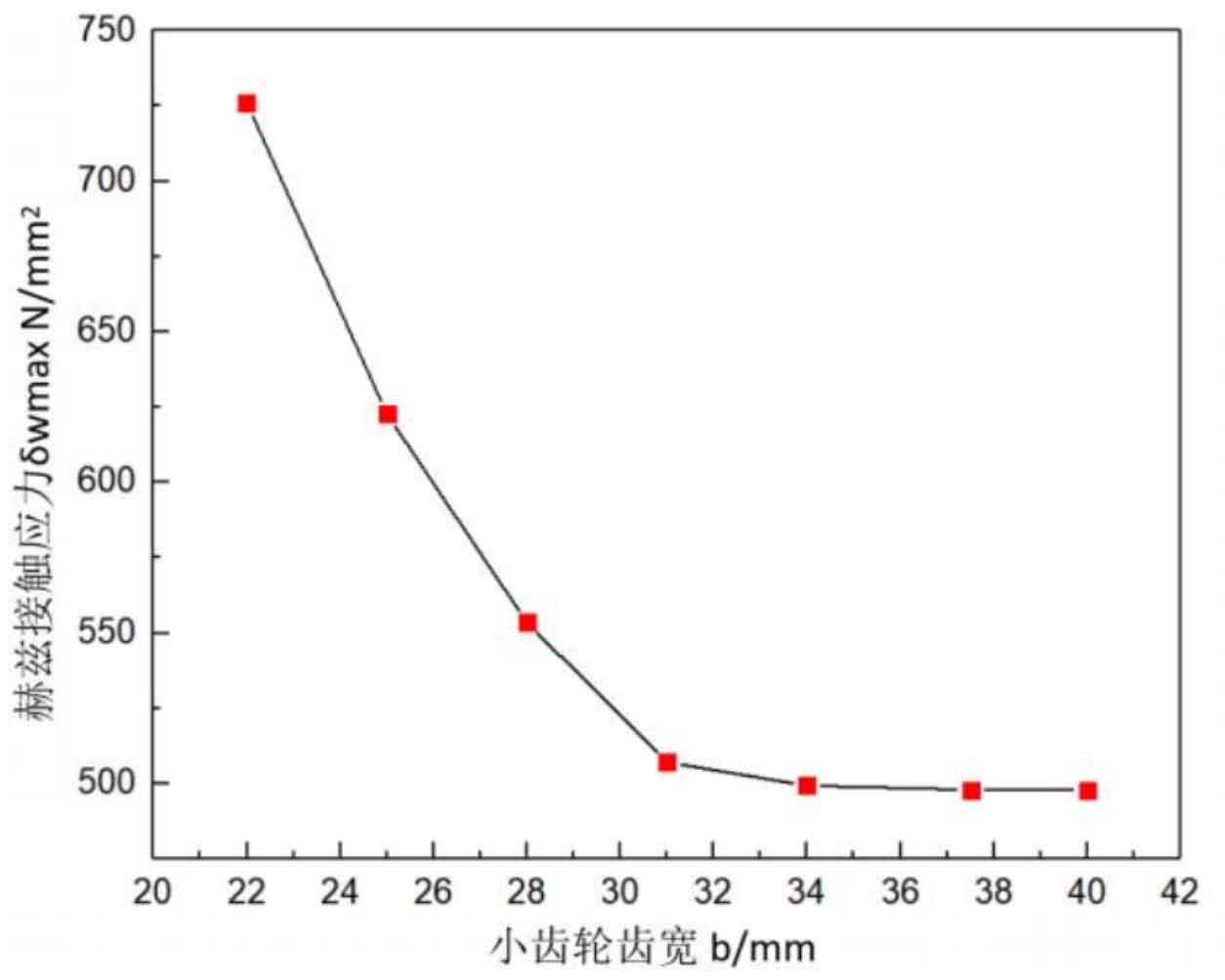
(2) Influence of Pinion Tooth Width on Hertz Contact Stress of Helical Gear
Figure 2 shows the relationship curve between the pinion tooth width and the Hertz contact stress of the helical gear. It can be seen from the figure that as the pinion tooth width increases, the Hertz contact stress first continues to decrease until the pinion tooth width exceeds 34mm, and the Hertz contact stress decreases to the lowest, 499.347N/mm2.
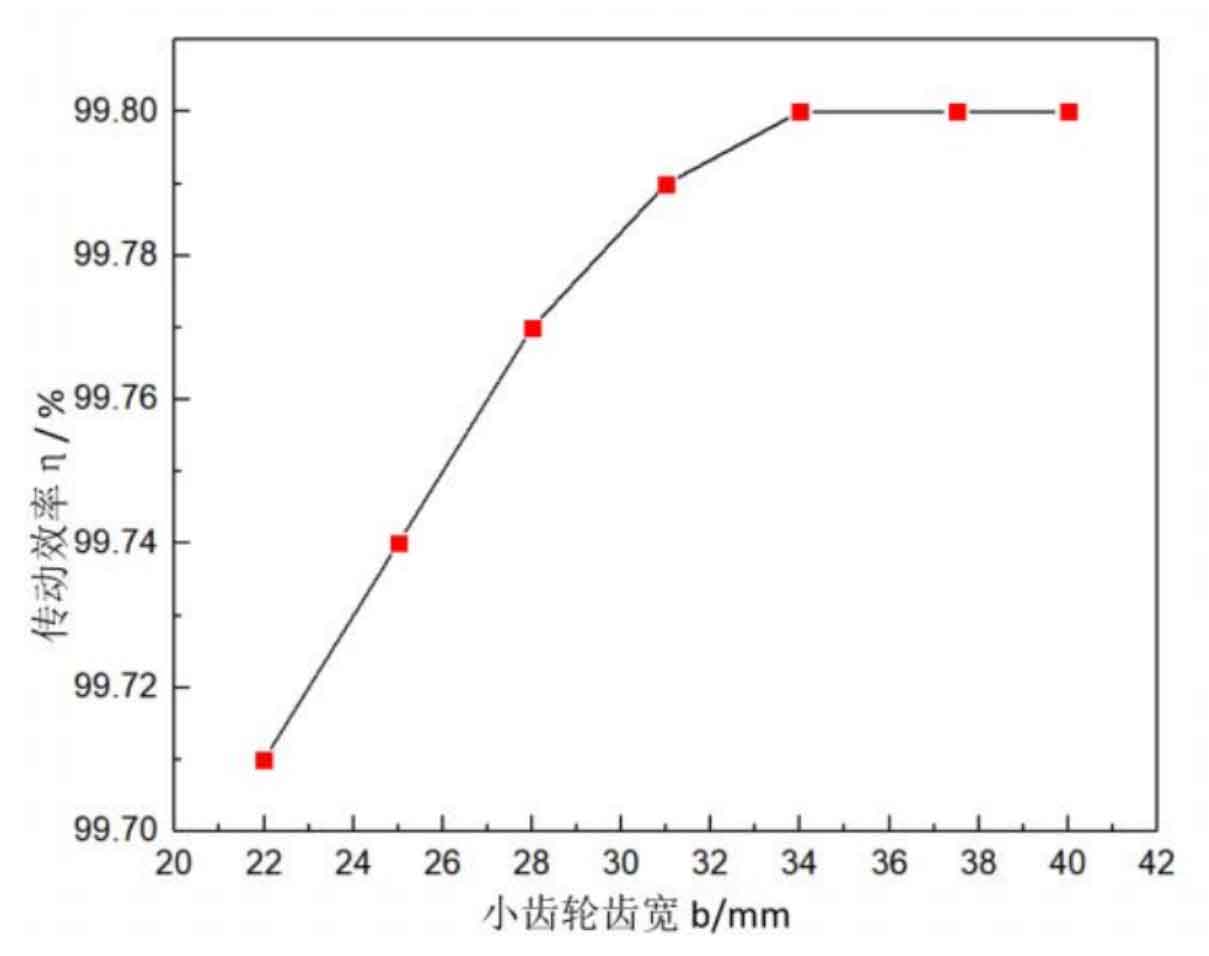
(3) Influence of pinion tooth width on helical gear transmission efficiency
Figure 3 shows the relationship curve between pinion tooth width and helical gear transmission efficiency. When the pinion tooth width changes in the range of 22mm~34mm, the transmission efficiency will be greatly increased to 99.8% with the increase of tooth width; However, when the pinion tooth width exceeds 34mm, the transmission efficiency remains unchanged.
To sum up, properly increasing the pinion tooth width is conducive to improving the transmission efficiency and Hertz contact stress of the helical gear, but it will increase the transmission error, thus exacerbating the vibration noise of the helical gear.
Therefore, we cannot blindly increase the tooth width of wheel and pinion, otherwise it will only increase the manufacturing cost without any benefit.
