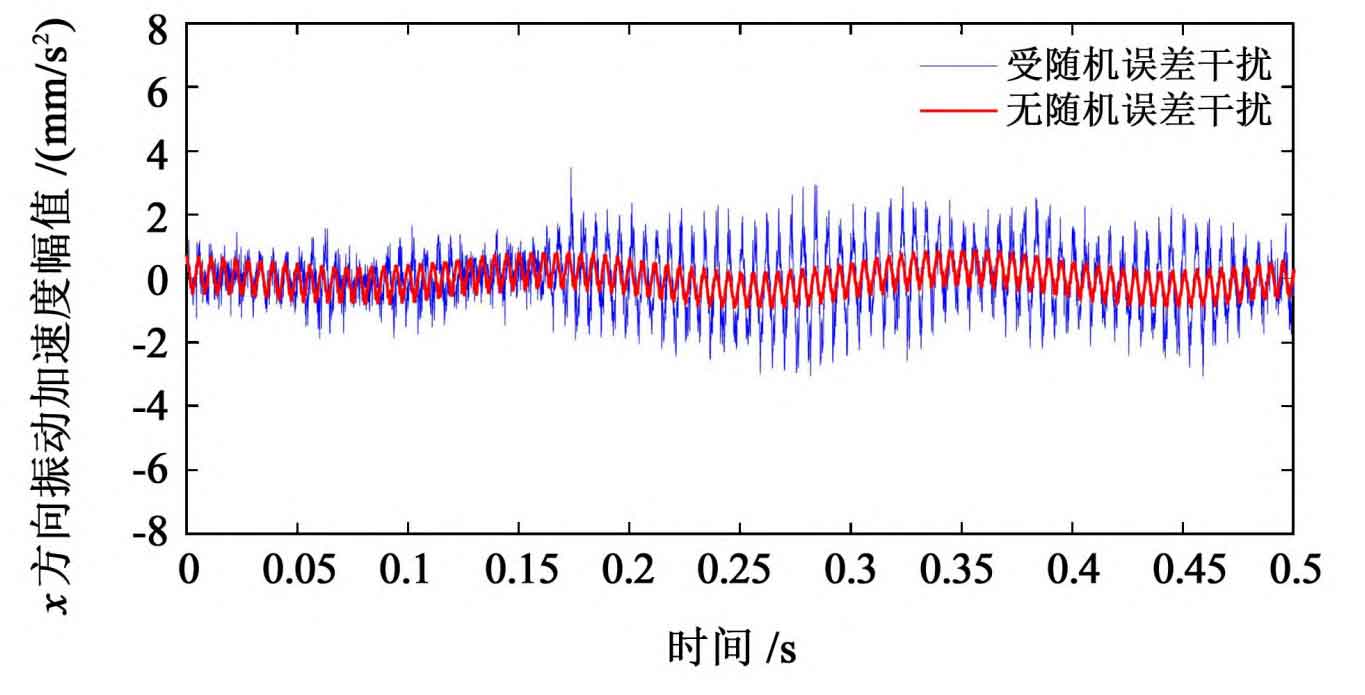
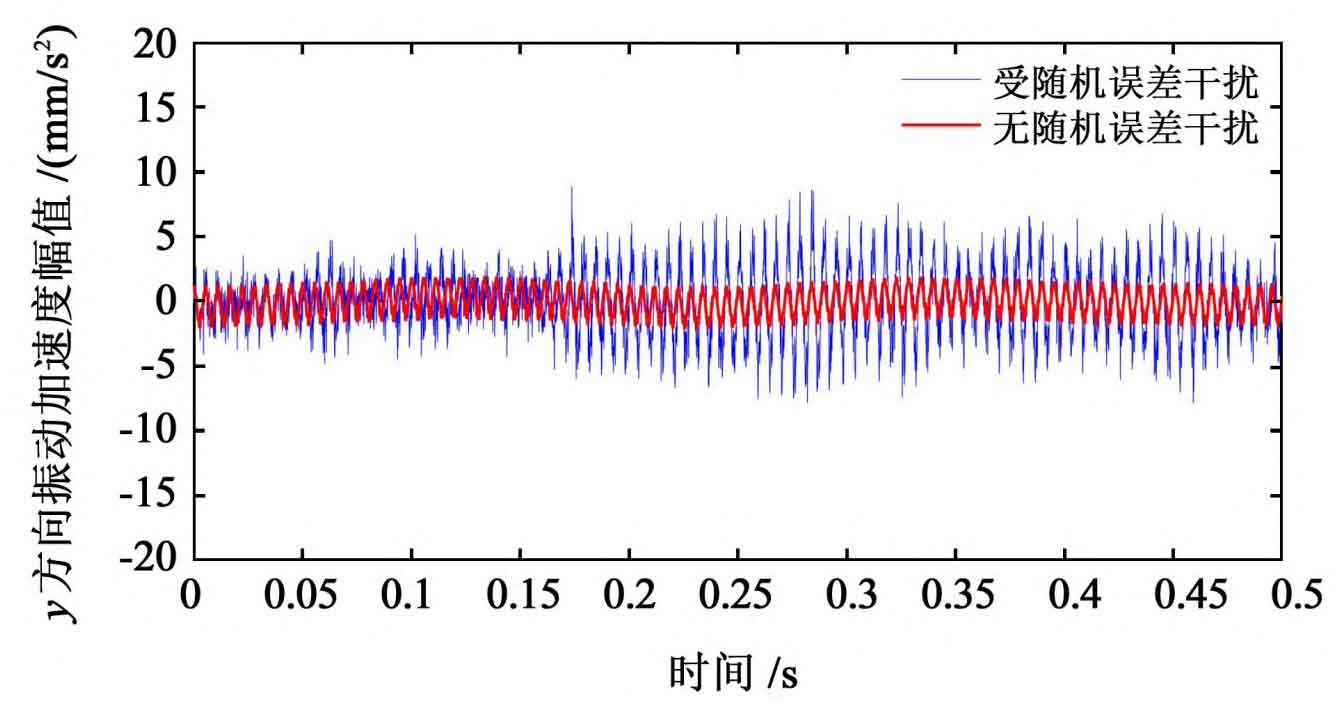
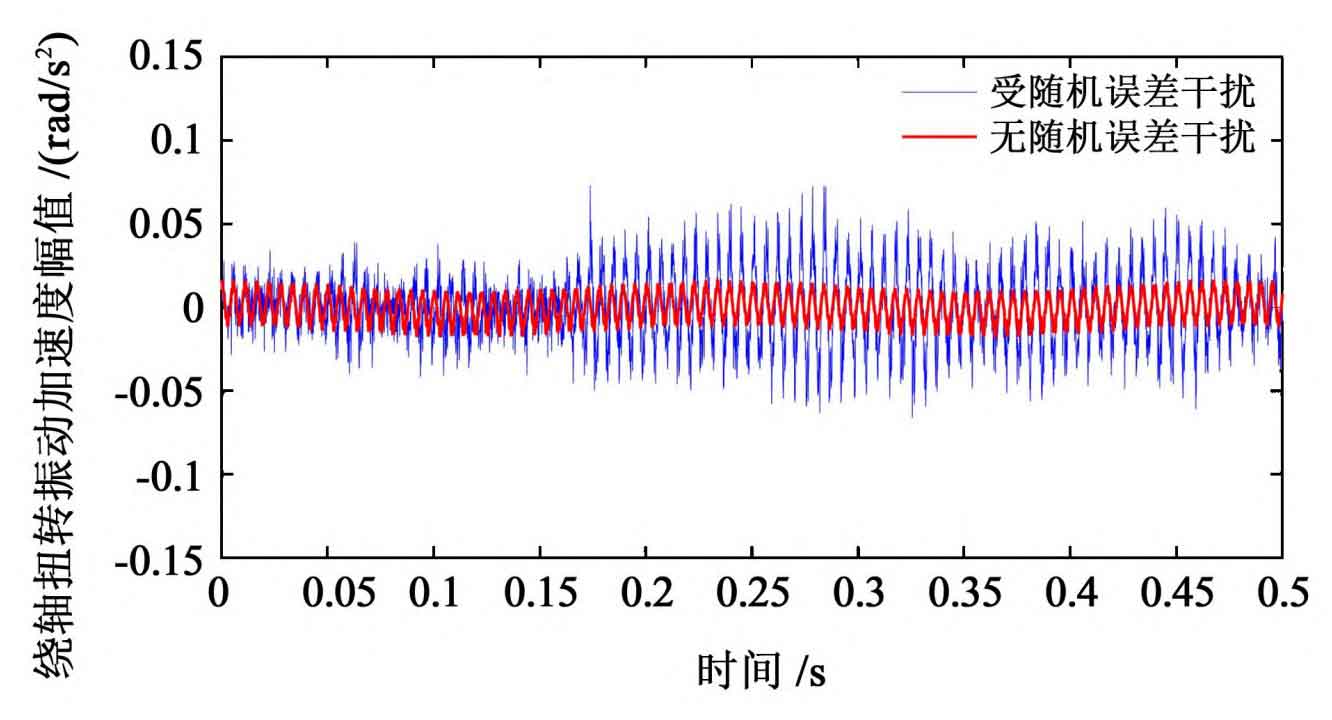
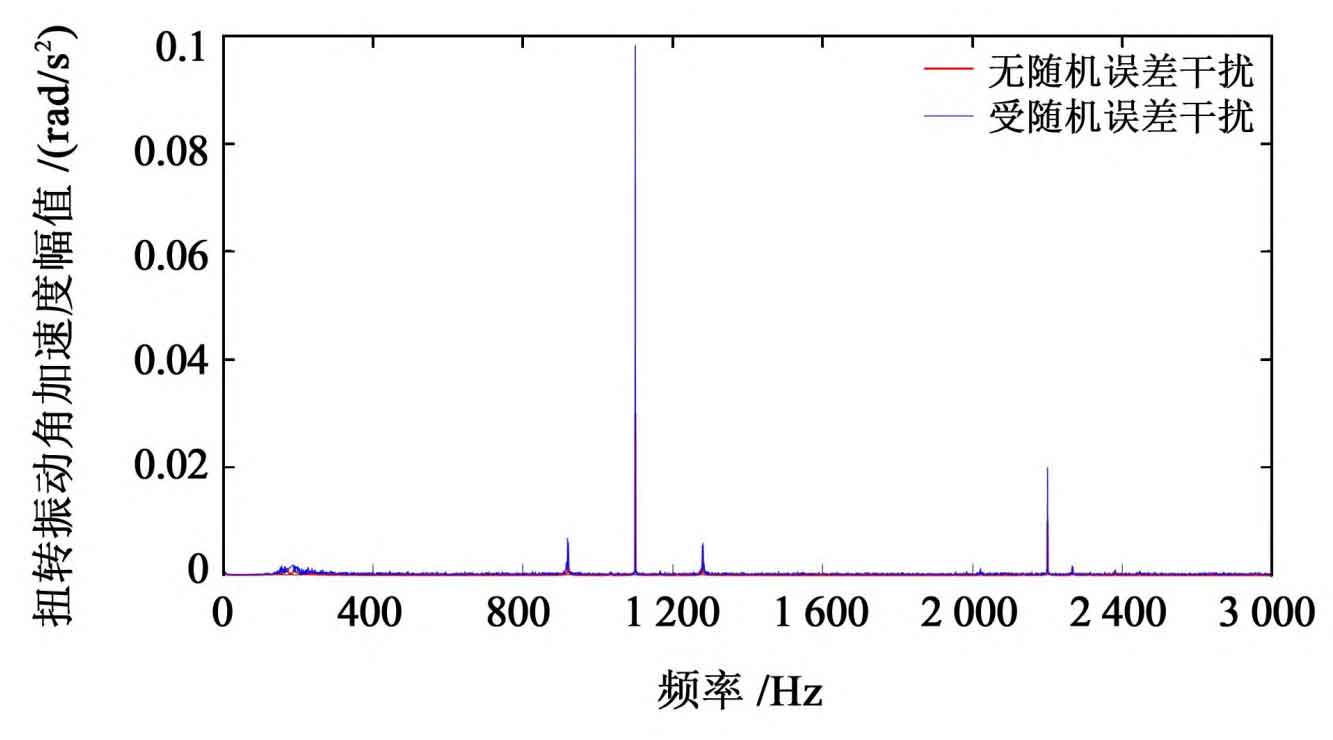
Since the change trend of vibration response of driving wheel and driven wheel is consistent, the driving wheel is taken as the research object. By comparing and analyzing the time domain and frequency domain characteristics of vibration response, the influence of random error on the vibration characteristics of spur gear transmission is obtained, as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
| Parameter | Disturbed by random error | No random error interference | |
| Response numerical characteristics | Mean square deviation | Mean square deviation | Growth rate |
| X direction (/ mm / S2) | 5.512 7 | 3.340 6 | 65.02% |
| Y direction (/ mm / S2) | 15.134 2 | 9.159 7 | 65.23% |
| Torsion (/ rad / S2) | 0.125 4 | 0.075 9 | 65.21% |
It can be seen from Figure 1 that the variation trend of vibration acceleration curve under ignoring random error is relatively gentle; Under the interference of random error, the acceleration of spur gear system fluctuates violently. It can be seen from table 1 that under the interference of random error, the randomness of the dynamic response of spur gear is further enhanced, indicating that the random error has a strong interference on the dynamic characteristics of spur gear.
| Parameter | Parameter | |
| 1 100HZ | 2 200HZ | |
| X direction | 227% | 113% |
| Y direction | 227% | 113% |
| Torsion direction | 227% | 112% |
As can be seen from Fig. 2, the acceleration response curve of spur gear driving wheel without random error is relatively smooth, with peaks at 1100 Hz and 2200 Hz. Due to the interaction between meshing frequency and random error frequency, symmetrical frequency divergence occurs at 860 Hz and 1340 Hz on both sides of meshing frequency. Under random error, the acceleration response amplitude of spur gear driving wheel increases, with strong randomness, continuous frequency spectrum and complex fluctuation. The vibration peak is greater than the vibration peak without random error. See Table 2 for specific statistical parameters.
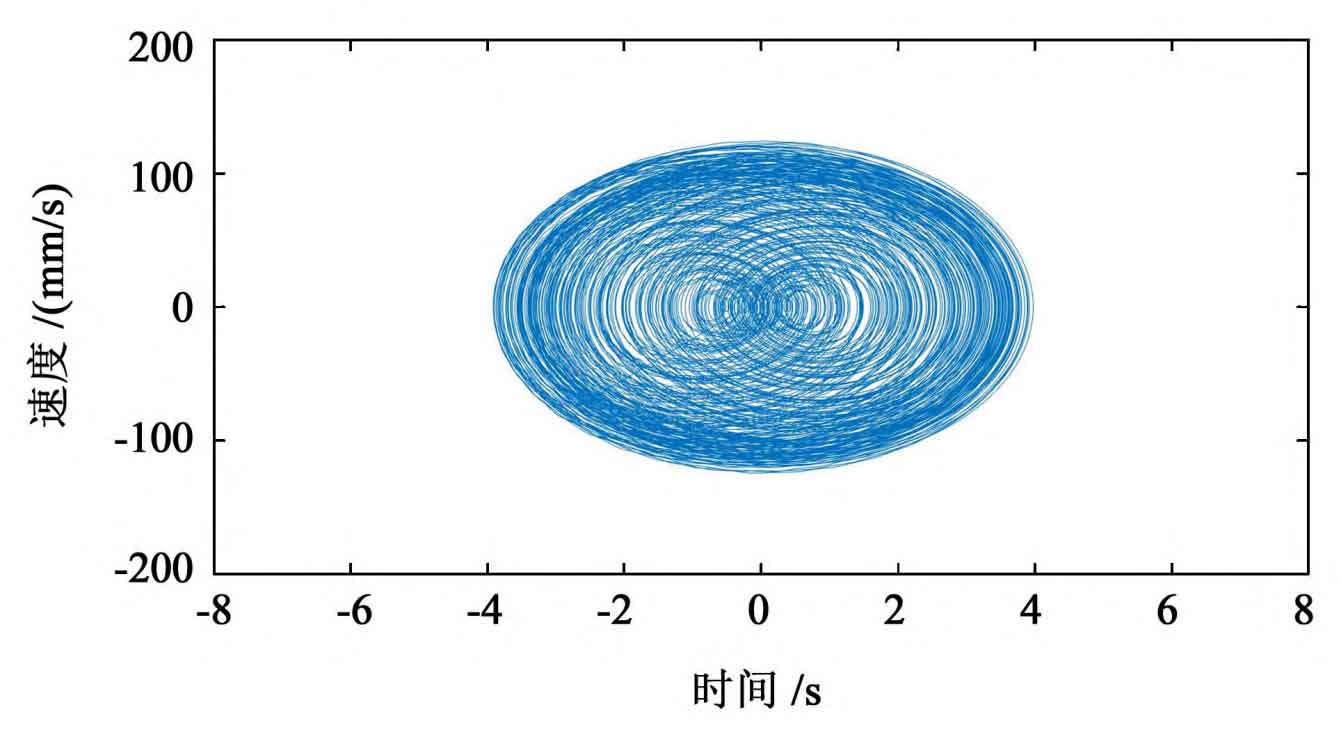
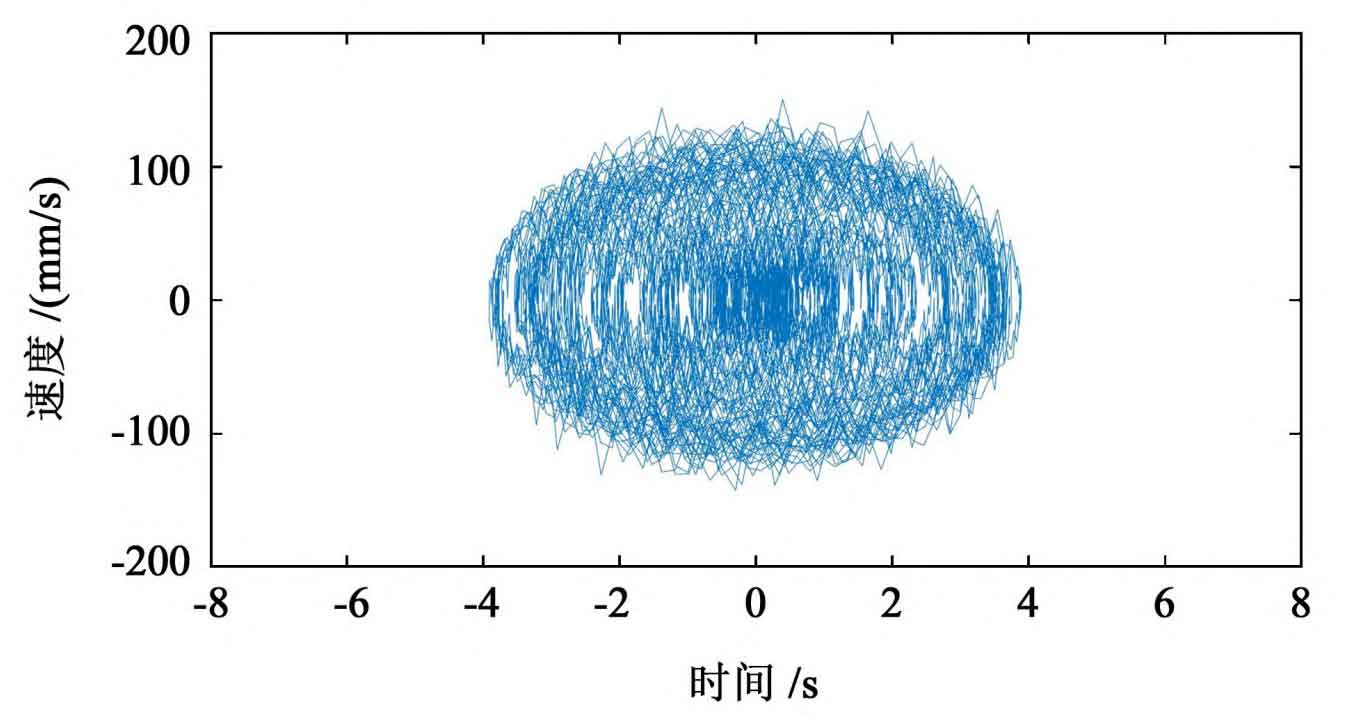
The phase diagram is the geometric expression of the state trajectory of the dynamic system on the phase plane. The phase diagram of the spur gear transmission process is shown in Figure 3. The motion form of spur gear pair without random error interference is a smooth closed curve, which shows that spur gear is doing simple periodic motion. Due to the intervention of random error, the phase diagram becomes more chaotic, and the phase orbit trace also has obvious randomness.