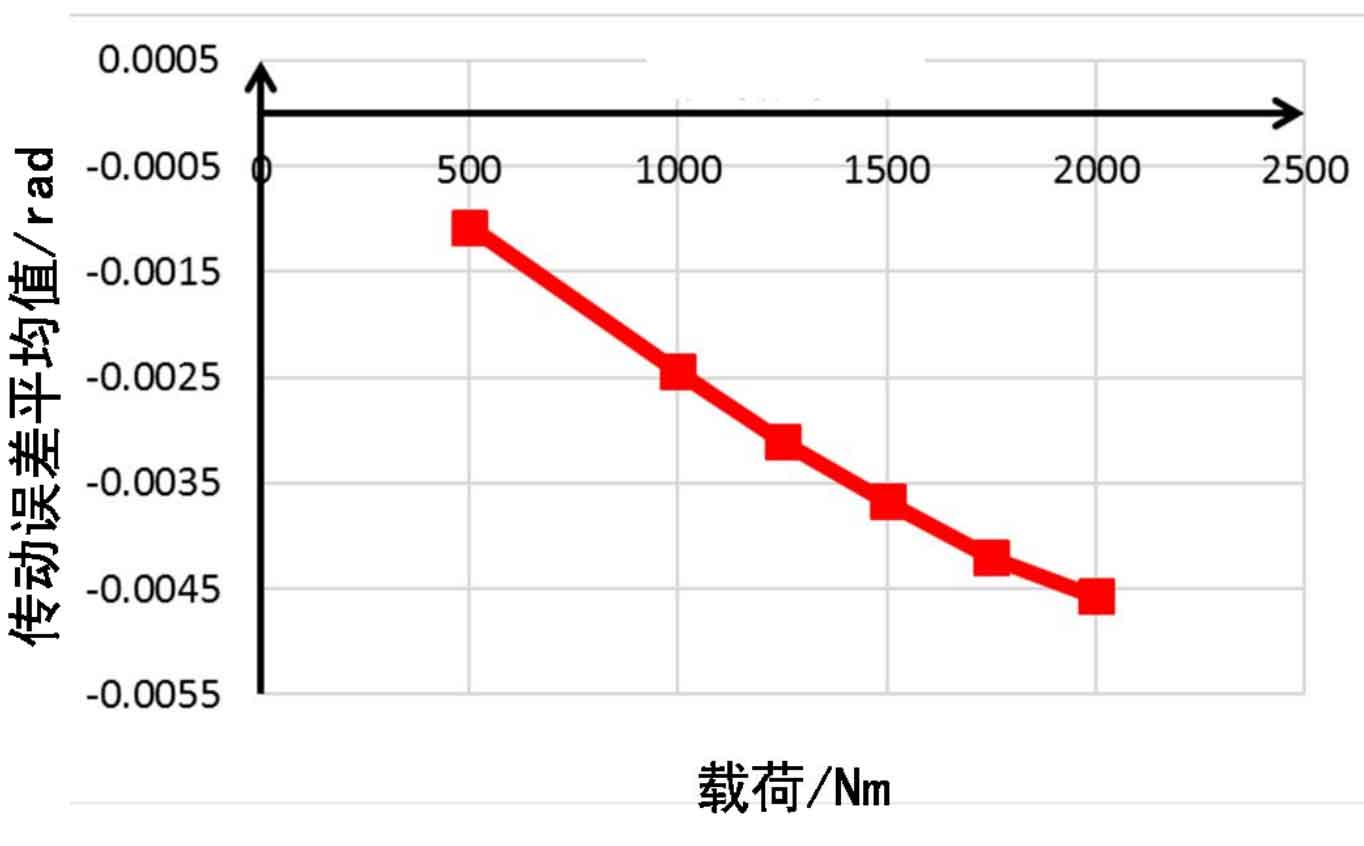
Load different resistance moments on the output end of the large gear, and the corresponding transmission error is shown in Figure 1 below. It can be seen from the figure that as the load increases, the corresponding transmission error will also increase. The transmission error is mainly divided into two parts. One part is the constant part, which does not change with the change of the gear meshing position. The corresponding value is shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen that the constant part of the transmission error increases nonlinearly with the increase of the load. This is because the constant part of the transmission error is mainly caused by the deformation of the gear base, and the load borne by the gear base is mainly related to the load loaded by the gear, and has little relationship with the gear meshing.
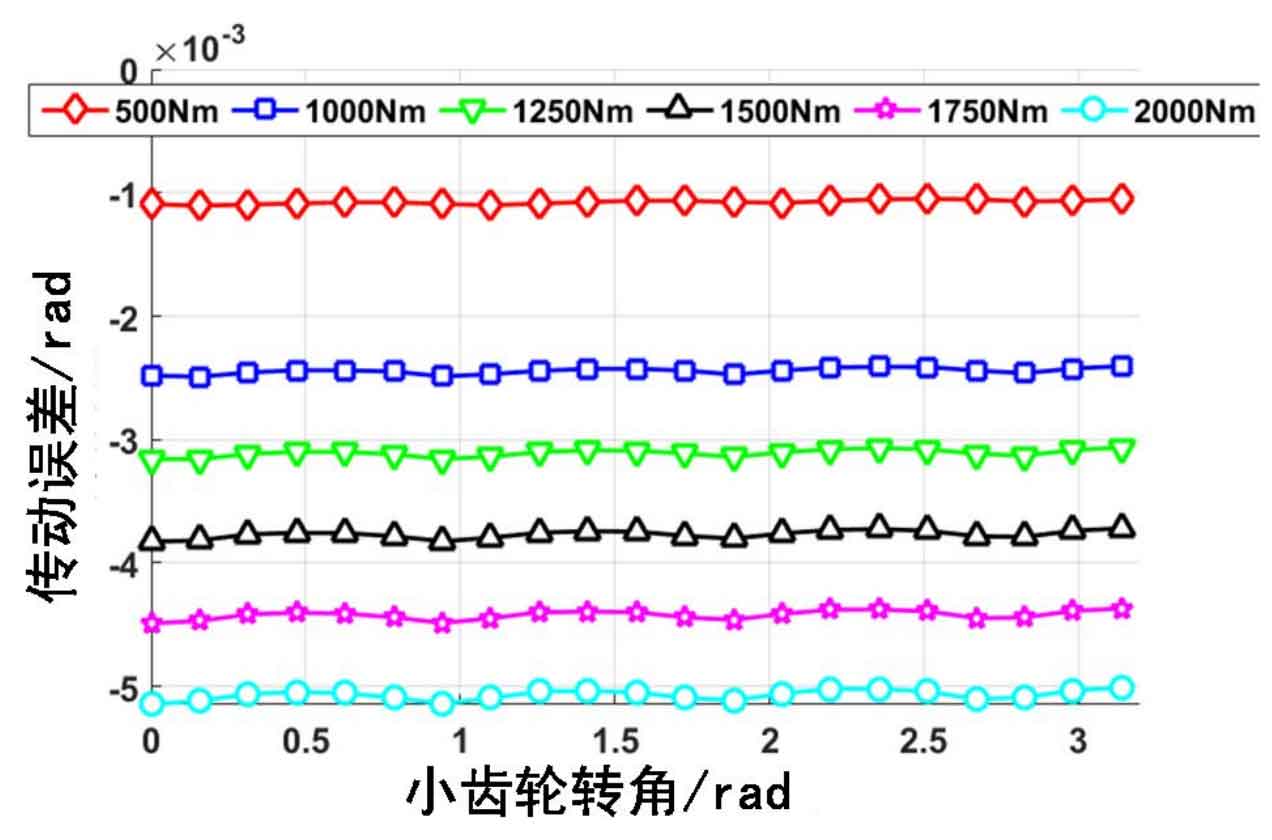
Another part of the gear transmission error is the fluctuation part, which changes with the change of the gear engagement position. As shown in Fig. 3, it can be seen that with the increase of the load, the transmission error fluctuation part is closer to the parabolic shape, and the transmission error change period is basically unchanged. This is mainly because the period of the transmission error fluctuation part is related to the gear engagement frequency and is a function corresponding to the gear engagement position.
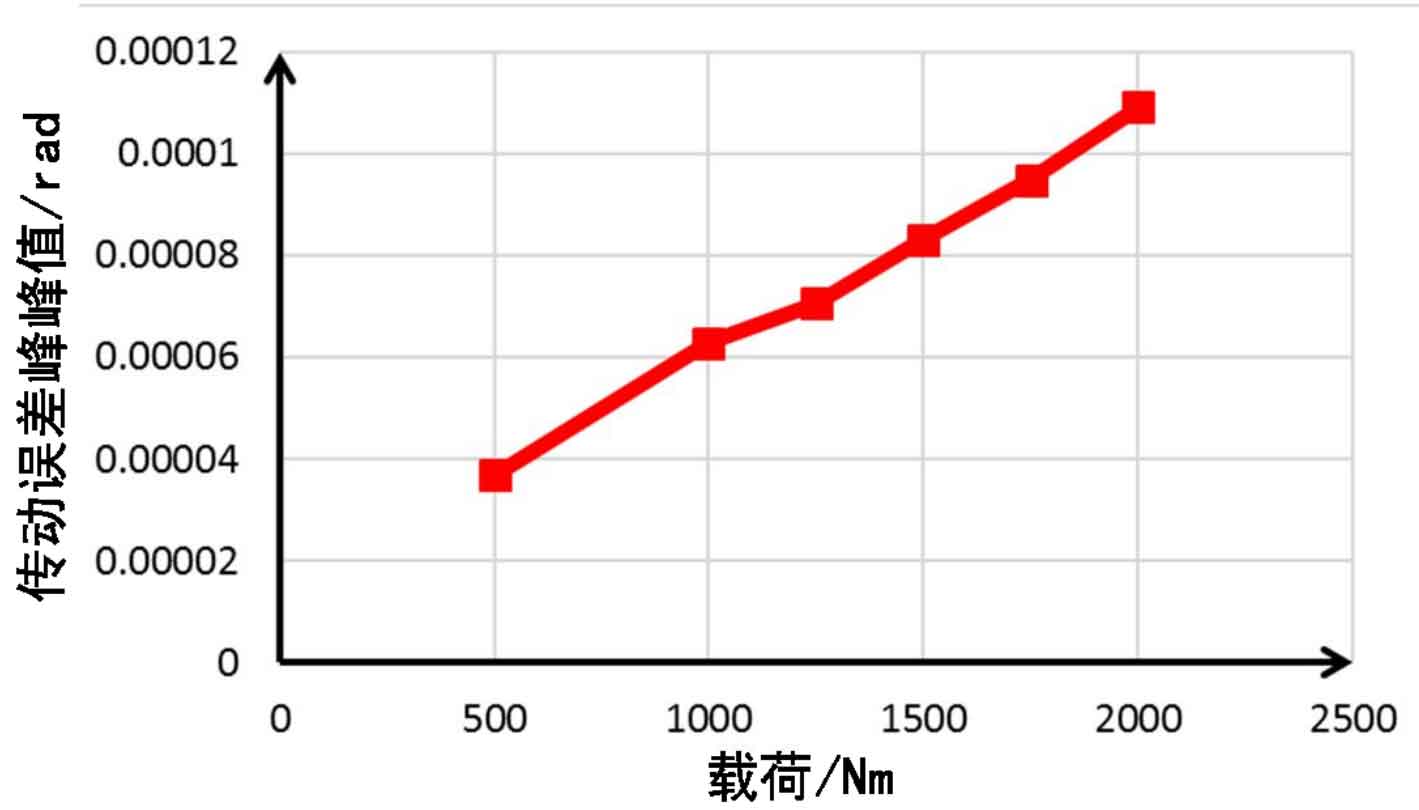
As shown in Fig. 4, the variation trend of transmission error peak and peak with load is not linear. The fluctuation of transmission error is mainly determined by the unevenness of gear meshing. During the meshing process of hypoid gears, the meshing coincidence degree changes continuously with the rotation of gears. When the load is small, there are fewer teeth participating in meshing at the same time, and the meshing force of a single tooth changes little during the process from meshing in to meshing out. At this time, the change of gear coincidence degree is also small, and the corresponding peak value of transmission error change is also small. When the load is increased, At the same time, the number of meshing teeth will increase, and the meshing force of a single tooth will change greatly during the process from meshing in to meshing out. At this time, the gear coincidence degree will also change greatly, and the corresponding transmission error fluctuation peak value will also be large.
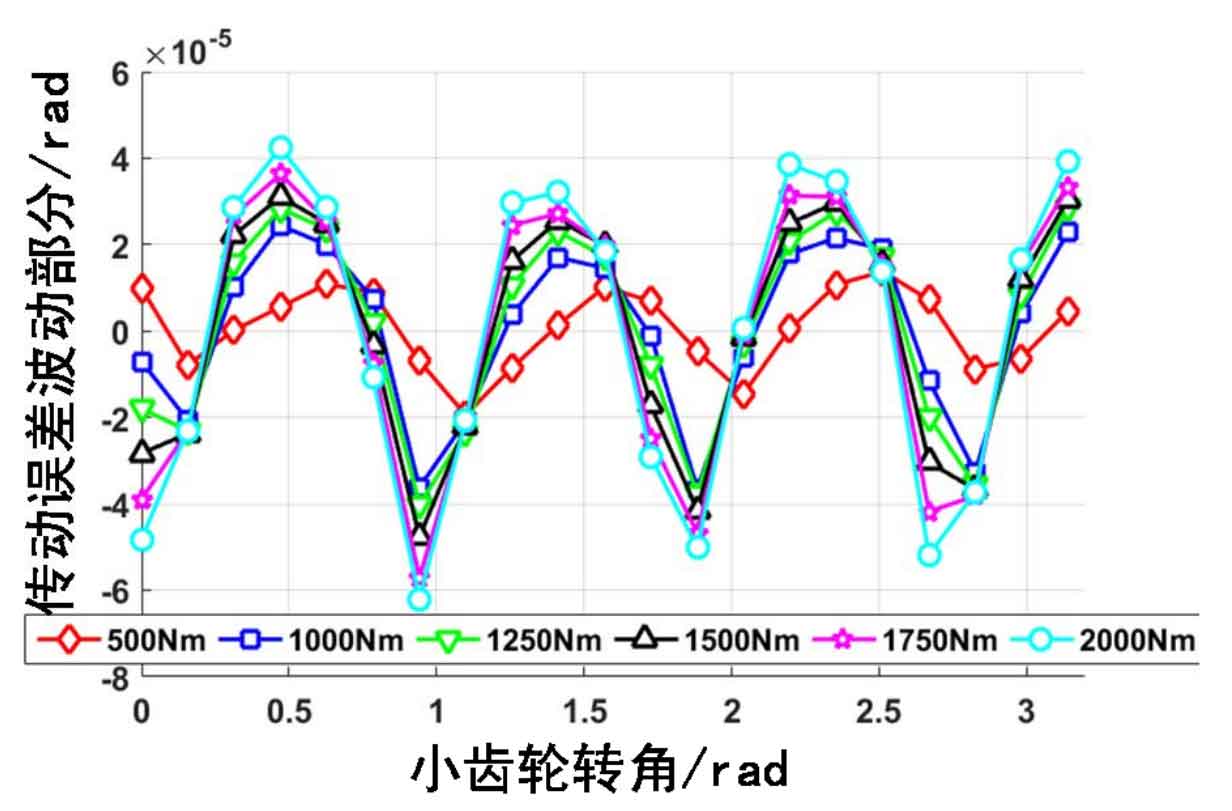
At the same time, it can also be seen that the hypoid gear is different from the ordinary involute gear, and its transmission error is continuous, so it can transmit torque more smoothly. When the load is increased, the static transmission error of the gear will move to the negative direction, which can increase the meshing coincidence of the gear and is conducive to the smooth transmission of the load.