1.Main names and definitions of gear teeth
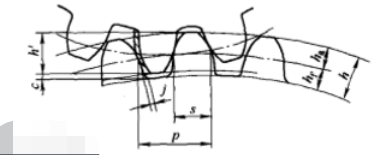
The code of the main names of each part of the gear tooth is shown in the figure.
(1) Tooth height H: the distance measured along the back cone generatrix between the tooth top circle and the tooth root circle.
(2) Tooth crest height h a: the distance measured along the back cone bus from the tooth crest circle to the indexing circle.
(3) Tooth root height H F: the distance measured along the back cone generatrix between the indexing circle and the tooth root circle.
(4) Working tooth height H ‘: when a pair of bevel gears mesh with each other, there is an intersection between their tooth top circle and the back cone bus, and the shortest distance measured along the above common bus between the two intersections.
(5) Top clearance C: the distance between the tooth top circle and its matching gear tooth root circle measured along the common bus of the two back cones.
(6) Pitch P: the arc length on the indexing circle of the tooth profile on the same side of two adjacent teeth.
(7) Tooth thickness s: the length of indexing arc between two sides of a tooth.
(8) Tooth groove width: on bevel gears, the length of the indexing arc between the tooth surfaces on both sides of a tooth groove.
(9) Side clearance J: the side clearance is the amount that the width of the tooth slot on the working pitch circle is greater than the tooth thickness of the meshing teeth.
2.Tooth line
Tooth length curve refers to the intersection of tooth surface and pitch cone. Generally, the tooth length curve of hypothetical plane gear is used as the basis for the characteristics and classification of bevel gear.
There are several kinds of common straight line and oblique curve.
In addition, there are quasi involutes machined with conical hobs, but they are rarely used.
Among the curved tooth lines, arc and long epicycloid are most widely used, and arc is mostly used. The arc tooth is easy to grind and can achieve high precision. It can be used for high-speed transmission. The long epicycloid tooth is an equal height tooth, which adopts continuous cutting without intermittent tooth splitting.