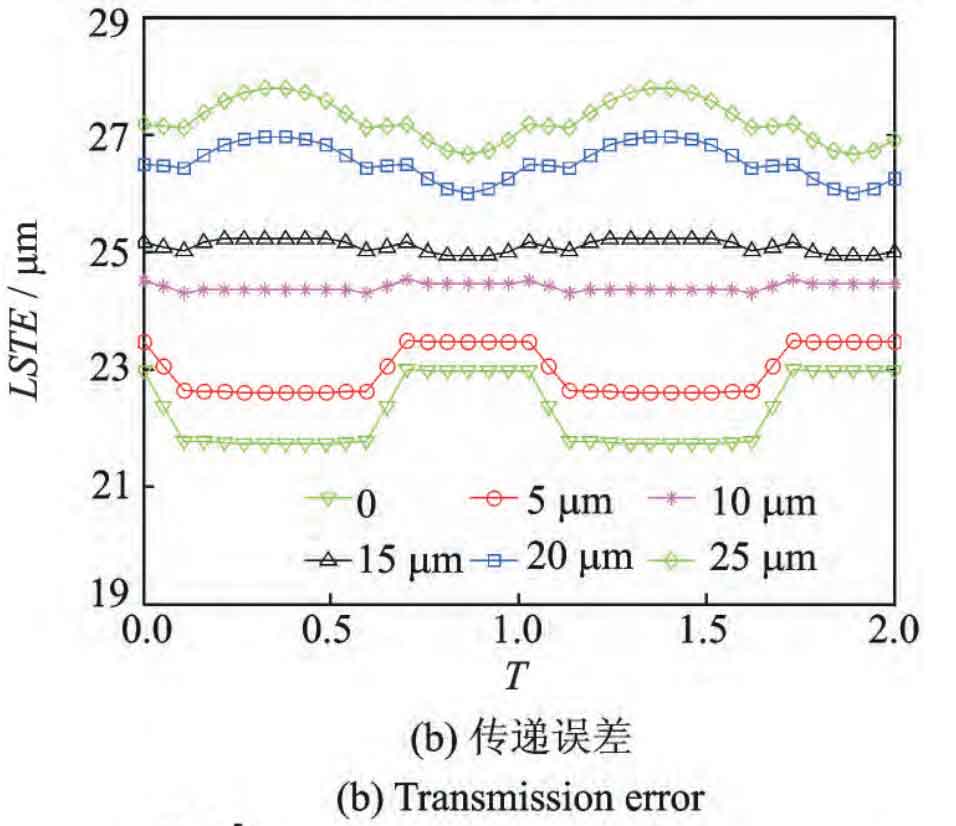
Figure 1 shows that the tooth profile modification length Lc = 10mm and the tooth profile modification amount CC are 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 respectively μ M, the comprehensive meshing stiffness, transmission error and stiffness mean square deviation of helical gear. Compared with figures 2 and 1, the same as tooth profile modification is that with the increase of tooth profile modification, the meshing stiffness value of helical gear gradually decreases and the transmission error increases; The fluctuation of meshing stiffness first decreases to a fixed value, and then increases with the increase of modification. The difference is that although the appropriate tooth profile modification also reduces the fluctuation of meshing stiffness, it has no obvious effect on the meshing stiffness in the alternating area of tooth number than the tooth profile modification.
Figure 3 shows the tooth direction modification CC = 15 μ m. When the tooth modification length LC is 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25mm respectively, the comprehensive meshing stiffness, transmission error and stiffness mean square deviation of helical gear. Comparing figures 1 and 3, it can be seen that, except for slightly different amplitude, the influence of tooth profile modification length on meshing stiffness and error is consistent with the influence of tooth profile modification amount on meshing stiffness and error. Combined with figures 1 (c) and 3 (c), it can be seen that when the modification amount is 15 μ m. When the modified length is 10mm, the mean square deviation of stiffness is the smallest, that is, the fluctuation of meshing stiffness is the smallest. Compared with the unmodified length, the mean square deviation of stiffness decreases by 94.587%.