(1) Linear addendum optimization of long tooth profile
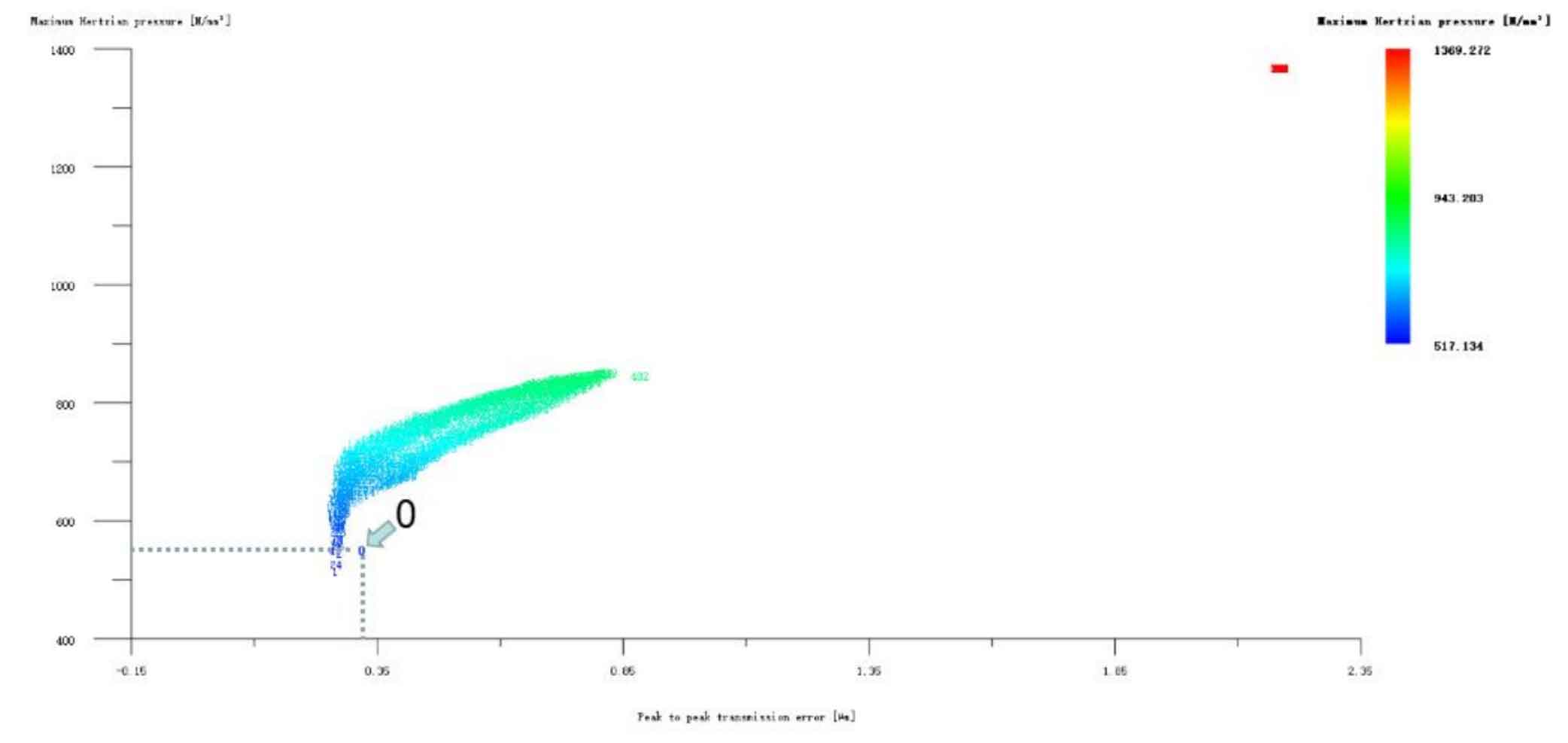
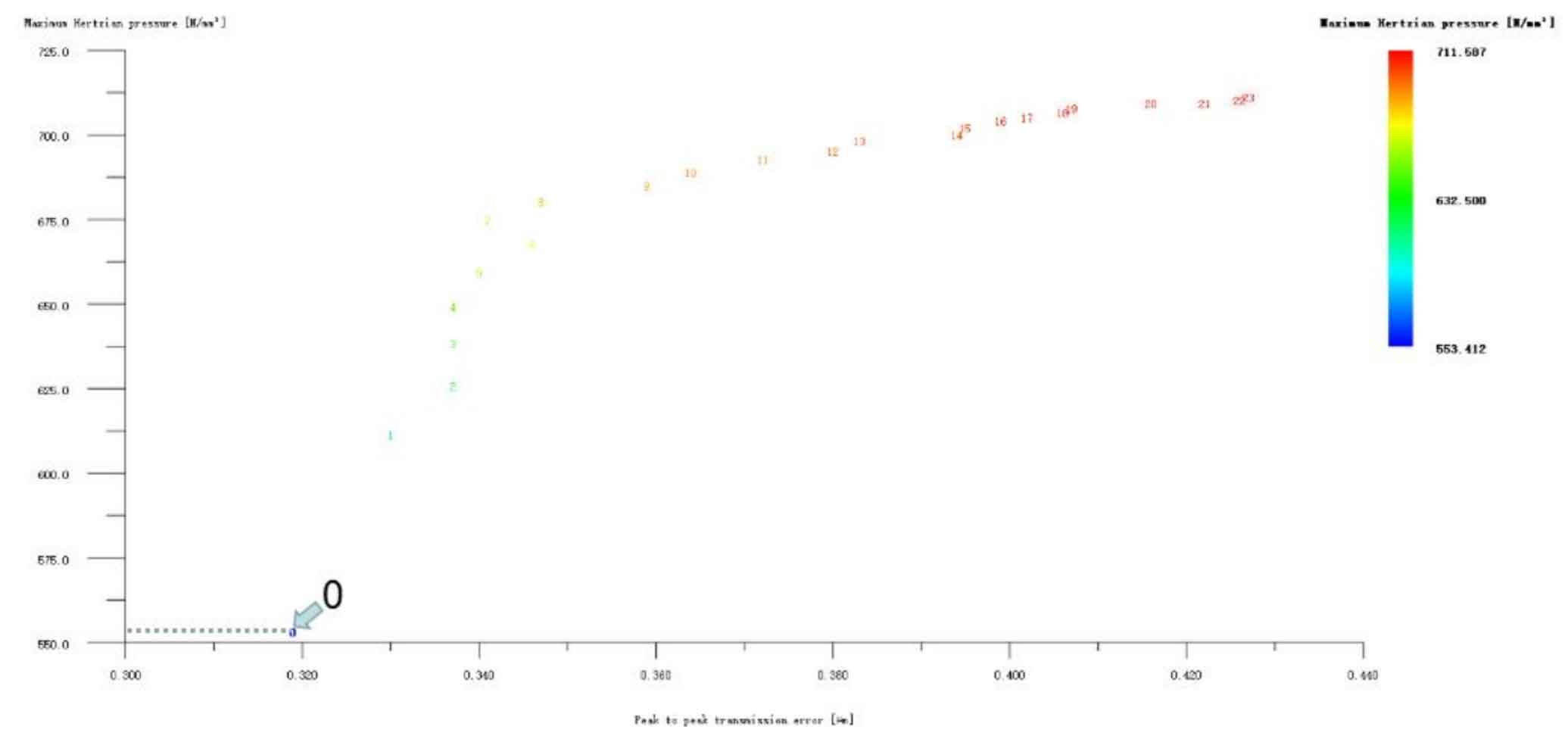
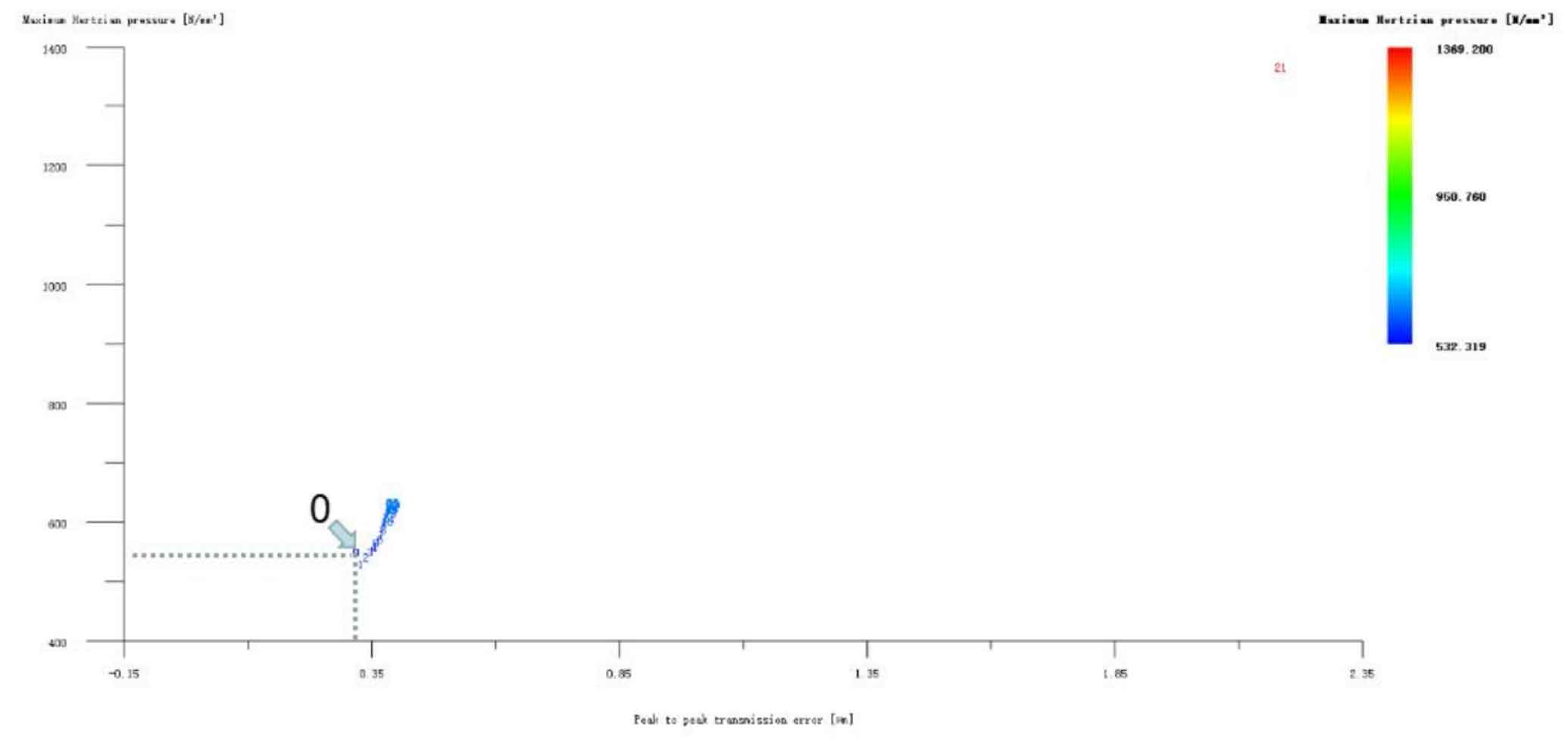
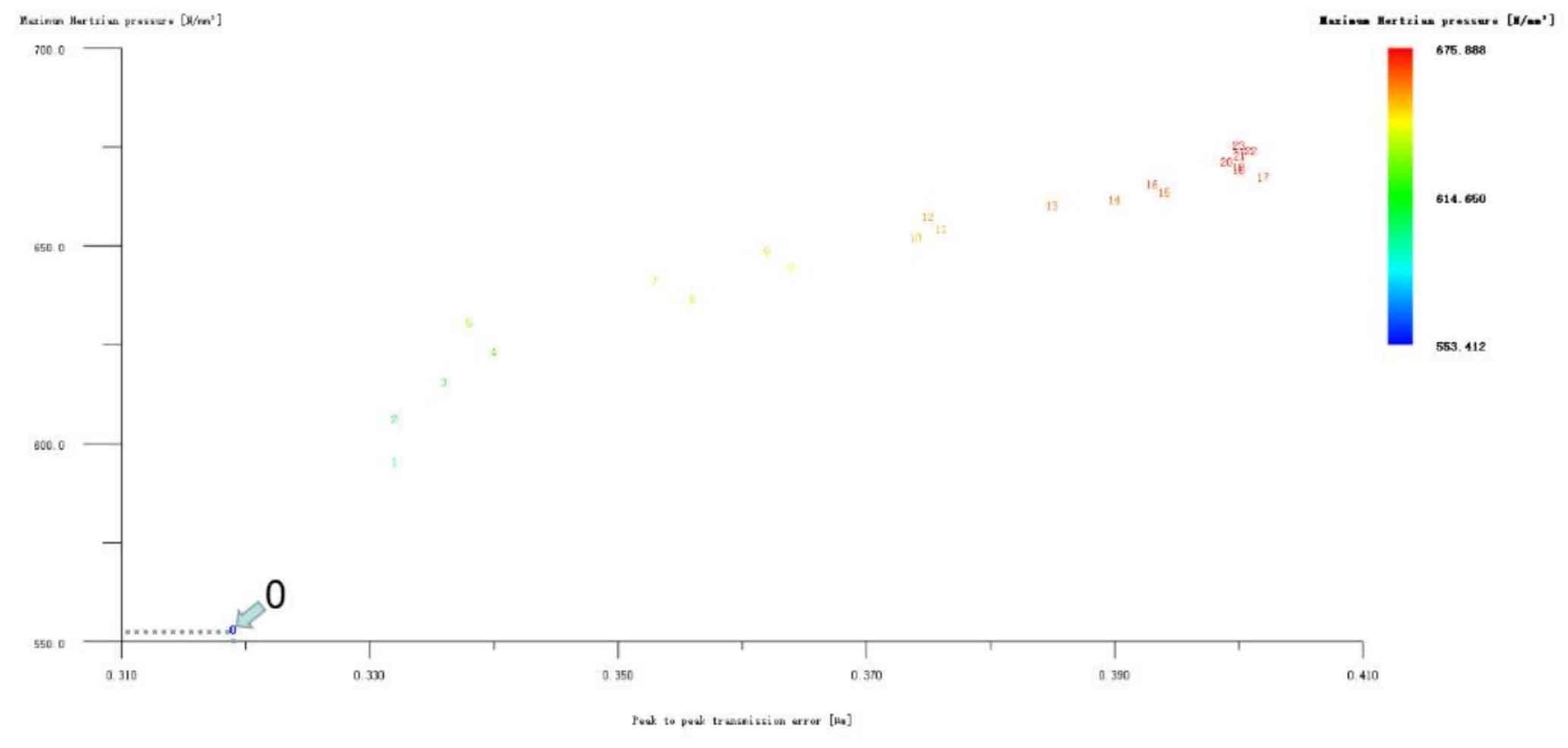
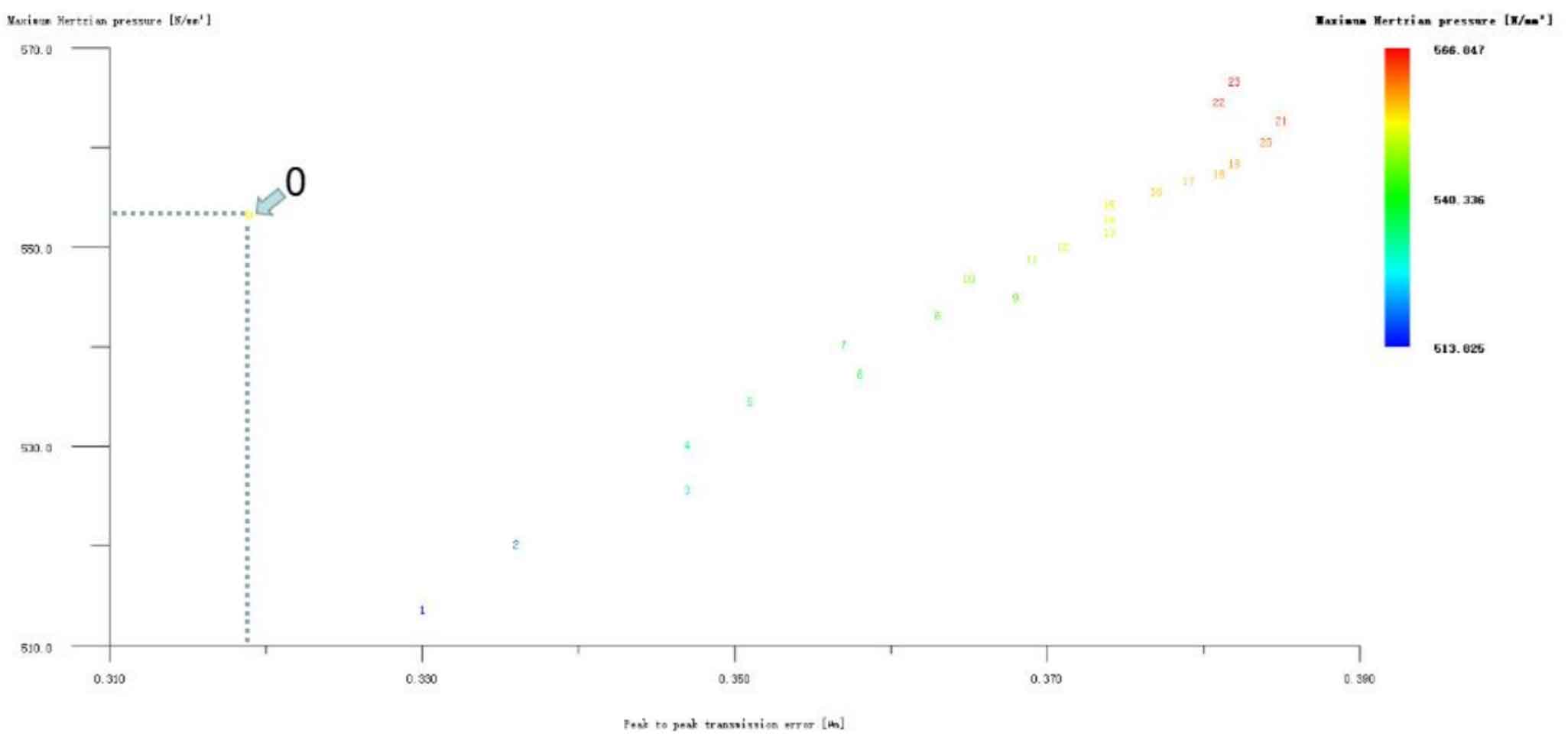
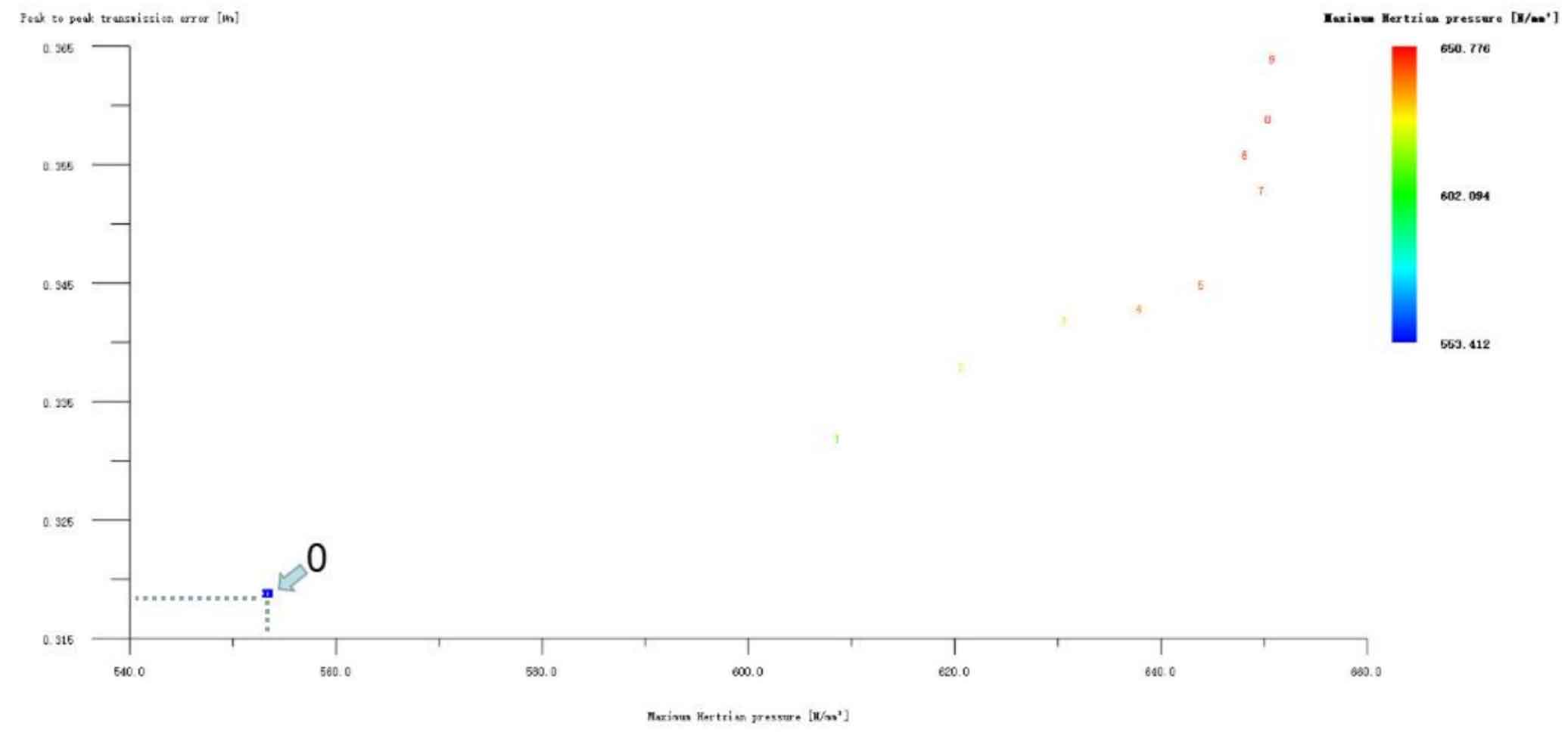
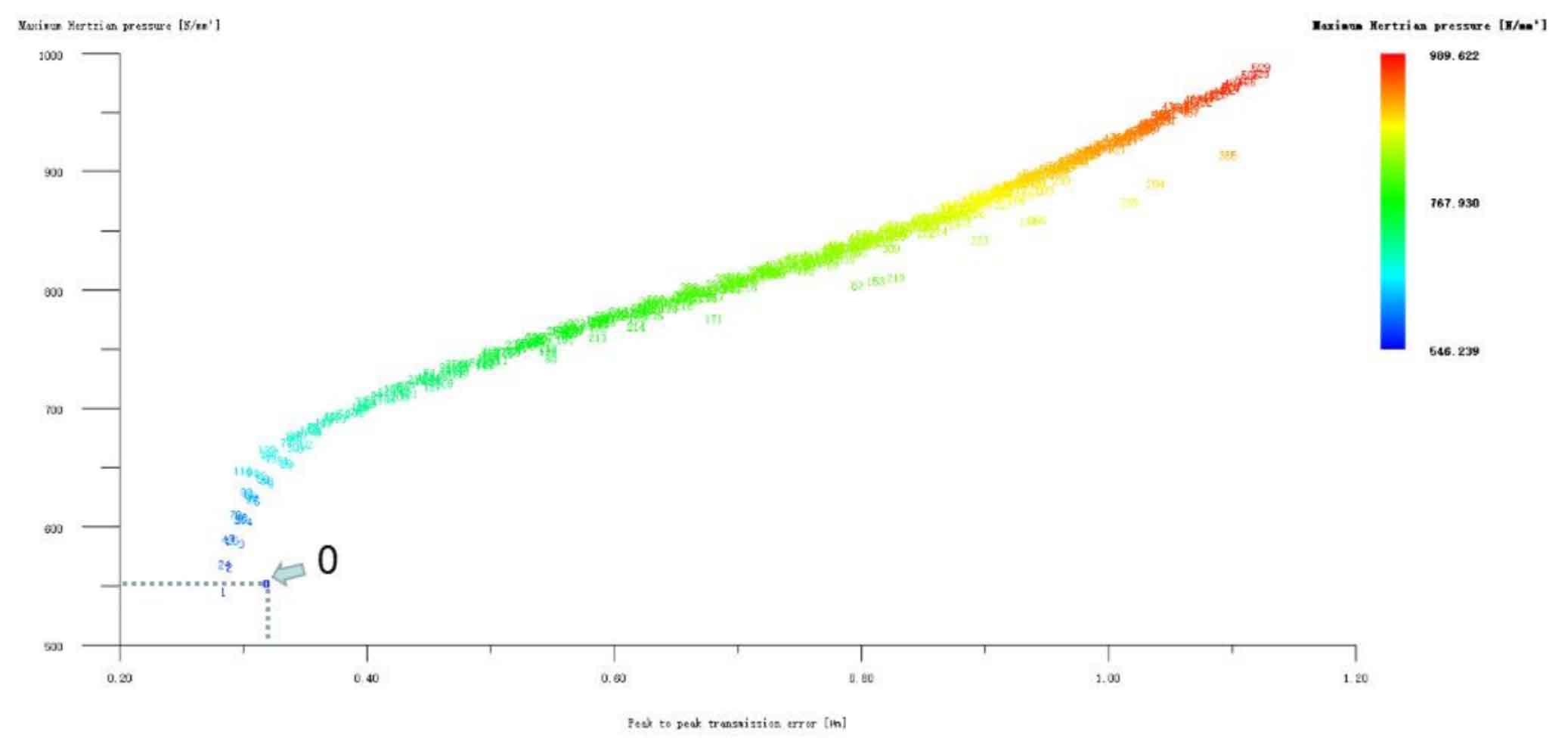
Figures 1, 2 and 3 show the linear tooth top modification of large and small gears with long tooth profile at the same time, the linear tooth top modification of helical gear 1 (pinion) with long tooth profile only, and the linear tooth top modification of helical gear 2 (big gear) with long tooth profile only. In all drawings, the ordinate represents Hertz contact stress, in N/mm2; The abscissa represents the transmission error, and the unit is μ m。 Scheme 0 on the drawing represents unreformed, with Hertz contact stress of 553.412N/mm2 and transmission error of 0.319 μ m。 It can be seen from Figure 1 that the linear tooth top modification scheme of the 1 #, 24 # and 2 # isometric tooth profile is good when the large and small gears are modified at the same time. Compared with the unmodified scheme, the transmission error and Hertz contact stress are decreased, and the 1 # scheme is the best. However, it can be seen from Fig. 2 and Fig. 3 that if only a single gear in the helical gear pair is subject to linear tooth top modification with long tooth profile, the modification effect of all schemes is poor. Therefore, the preliminary optimized modification scheme of the linear addendum of the long tooth profile is No. 1 in the simultaneous modification of the large and small gears, and its modification amount is big gear 3 μ M. Pinion 3 μ m. Hertz contact stress and transmission error are reduced to 517.134N/mm2 and 0.263 respectively μ m。
(2) Optimization and modification of arc tooth crest with long tooth profile
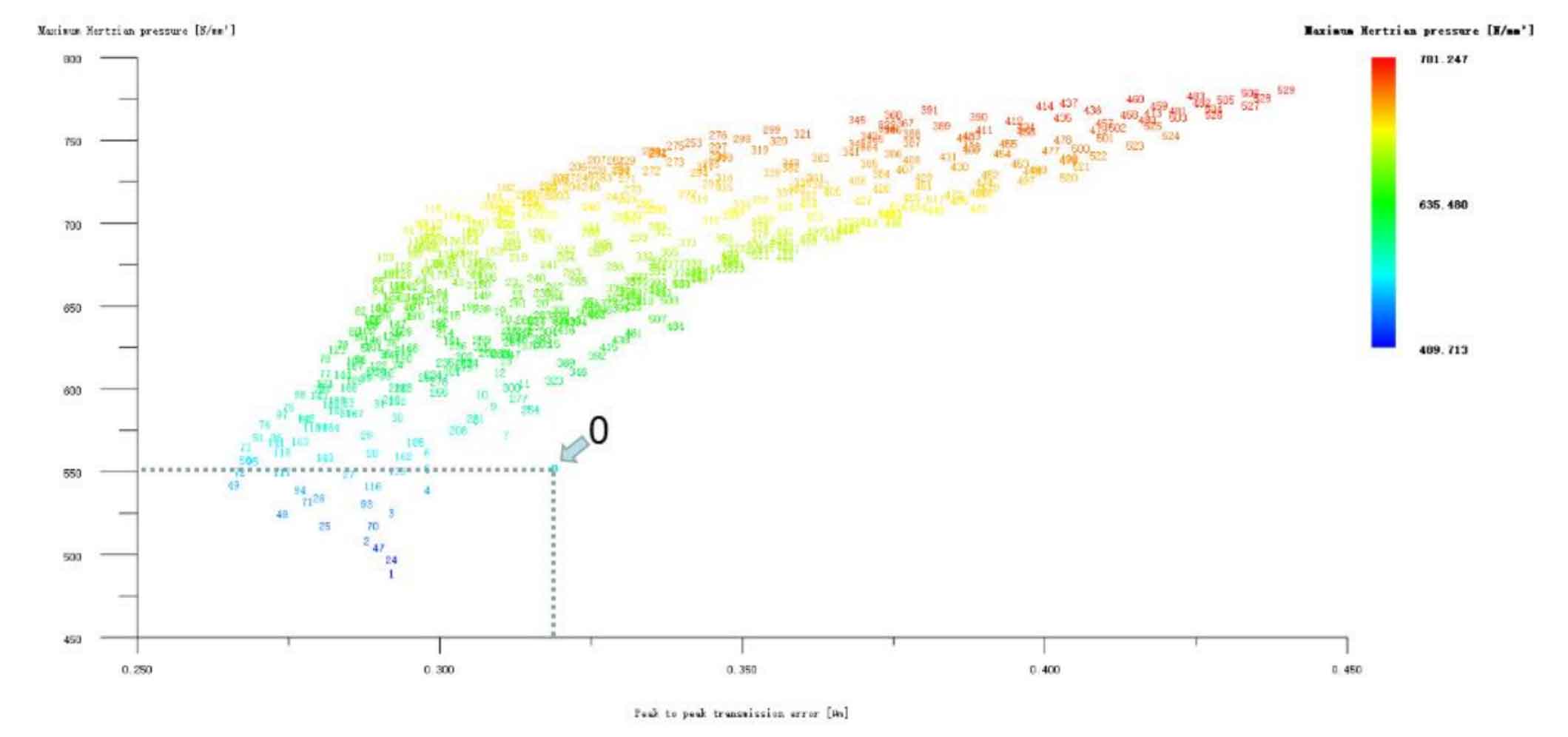
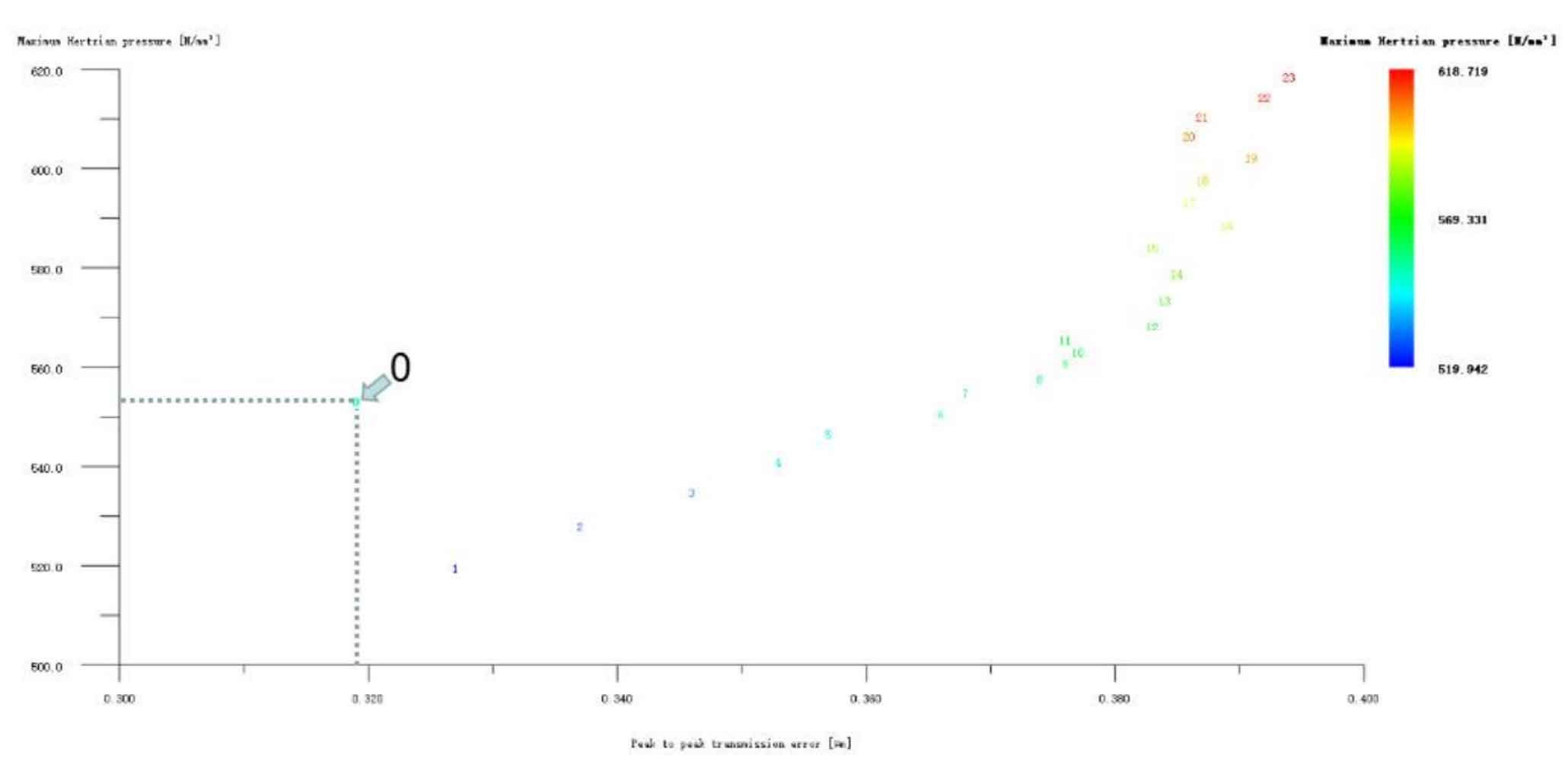
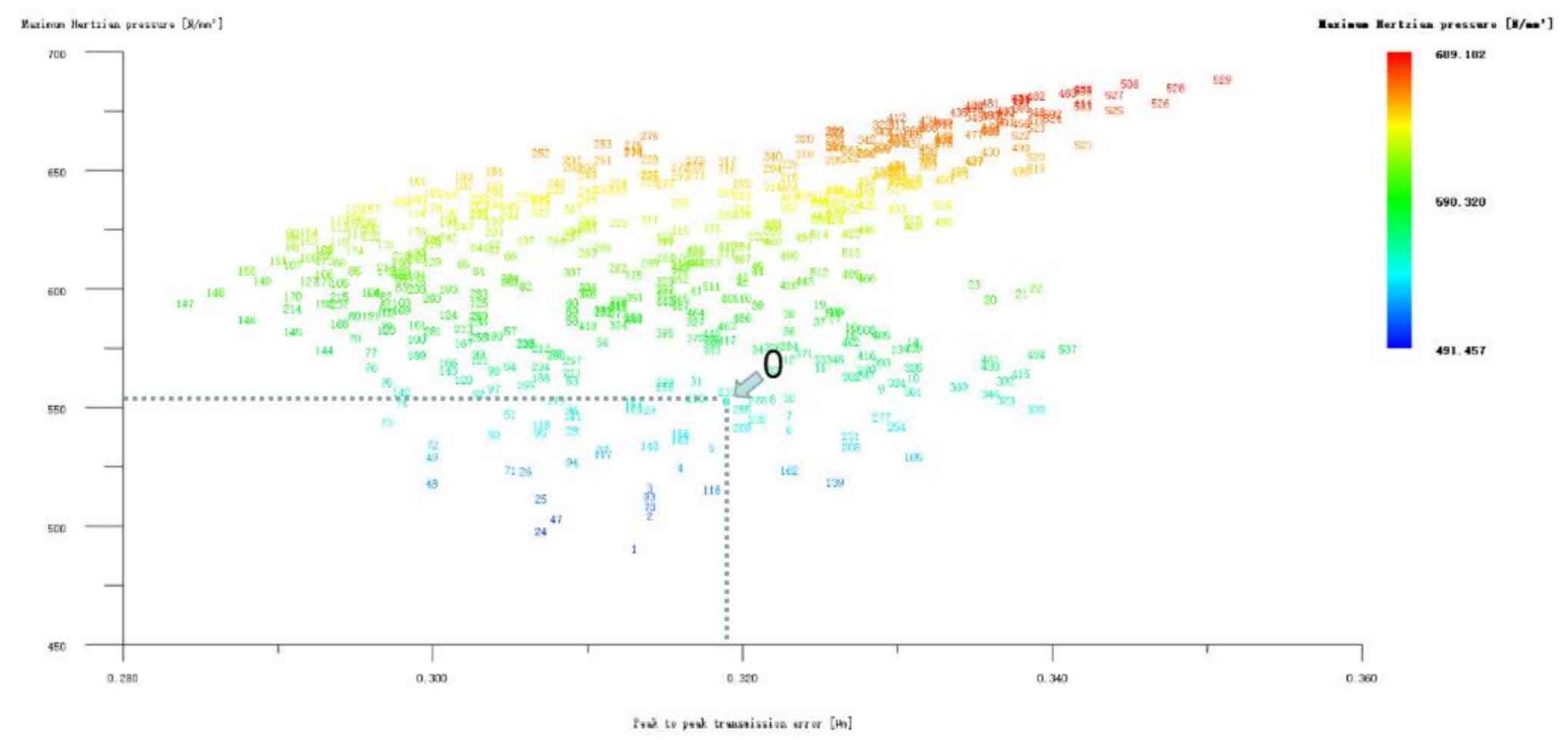
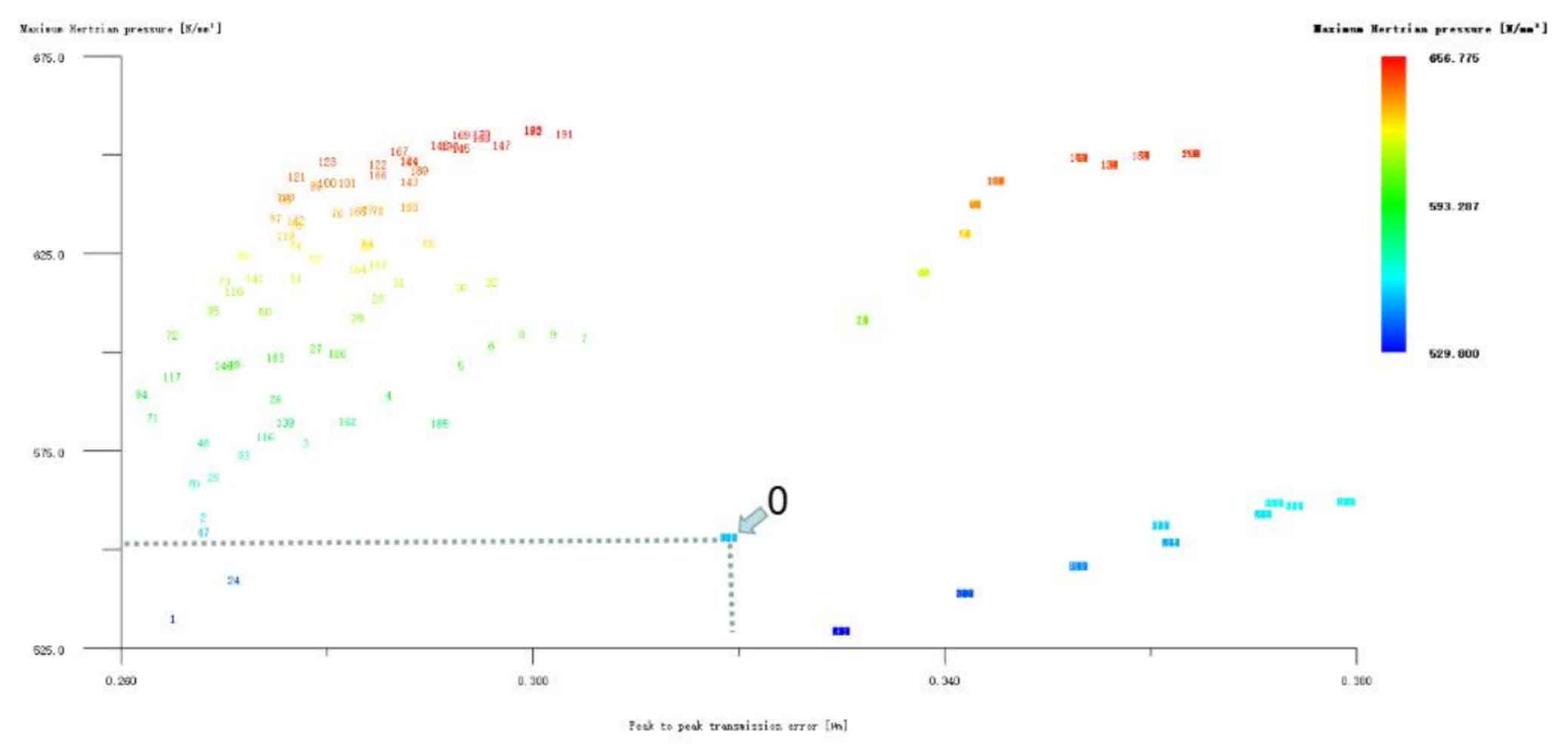
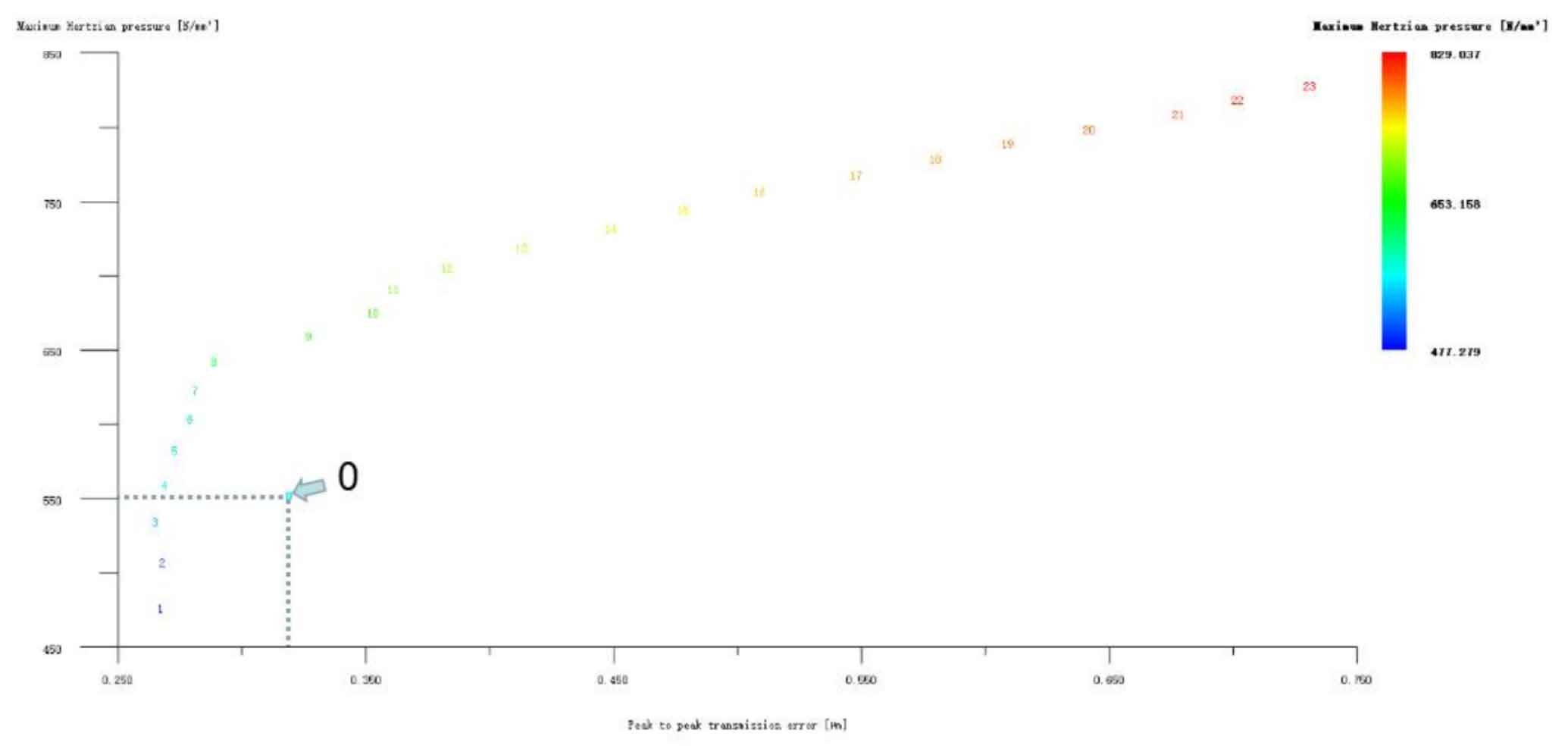
The big and small gears are modified simultaneously by the long profile arc tooth top h’h’h, only for the small gear long profile arc tooth top, and only for the big gear long profile arc tooth top, as shown in Figure 4, 5, and 6. It can be seen from Figure 4 that the profile modification schemes of large and small gears such as No. 1, No. 2 and No. 48 with long tooth profile at the same time have good effects. Compared with No. 0, the transmission error and Hertz contact stress of these modification schemes have been significantly reduced. The Hertz contact stress of the No. 1 modification scheme is the lowest, 489.713N/mm2; Scheme 49 has the lowest transmission error of 0.266 μ m; Scheme 48 has the best comprehensive performance, with its Hertz contact stress of 525.853N/mm2 and transmission error of 0.274 μ m。 Since this project is not only to achieve vibration reduction and noise reduction of helical gear pair, but also to improve the strength of gear teeth as much as possible, it is necessary to take both values into consideration. After comprehensive consideration, the No. 48 scheme is selected, and its modification amount is large gear 5 μ m. Pinion 4 μ m。 Looking at Figure 5 and Figure 6, although the modification effect of each scheme in the two figures is not ideal, according to the previous analysis, the tooth profile modification is mainly to reduce Hertz contact stress and improve the strength and bearing capacity of helical gears; Tooth alignment modification is mainly to reduce transmission error and affect the vibration and noise of helical gears. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the possibility of reducing the Hertz contact stress by tooth profile modification, and then reducing the transmission error by tooth drum modification. However, No. 1, No. 2 and No. 3 in Figure 6 only reduce the Hertz contact stress of the large gear long profile arc tooth top modification scheme. After weighing, the No. 1 scheme is also taken as the preliminary optimization modification scheme, and its modification amount is large gear 3 μ m. Pinion 0 μ m. Hertz contact stress and transmission error are 519.942N/mm2 and 0.327 respectively μ m。
(3) Optimal modification of involute tooth crest with long tooth profile
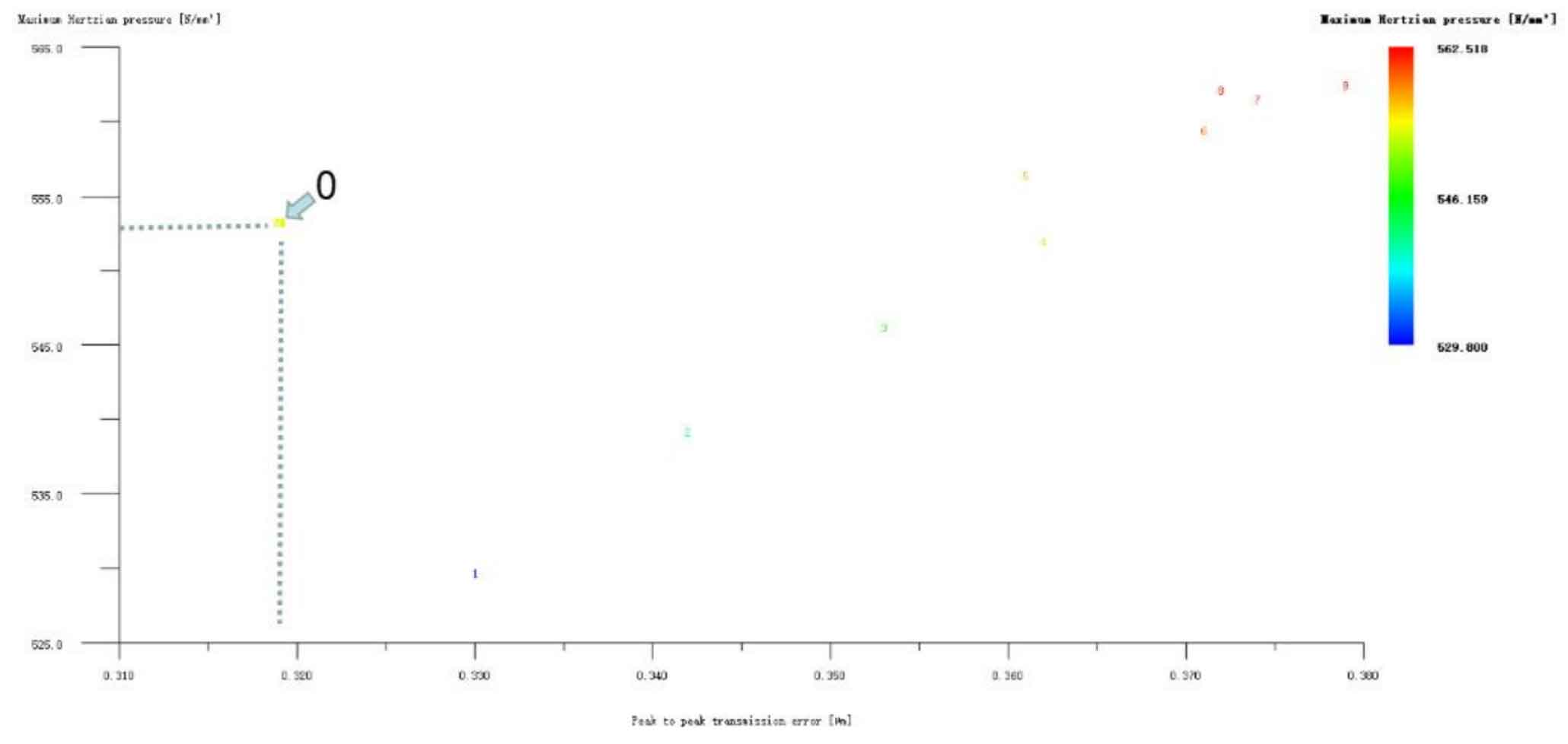
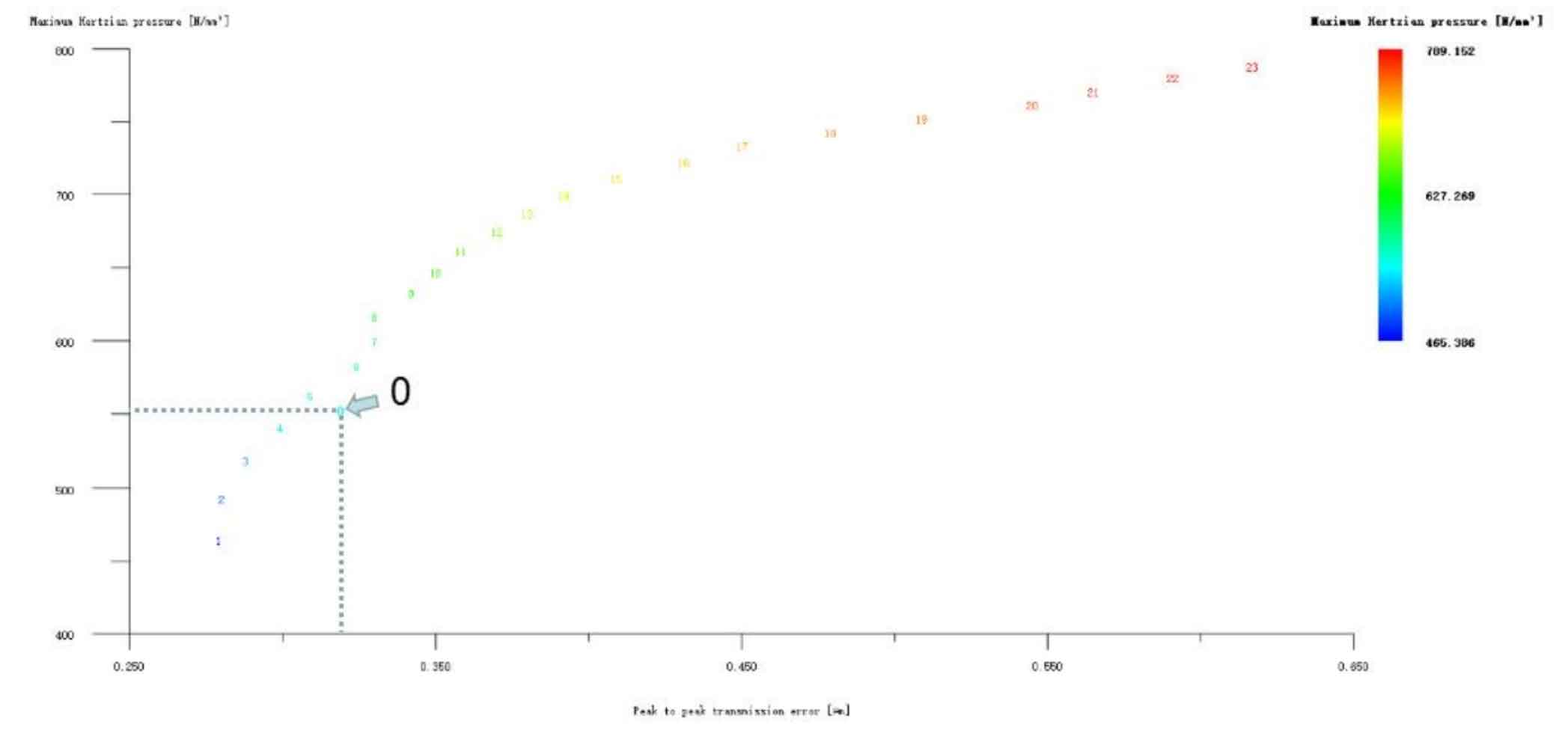
Figures 7, 8 and 9 show the modification of the involute tooth top of the large and small gears with long tooth profile at the same time, the modification of the involute tooth top of the small gear with long tooth profile only, and the modification of the involute tooth top of the large gear with long tooth profile only. It can be seen from Figure 7 that there are many optimization schemes for large and small gears with long tooth profile and involute tooth top modification at the same time. After comprehensively weighing the values of transmission error and Hertz contact stress, the No. 48 scheme is selected, and its Hertz contact stress and transmission error are 518.615N/mm2 and 0.300 respectively μ m. The modification amount is big gear 5 μ m. Pinion 4 μ m。 It can be seen from Figure 8 that if only the pinion is modified, the Hertz contact stress and transmission error values of all schemes will increase instead, so they are all rounded off. Then we can see from Fig. 9 that the Hertz contact stress of the helical gear pair can be reduced by No. 1, No. 2 and No. 3 schemes, and the No. 1 scheme is the lowest, 513.825N/mm2. Therefore, the No. 1 scheme, which is only used to modify the involute tooth top of large gear with long tooth profile, is also taken as the preliminary optimization modification scheme, and its modification amount is large gear 3 μ m. The pinion is not shaped.
(4) Optimal modification of long tooth profile broken arc addendum
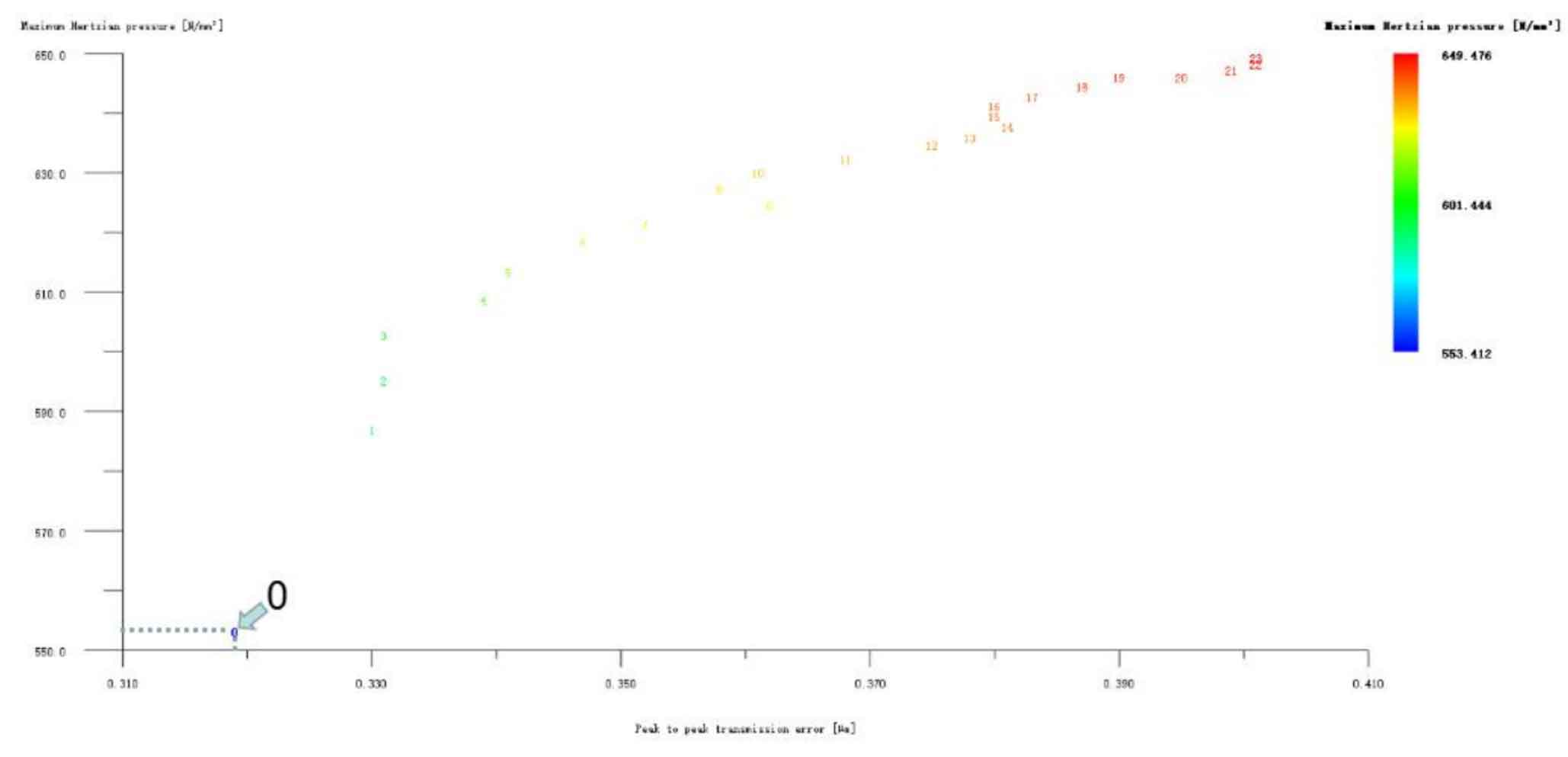
Figures 10, 11 and 12 show the modification of the large and small gears simultaneously with the long tooth profile broken arc tooth top, the modification of the small gear long tooth profile broken arc tooth top, and the modification of the large gear long tooth profile broken arc tooth top. It can be seen from Figure 10 that the shape modification effect of No. 1 and No. 24 schemes is ideal, of which No. 1 scheme is the best, and its Hertz contact stress and transmission error are 532.917N/mm2 and 0.265 respectively μ m. The modification amount is big gear 3 μ m. Pinion 3 μ m。 It can also be seen from Figure 11 that the transfer error and Hertz contact stress values of schemes 10 to 23 are equal to those of the unmodified ones, and the other schemes have worse modification effects, so they are all excluded. Observe Figure 12 again. Although there is no optimization scheme that can reduce the transmission error and Hertz contact stress, the Hertz contact stress is reduced by Scheme 1, 2 and 3, and the effect of No. 1 is good. The Hertz contact stress is reduced to 529.8N/mm2, and the modification amount is large gear 3 μ m. The pinion is not shaped.
(5) Optimization and modification of tooth profile drum
Figures 13, 14 and 15 show the drum profile modification of large and small gears at the same time, the drum profile modification of small gears only, and the drum profile modification of large gears only. It can be seen from Figure 13 that No. 1 is the only optimization scheme with ideal effect, and its Hertz contact stress and transmission error are 546.239N/mm2 and 0.284 respectively μ m. The modification amount is big gear 3 μ m. Pinion 3 μ m。 It can be seen from Figure 14 that, unlike other tooth profile modification methods, which only have poor effect on pinion modification, the 1 #, 2 # and 3 # modification schemes have better effect. Scheme 1 has the best effect, with Hertz contact stress and transmission error of 477.279N/mm2 and 0.267 respectively μ m. The modification amount is big gear without modification, and small gear 3 μ m。 It can be seen from Figure 15 that even if only the tooth profile drum modification is carried out for the big gear, the modification effect of No. 1, No. 2 and No. 3 schemes is also very ideal, of which the No. 1 scheme is the best, and its Hertz contact stress and transmission error are 465.386N/mm2 and 0.279 respectively μ m. The amount of modification is that the pinion is not modified, and the big gear is 3 μ m。
To sum up, the summary is as follows: 1. After the large and small gears of the helical gear pair are modified simultaneously by the above-mentioned arbitrary tooth profile modification method, the optimal modification scheme with ideal effect can be obtained. 2. Except for the drum profile modification, if only the pinion of the helical gear pair is modified, the modification effect of the other long profile tooth top modification methods is generally poor. 3. Except for the linear modification method of the tooth top of the long tooth profile (which can only slightly reduce the Hertz contact stress, while from the previous research work of the research group, it is found that the tooth drum modification will increase the Hertz contact stress, so this method is excluded), if only the large gear modification of the helical gear pair is considered, all the modification methods have the optimization scheme that can significantly reduce the Hertz contact stress. This is consistent with the analysis mentioned above that the tooth profile modification is mainly to reduce the Hertz contact stress of the helical gear pair, that is, to improve the strength (life) of the helical gear. 4. If the drum modification method of tooth profile is adopted, it is necessary to analyze and compare the modification effect of the optimized plan of the simultaneous modification of large and small gears, only the modification of large gears or small gears, because the meshing performance of the helical gear pair after the three optimization modifications has advantages and disadvantages.