The precision manufacturing of hypoid gears requires advanced techniques and expertise to ensure accurate gear geometry, high-quality tooth surfaces, and precise alignment. Due to their unique design and complex tooth profiles, the production of hypoid gears presents several challenges that need to be addressed. In this article, we will explore the techniques used in the precision manufacturing of hypoid gears and discuss the challenges associated with their production.
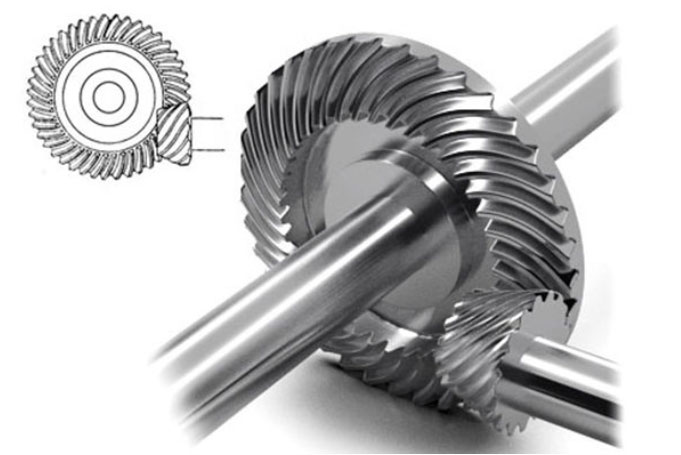
- Gear Design and Simulation: Precise gear design is the foundation of manufacturing high-quality hypoid gears. Computer-aided design (CAD) software is commonly used to create the 3D models of the gears, taking into account the desired gear ratio, tooth profiles, and contact patterns. Simulation software can also be employed to analyze the gear meshing behavior and optimize the tooth surface contact.
- Gear Cutting Techniques: Gear cutting is a critical process in manufacturing hypoid gears, and several techniques can be used depending on the specific requirements and gear size. The most common methods include:
- Face Milling: Face milling is used for roughing the gear tooth surface. It involves using a face mill cutter with multiple inserted cutting edges to remove excess material.
- Form Milling: Form milling uses specialized cutters to generate the gear tooth profile. The cutter shape corresponds to the desired tooth geometry, and multiple passes are made to achieve the final shape.
- Gear Grinding: Gear grinding is a precise process used to refine the tooth surface and ensure accurate tooth geometry. It involves using abrasive wheels to remove material and achieve the desired tooth profile.
- Gear Inspection and Metrology: To ensure the precision and quality of hypoid gears, thorough inspection and metrology processes are essential. Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and gear inspection machines are used to measure critical parameters such as tooth profile, tooth contact pattern, backlash, and runout. These measurements help verify that the manufactured gears meet the required specifications.
- Gear Alignment and Assembly: Aligning hypoid gears accurately is crucial for their proper functioning and efficient power transmission. Achieving the correct offset shaft alignment and ensuring accurate positioning of the gears can be challenging. Specialized assembly fixtures, jigs, and alignment tools are used to ensure precise gear alignment during assembly.
- Heat Treatment and Surface Finishing: Heat treatment processes, such as carburizing or nitriding, are often employed to enhance the hardness and wear resistance of hypoid gears. Surface finishing techniques, such as grinding or honing, can be applied to achieve the desired surface quality and reduce friction.
Challenges in Hypoid Gear Manufacturing:
- Complex Geometry: The complex tooth profile of hypoid gears poses challenges in achieving accurate tooth geometry and proper gear meshing. Precise machining and grinding techniques are required to maintain the desired tooth shape and ensure optimal contact patterns.
- Tight Tolerances: Hypoid gears often have tight tolerances, requiring strict control over the manufacturing processes to meet the specified dimensions and ensure proper gear meshing.
- Tooling and Equipment: Specialized tooling, cutters, and grinding wheels are needed for manufacturing hypoid gears. These tools must be designed and maintained properly to achieve the desired gear quality.
- Gear Inspection: Inspecting hypoid gears for accurate tooth profile, tooth contact pattern, and other parameters can be challenging due to their complex geometry. Advanced inspection equipment and techniques are necessary to ensure the gears meet the required specifications.
- Noise and Vibration Control: Hypoid gears are prone to noise and vibration issues due to their offset shaft alignment and complex tooth surfaces. Manufacturers must address these challenges through careful gear design, precise manufacturing processes, and effective noise reduction techniques.
In conclusion, the precision manufacturing of hypoid gears requires specialized techniques, advanced equipment, and expertise to overcome the challenges associated with their complex geometry and tight tolerances. By employing these techniques and addressing the challenges, manufacturers can achieve high-quality hypoid gears with accurate tooth geometry, optimal gear meshing, and efficient power transmission. The advancements in gear design software, CNC machining, and gear inspection technology have greatly facilitated the precision manufacturing of hypoid gears.
It is important to note that the manufacturing of hypoid gears may require specialized knowledge and experience. Collaborating with skilled gear manufacturers or consulting with experts in the field can help ensure successful production and optimal performance of hypoid gears.
The precision manufacturing of hypoid gears plays a vital role in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. These gears are used in applications such as automotive differentials, power transmission systems, heavy machinery, and robotics, where their unique characteristics and advantages are leveraged to enhance performance, efficiency, and reliability.
As technology continues to advance, the manufacturing processes for hypoid gears are likely to benefit from further automation, improved tooling, and advanced simulation techniques. These advancements will contribute to even higher precision, tighter tolerances, and enhanced efficiency in the production of hypoid gears.
In conclusion, the precision manufacturing of hypoid gears requires a combination of advanced techniques, precise gear design, accurate machining processes, thorough inspection, and proper assembly. Overcoming the challenges associated with their complex geometry and achieving high-quality gear performance are essential for meeting the demanding requirements of modern machinery and driving technological advancements in various industries.
