Warm cold composite forming technology is a new process abroad in the 1970s, but it was not widely used in automobile manufacturing until the 1980s. Represented by Germany ThyssenKrupp, their warm and cold composite process technology is at the leading level in the world. In recent years, warm and cold composite technology has been widely used in the United States, Japan and other countries, and there is a trend to replace hot forging technology.
German scholar Dr. Ekkehard komerf discussed the feasibility of using warm and cold composite process to produce complex parts. Through the analysis of the forming methods of differential bevel gear and constant velocity universal joint, the technical and economic advantages of warm and cold composite process were discussed. The warm forging of warm cold composite process completes the processing of complex shapes of parts. The purpose of cold forging is to ensure the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of parts. The purpose of reducing forming load, reducing intermediate forming steps, improving production efficiency and reducing production cost is achieved, and the precision and surface quality of parts are equivalent to that of cold precision forging.
Japanese scholars t. Nagahama and s. enomae introduced the forging equipment of Japanese automobile industry. It is pointed out that the warm and cold composite forming process puts forward new requirements for forging equipment, including die accuracy, service life, die lubrication and so on.
Taking SCM420 spur gear as the research object, Japanese scholars Takahashi and others have made a comprehensive study on warm precision forging process through experimental methods. The forming temperature of the material is 800 ℃, and the forming effect of spur gear is the best; Preheating the die can reduce the temperature gradient and prevent cracks, but the higher the preheating temperature is, the higher the forging temperature will be, and the radial dimension error of the forging will increase.
Korean scholar Y.C. Chang and others adopted the processing technology of warm forging blank + subsequent cold finishing for spur gear, and established the finite element model for simulation. In order to improve the operation efficiency, the finite element model of spur gear was simplified to a single tooth profile. Through experimental verification, the results show that the surface roughness and shape and dimensional accuracy of the spur gear machined by this process meet the requirements of “net forming”.
Although the warm cold composite forming technology in China has developed rapidly, compared with the developed countries in Europe and America, the technology is relatively backward. In order to narrow the gap between China and developed countries, based on the digestion and absorption of some mature foreign processes, the key technologies such as forming law and forming mechanism of warm cold composite forming are deeply studied, and the domestic automobile industry has developed rapidly.
In China, Shanghai Tiefu transmission shaft Co., Ltd. produces passenger car constant velocity universal joint alien wheels in large quantities by warm and cold compound forming, and Jiangsu Pacific Co., Ltd. produces spur gear precision forgings in large quantities by warm and cold forming. Zhang Zhimin and others have studied the open warm upsetting extrusion cold extrusion process. Compared with the closed upsetting extrusion of traditional spur gears, this process can better improve the defects in the forming process of spur gears and has good performance.
Zhu Huaishen and others adopted the processing method of warm forging and cold extrusion for large module spur gears, and carried out elastic-plastic finite element simulation for the cold finishing process. The laws among cold finishing quantity, rebound and relative wall thickness were studied. It was obtained that the reasonable range of cold finishing quantity was 0.1-0.2 mm.
Li Qian of Beijing Electromechanical Research Institute designed the finishing process of straight tooth planetary gear with M = 4 and tooth width H = 60 mm. The composite forming scheme of hot forging cold extrusion cold finishing was adopted, and the finite element simulation was carried out. According to the results, the best forming parameters were obtained. Based on the simulation results, the experimental die is designed, and the expected spur gear forging is obtained.
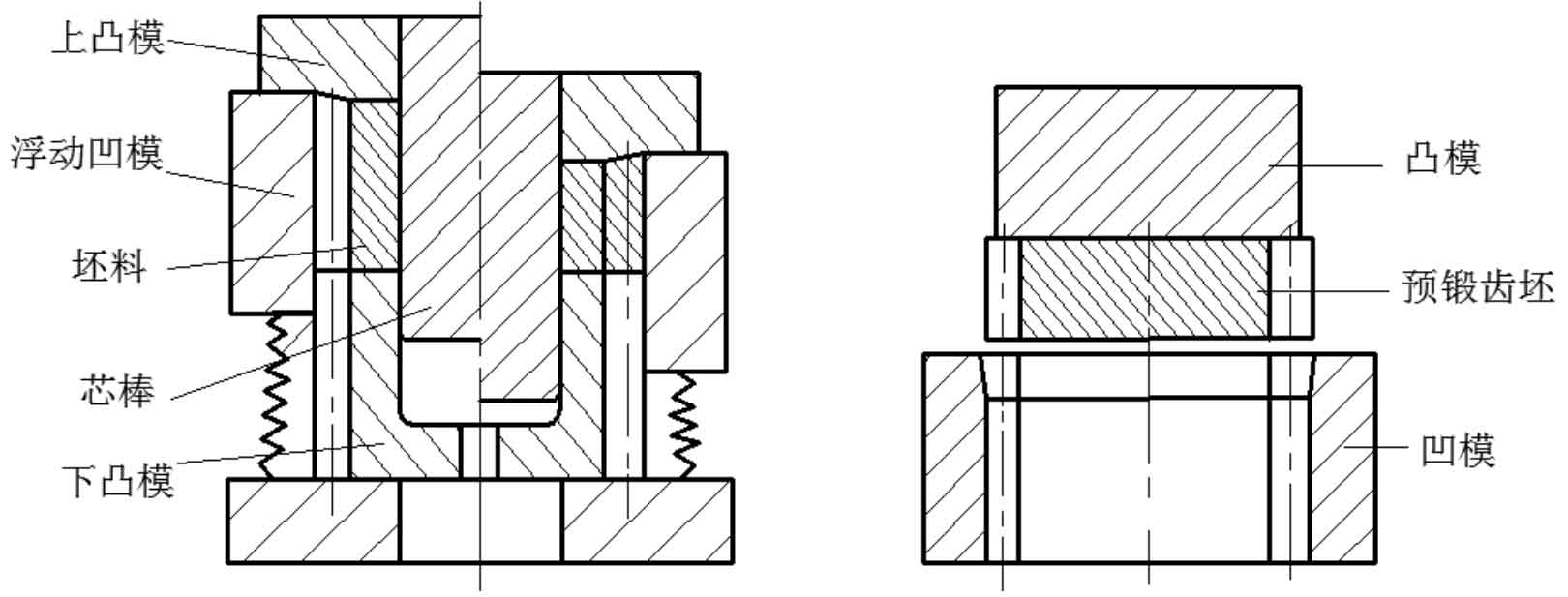
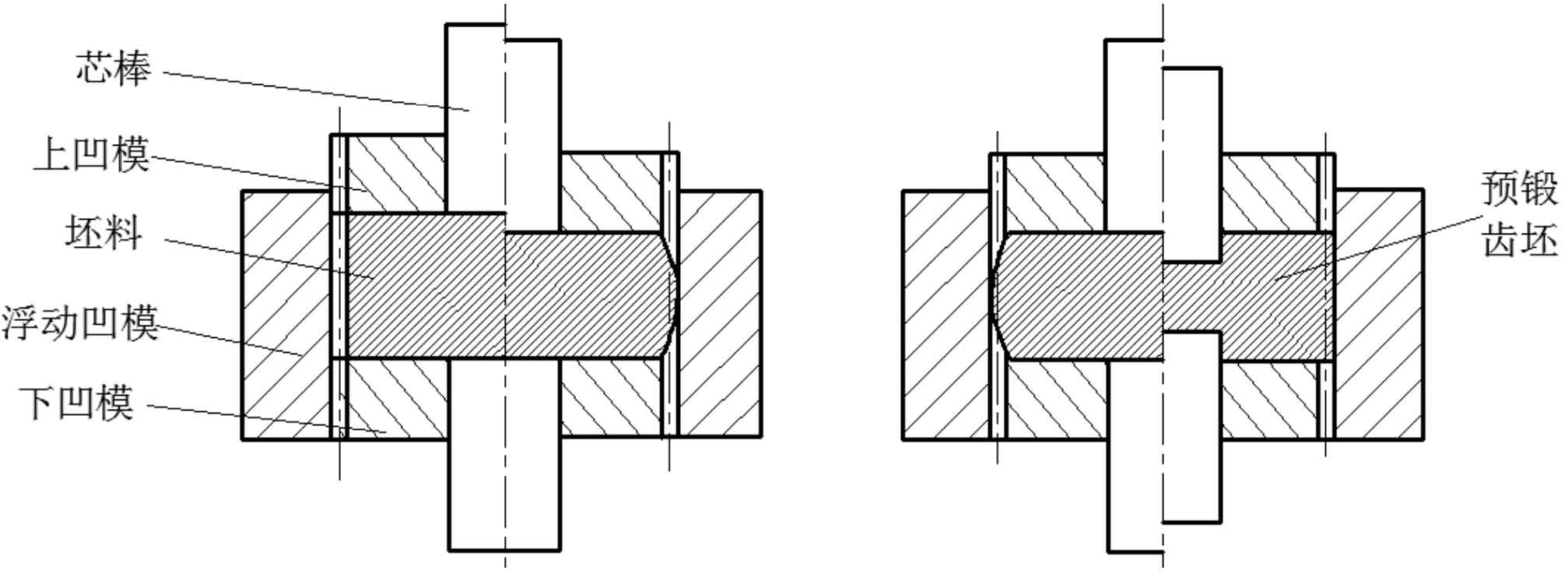
Xie Jinshi and others adopted the composite process of warm forging and cold extrusion for spur gears, and the process scheme is shown in Figure 1.1. The influence of blank size on workpiece forming is analyzed. The orthogonal test is carried out by finite element method to obtain the best combination of warm forging process parameters. The simulation results of different cold finishing quantities are analyzed. Taking the tooth profile error and die wear into account, the best finishing allowance is 0.2 mm, which is verified by experiments.
Zuo bin and others analyzed the forming schemes under three kinds of billets by using the finite element method, and found that compared with the hollow billet, the solid billet is the best scheme for precision forging. The effects of die structure and decompression groove on the hot precision forging of spur gear are analyzed, and the effects of cold finishing extrusion allowance and other process parameters on the metal flow, forming load and workpiece stress of spur gear are analyzed.
Qiu Mingxia and others adopted the scheme of open warm upsetting extrusion + cold extrusion for 20CrMnTi spur gear, which alleviated the problem of rapid increase of closed upsetting extrusion load and ensured the complete filling of tooth cavity. The finite element model is established in DEFORM-3D, the effects of displacement coefficient, friction coefficient, die fillet size and speed on spur gear forming are analyzed, and the die structure and material are designed and verified by experiments.
Li Zhenhong and others put forward the semi closed warm forging scheme for cylindrical gears, and analyzed three different schemes by finite element method. The results show that the strain distribution of boss shunting scheme is relatively uniform, the load is the smallest, and the forming quality of tooth top shunting is poor.
Yan Kelong et al. Studied the precision forging process of large module spur gear, adopted warm and cold compound forming, designed three schemes of die fixed closed reverse extrusion, die moving two-way opposite extrusion and die floating two-way opposite extrusion, and simulated with DEFORM-3D to obtain the best combination of process parameters of initial temperature, skin connection form and friction factor.
Wang Minghui and others studied the precision forming process of 45 steel cylindrical spur gear with modulus of 4. By using the method of comparative research, the finite element analysis of upsetting extrusion, end face shunting and upsetting extrusion bulging composite process was carried out respectively, and the influence of forming process parameters on forming quality was studied. The forming method of upsetting extrusion pre forging upsetting extrusion bulging final forging is put forward, which solves the problem of microcracks at the tooth root of spur gear, and a self-adjusting upsetting extrusion bulging compound hydraulic press is developed.