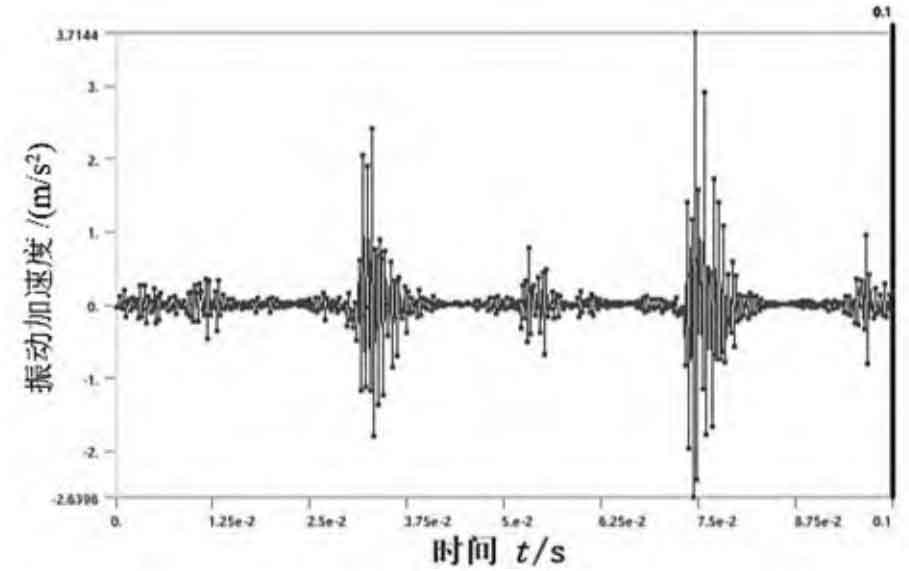
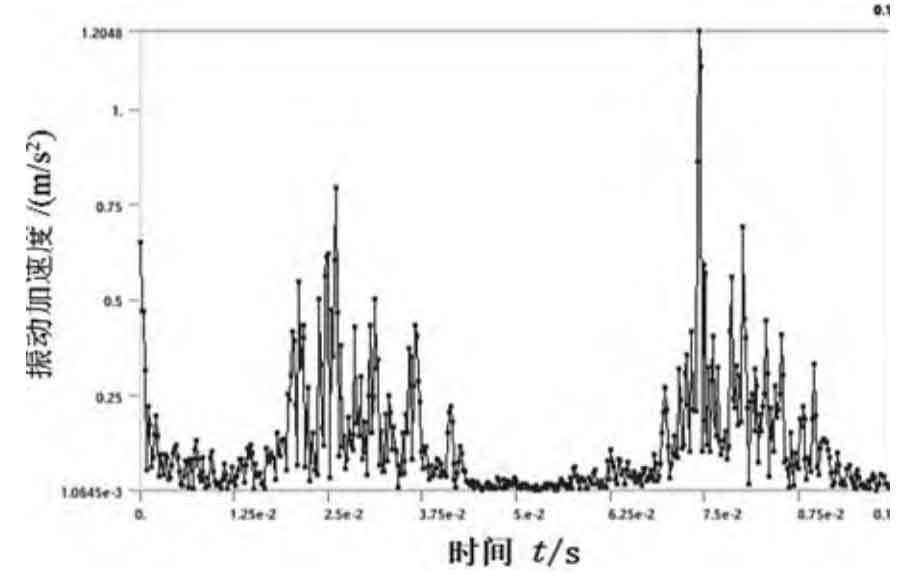
As shown in Figure 1, the vibration acceleration in X, Y and Z directions at the selected nodes with input speed of 1400 r/min and load torque of 80 N · m is listed as the research subject. The maximum vibration acceleration of node 310580 on the internal gear of fixed planetary gear is the smallest in Y direction and reaches the peak in Z direction, but the vibration laws in both directions are relatively consistent. The large peak of vibration acceleration is caused by the instantaneous meshing impact collision between the external gear and the internal gear. Under this working condition, because the difference between the number of teeth of the outer gear of the inner and planetary gears is 2, the outer gear of the planetary gear near the hole ring rotates for 4.67 teeth within 0.1 s, which causes the fifth wave peak in Figure 1 (d). Because the distance between the vibration acceleration research node and each meshing impact is different, the peak value is not completely consistent.
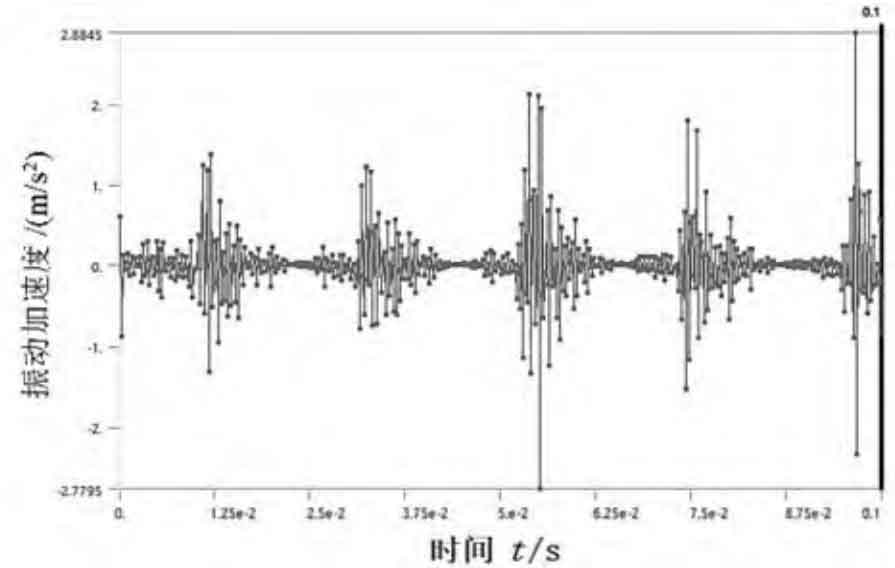
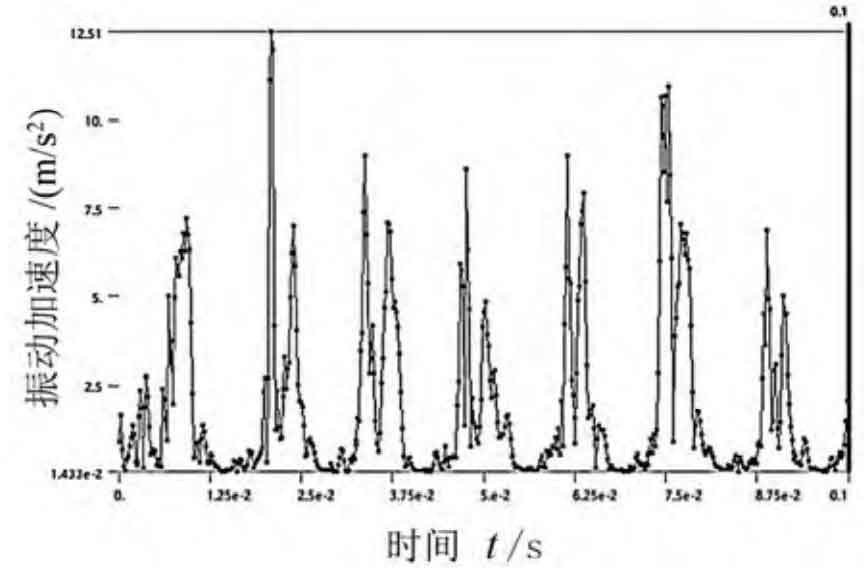
Combined with Fig. 1 (d) and Fig. 2, when the load torque is kept at 80 N · m, the input speeds are 600 r/min, 1400 r/min and 2200 r/min respectively. With the increase of the speed, the number of times the planetary gear pair engages in 0.1 s increases, and there is an eccentricity, so the vibration acceleration increases, and the vibration of the planetary gear reducer becomes stronger.
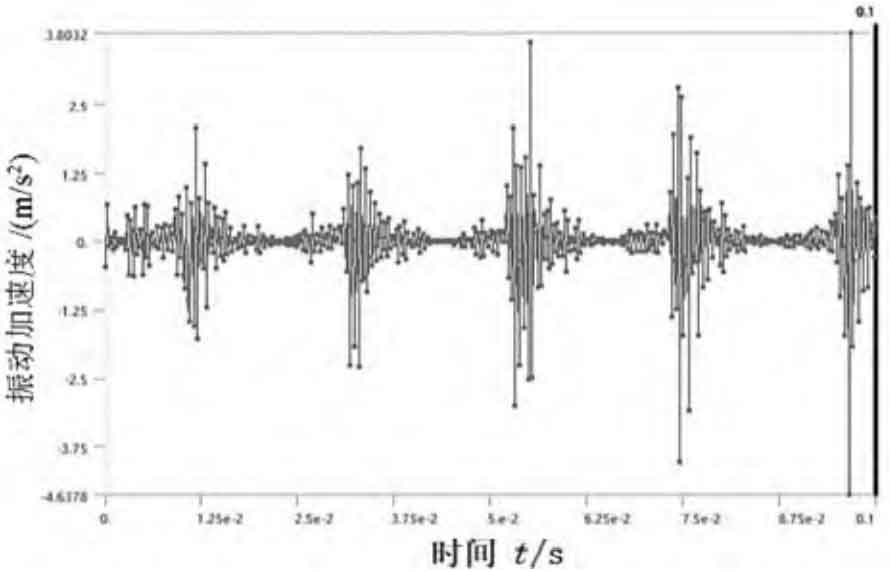
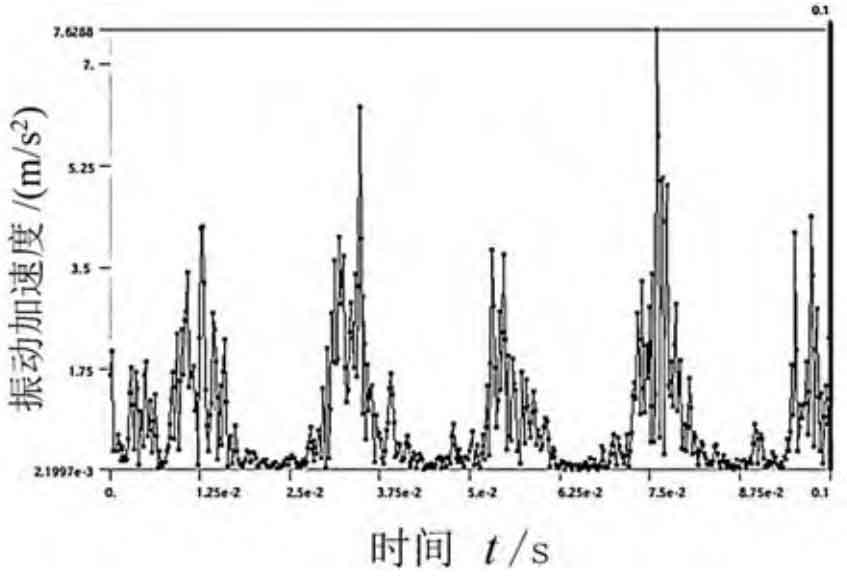
Combined with Fig. 1 (d) and Fig. 3, when the input speed is kept at 1400 r/min, the load torque is 40 N · m, 80 N · m and 120 N · m respectively, and there are five peaks in the same figure. The vibration acceleration law of the node is basically the same, but the maximum vibration acceleration increases slightly.