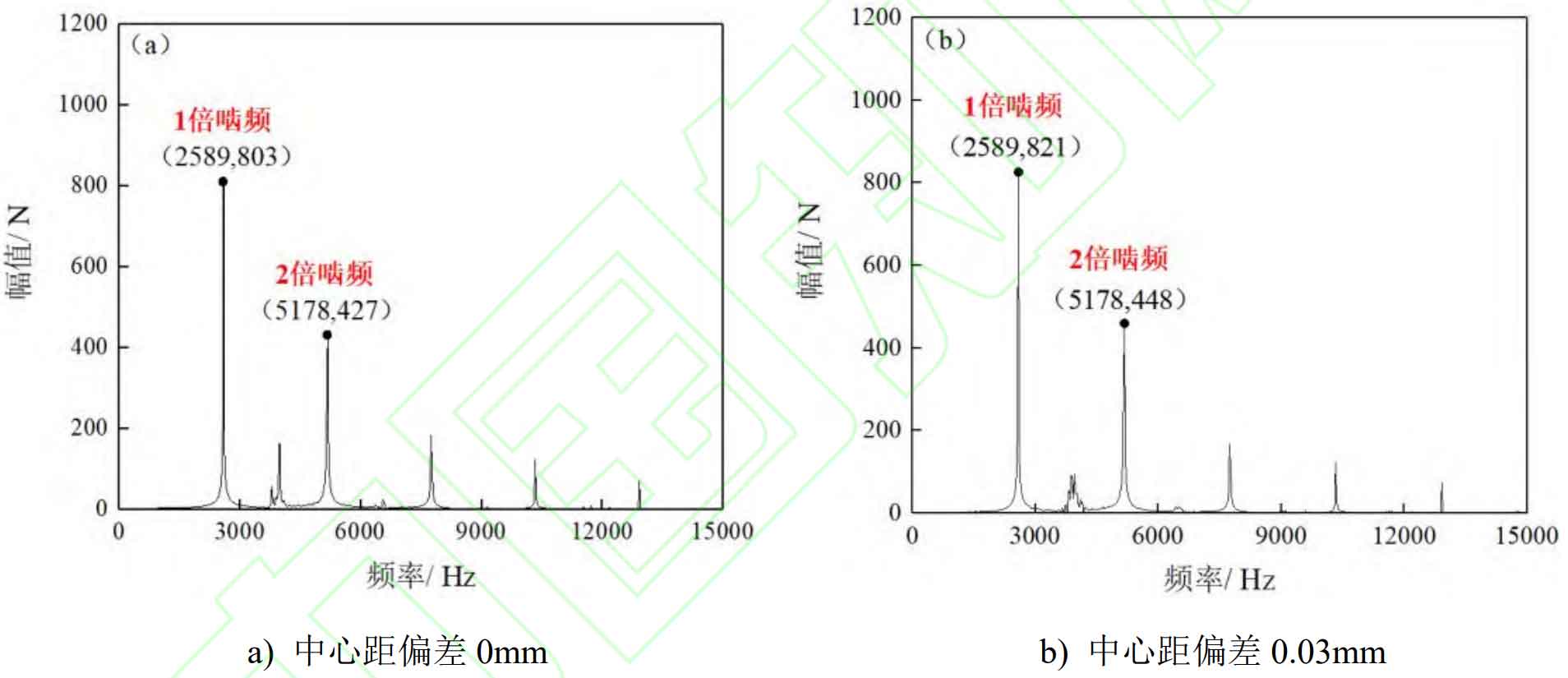
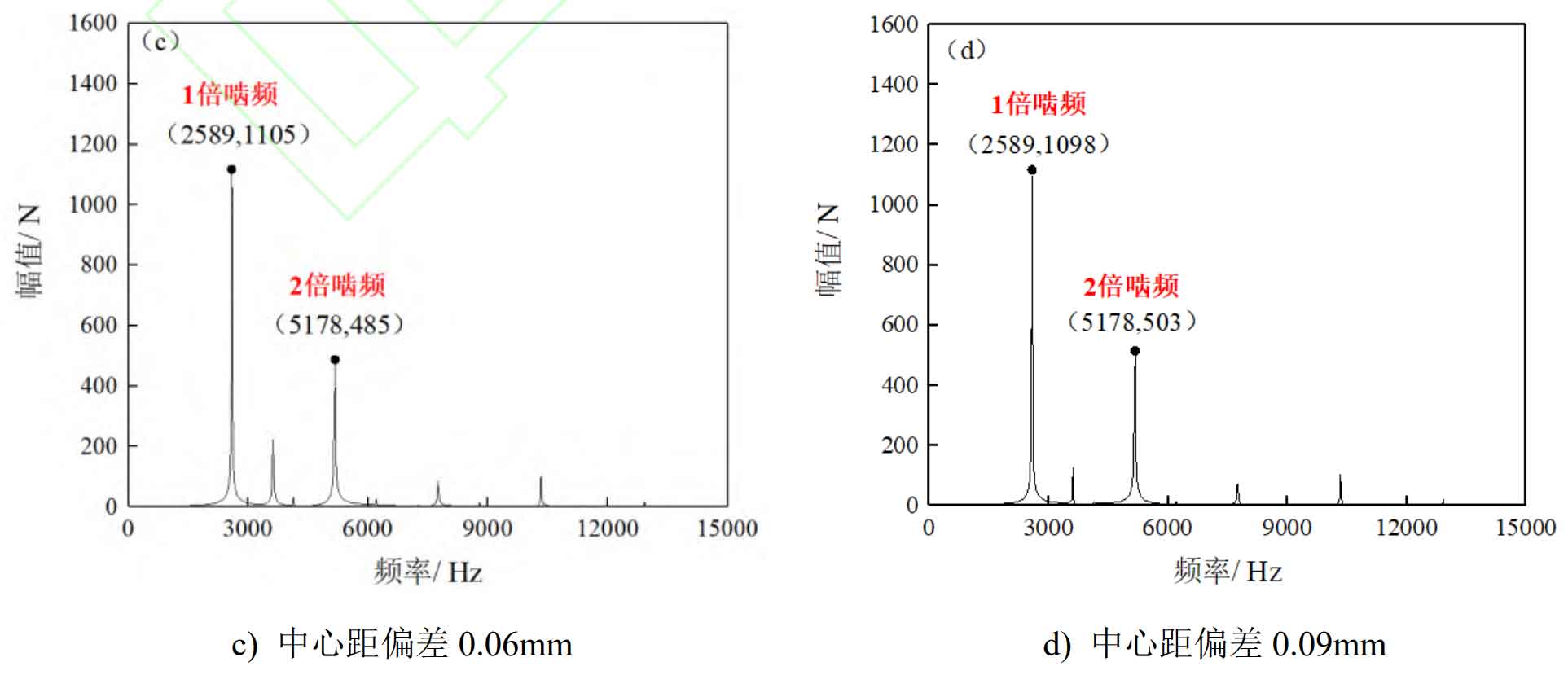
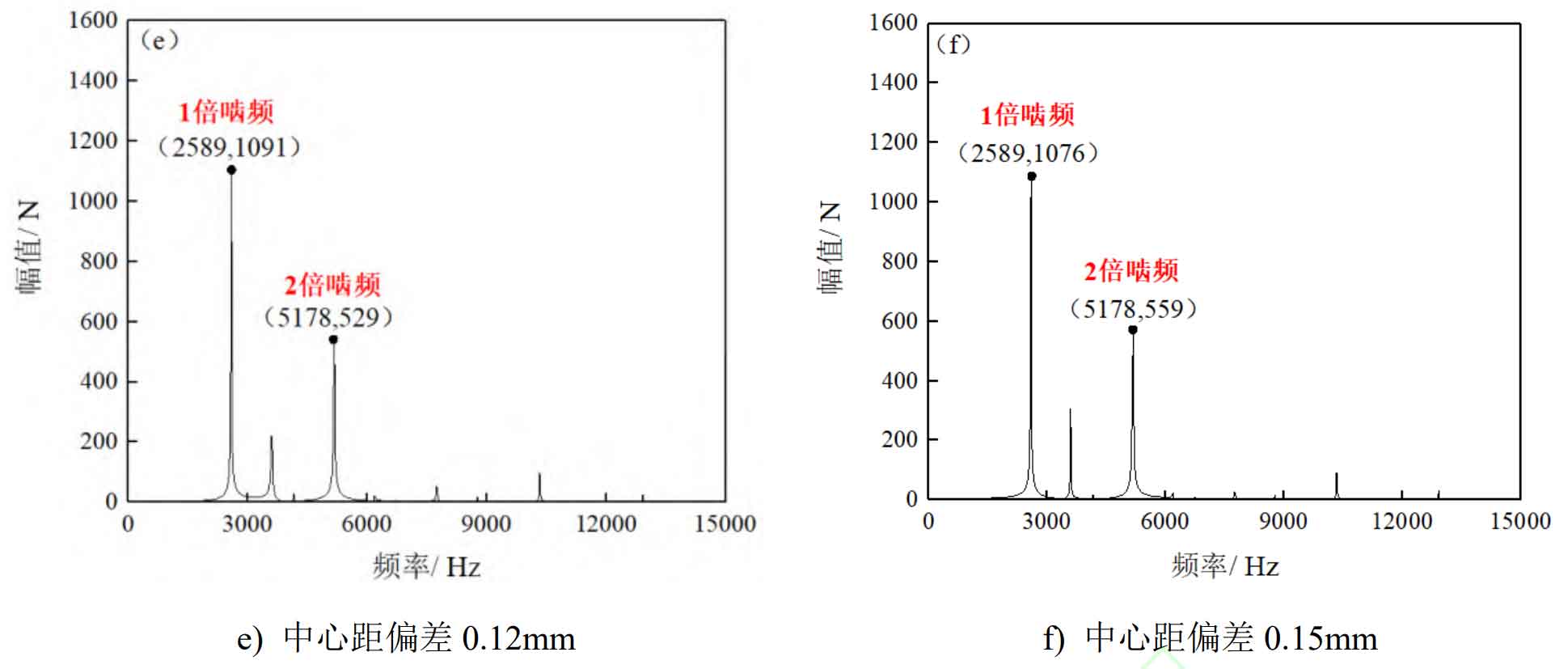
Perform Fourier transform on the meshing force curve of the spur gear pair in Figure 1 to obtain the meshing frequency spectrum of the spur gear pair under different center distance deviations, as shown in Figure 2.
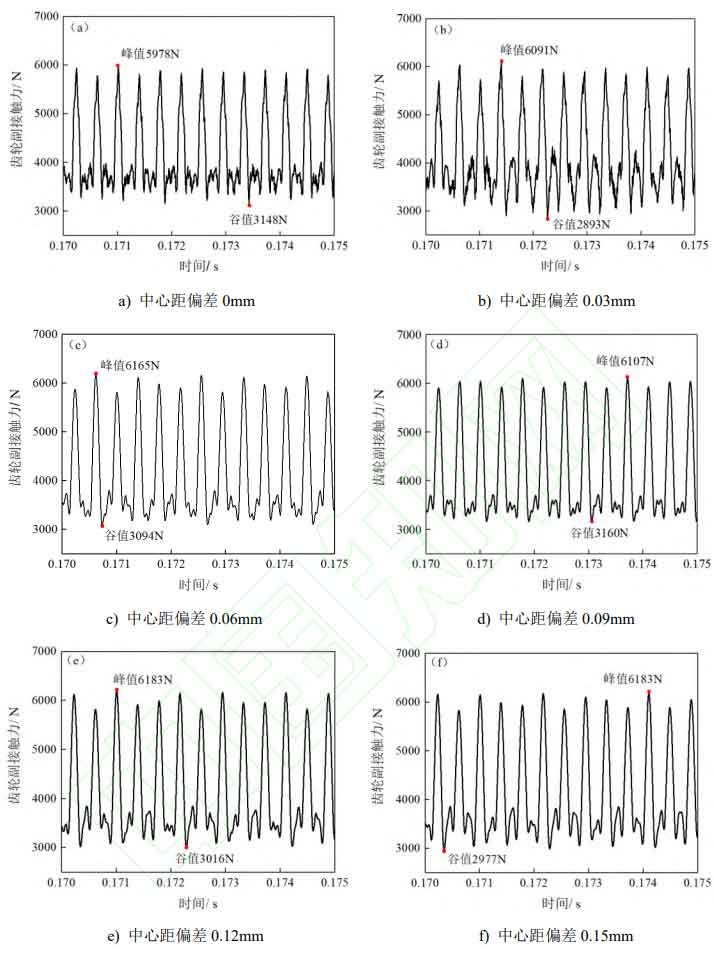
During the meshing process of spur gear pairs, the main excitation of the system comes from the excitation force generated by gear tooth meshing, so the main frequency component in the spectrum diagram should be the meshing frequency of the spur gear pair. If the meshing gear teeth undergo multiple impacts such as meshing in and out in a cycle, there must also be a twice meshing frequency component in the spectrum.
The relationship between the meshing frequency f of the spur gear pair and the rotational speed n1 of the driving wheel is as follows:
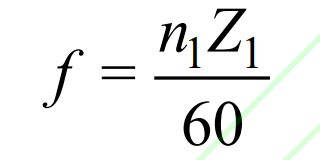
In the formula, n1 represents the rotational speed of the driving wheel, in r/min. Using the formula, it can be calculated that the meshing frequency of the spur gear pair is 2583Hz. Based on the analysis of the meshing frequency and frequency spectrum of the spur gear pair, it can be seen that the frequency spectrum of the meshing force of the spur gear pair under each center distance deviation is mainly composed of 1 and 2 times the meshing frequency spectrum, while the amplitude of other sidebands is relatively low. The amplitude of the 1-fold meshing spectral line increases as the center distance deviation increases. When the center distance deviation reaches 0.06 mm, the amplitude of the 1-fold meshing spectral line remains relatively constant as the center distance deviation increases. In addition, compared to the 2-octave spectral line amplitude without center distance deviation, the 2-octave spectral line amplitude increases by 5%, 14%, 18%, 24%, and 31% when the center distance deviation is 0.03 mm, 0.06 mm, 0.09 mm, 0.12 mm, and 0.15 mm, respectively.
In summary, an increase in the center distance deviation will exacerbate the meshing vibration of the spur gear pair, but there is a critical value for this effect. Within a certain range, when the deviation reaches the critical value, the meshing vibration of the spur gear pair will maintain a relatively constant state. In addition, the increase in center distance deviation will continue to exacerbate the meshing in and out impact of the gear teeth, leading to a decline in meshing stability.