(1) Time-varying meshing stiffness
Because the gear teeth will produce elastic deformation when the gear is engaged, and the gear coincidence is usually a real number greater than one, the gear comprehensive stiffness will change periodically with the change of the number of teeth when the gear pair is engaged alternately. In short, the dynamic excitation caused by the time-varying stiffness of the meshing gear pair is called stiffness excitation.
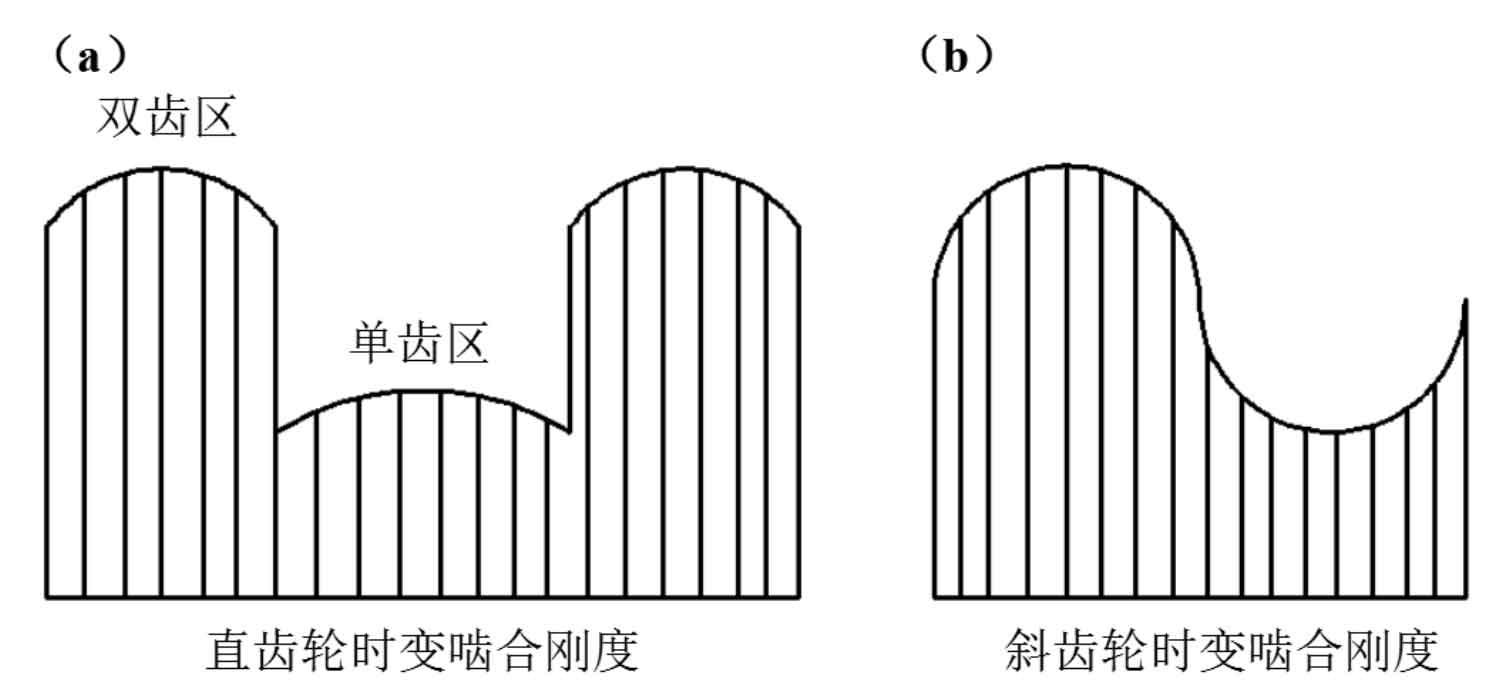
Figure 2.6 shows the time-varying meshing stiffness prediction model of involute spur gear and helical gear under ideal conditions. Since there are only two kinds of teeth engaged in spur gear meshing, when the spur gear pair changes from double teeth to single teeth meshing at a certain moment, there will be a sudden change in the gear comprehensive stiffness as shown in Figure 1 (a). That is, the elastic deformation of gear teeth is larger and the comprehensive meshing stiffness is smaller in the single tooth meshing area; In the double tooth meshing area, the elastic deformation of gear teeth is small and the comprehensive meshing stiffness is large. However, because of its “point line point” meshing track, helical gears will have a more stable transmission than spur gears, resulting in a time-varying meshing stiffness curve similar to the “sinusoidal” distribution as shown in Figure 1 (b).
(2) Time-varying meshing force
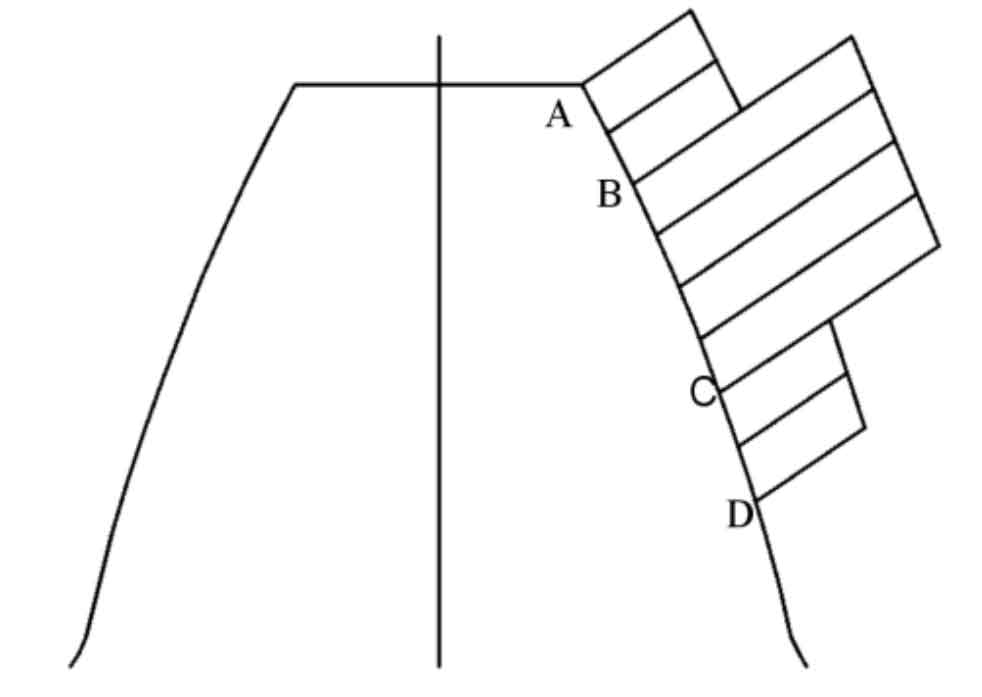
Take a spur gear as an example. Because the number of teeth engaged in the meshing is constantly changing, the load on the gear teeth shows a periodic change law as shown in Figure 2. When the number of meshing gear teeth is double (A-B section, C-D section), the load is small; When the number of meshing gear teeth is single (B-C segment), the load is large. Similarly, the load borne by helical gear teeth will also show a “sinusoidal” distribution with the number of meshing teeth, but the change process is slower than that of spur gears. However, whether spur or helical gears, as long as the gear comprehensive stiffness and the load borne by the gear teeth fluctuate periodically, dynamic excitation will be caused, resulting in severe vibration of the gear and then noise.
