Gear hobbing is a widely used manufacturing process for producing gears. It is a highly efficient method that utilizes a specialized cutting tool called a hob to generate teeth on a gear blank. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the gear hobbing process, covering the equipment, setup, operation, and common considerations in gear manufacturing.
- Gear Hobbing Equipment:
- Hobbing machine: A gear hobbing machine is the primary equipment used for gear hobbing. It consists of a spindle, workholding device, hob, and various mechanisms for gear cutting and control.
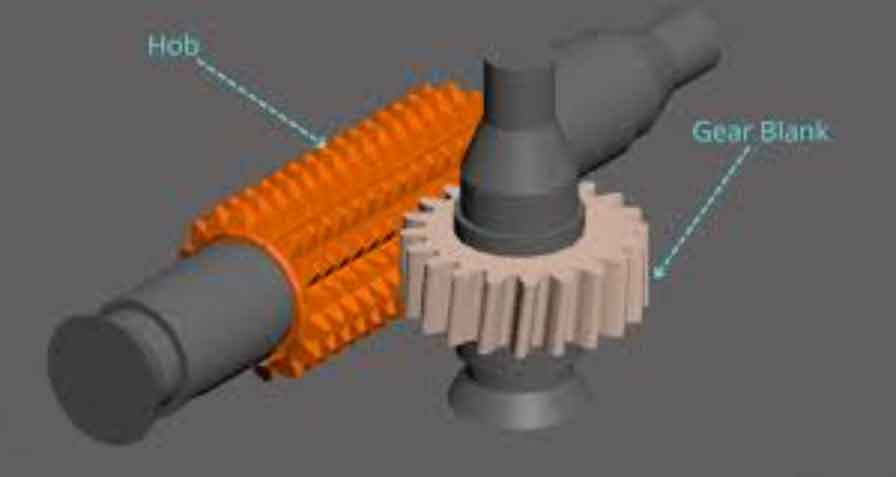
- Hob: The hob is a cutting tool with helical teeth that matches the desired gear tooth profile. Hobs are made of high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide materials and come in various sizes and designs.
- Gear Hobbing Setup:
- Gear Blank: Start with a gear blank, which is a cylindrical workpiece made of suitable gear material, such as steel or cast iron.
- Workholding: Secure the gear blank on the machine’s workholding device, which may include chucks, centers, or special fixtures.
- Hob Mounting: Mount the hob onto the hobbing machine’s spindle and align it with the gear blank. Ensure proper center distance and alignment for accurate gear cutting.
- Gear Hobbing Operation:
- Cutting Parameters: Set the appropriate cutting parameters, such as hob speed, workpiece rotation speed (known as the gear blank’s indexing), and axial and radial feeds.
- Gear Hobbing Process: The hob and the gear blank rotate simultaneously. As they engage, the hob progressively cuts into the gear blank, generating gear teeth as the blank is fed axially. The hob’s helical teeth create the desired gear tooth profile.
- Considerations in Gear Manufacturing:
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate gear material based on the intended application, considering factors like strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
- Heat Treatment: After gear hobbing, heat treat the gear to improve its hardness and strength. Common heat treatment methods include carburizing, quenching, and tempering.
- Quality Control: Implement quality control measures throughout the gear manufacturing process to ensure the accuracy and precision of the final product. This includes inspection of gear tooth profile, dimensions, surface finish, and hardness.
- Gear Design: Understand gear design principles, including tooth profile, pressure angle, helix angle, and gear ratio calculations. Proper gear design ensures smooth operation, load distribution, and noise reduction.
It’s important to note that gear hobbing is just one of several methods for gear manufacturing. Other processes like gear shaping, gear milling, and gear grinding may be more suitable depending on the gear specifications and production requirements.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and follow best practices to ensure safe and efficient gear hobbing operations.
