The helical gear is a type of cylindrical gear with teeth that are cut at an angle to the gear axis, forming a helix shape. This design allows for smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears, which have teeth that are cut straight and parallel to the gear axis. The helix angle, which is the angle between the helical teeth and the gear axis, plays a significant role in the performance of the gear.
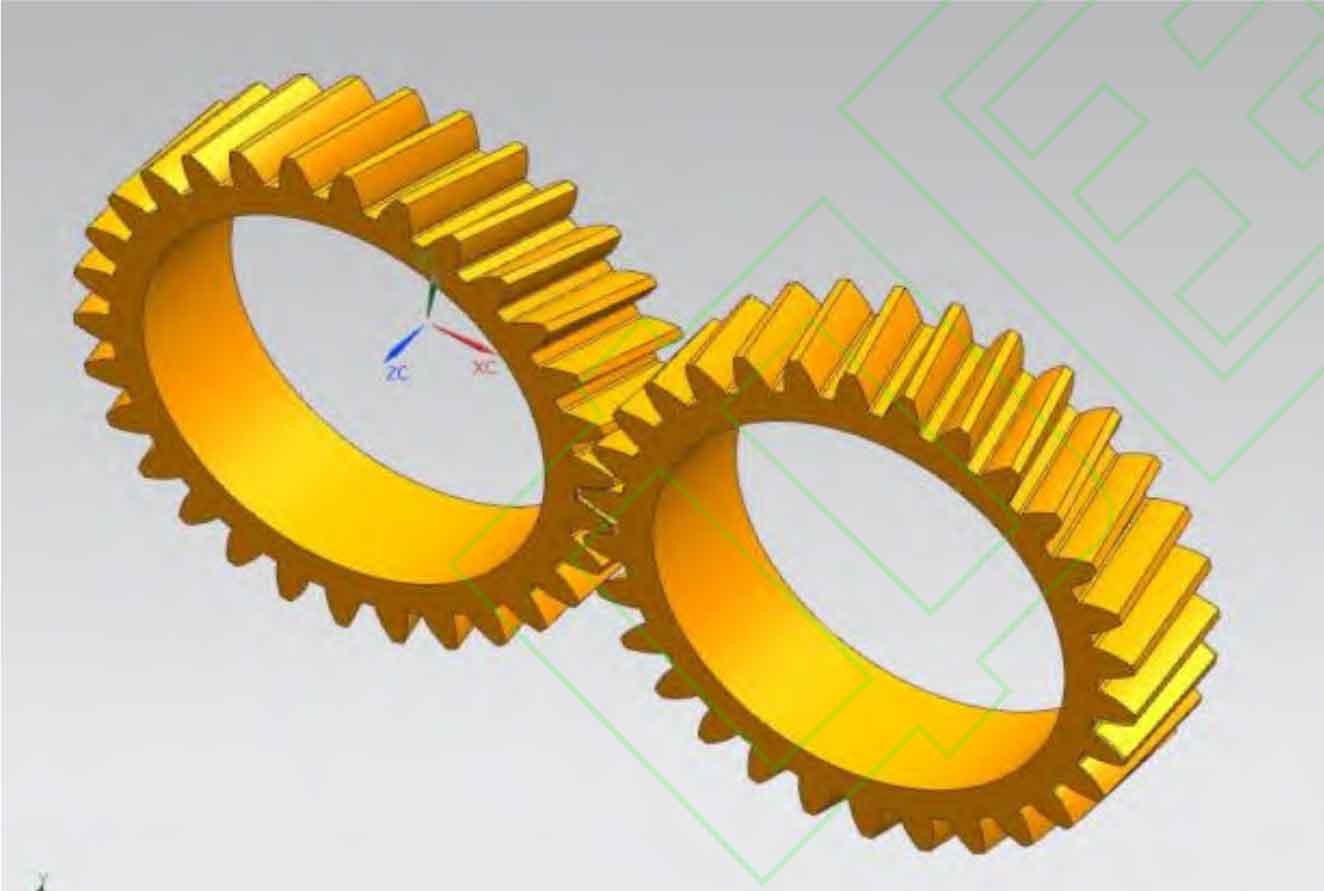
There are several advantages of using helical gears over spur gears:
- Smoother engagement: The angled teeth of helical gears allow for a gradual engagement between the gear teeth, which results in a smoother and more silent operation.
- Higher load capacity: Due to the increased contact area between the teeth of helical gears, they can handle higher loads than spur gears.
- Greater efficiency: Helical gears generally have better power transmission efficiency compared to spur gears, as there is more contact between the mating gear teeth.
- Reduced vibration and noise: As the teeth engage gradually, the contact between the teeth is distributed over a larger area, reducing the vibration and noise generated during operation.
However, helical gears have some disadvantages, such as:
- Higher manufacturing cost: Due to their complex tooth geometry, helical gears are more challenging and expensive to manufacture compared to spur gears.
- Axial thrust: The helix angle generates an axial force along the gear axis, which requires additional bearings or thrust washers to counteract this force.
Helical gears are used in a wide range of applications, including automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and power tools. They can be used in parallel or crossed-axis configurations for power transmission between non-parallel shafts.
