The factors that cause transmission errors in the spur gear system include manufacturing errors of the spur gear itself, tooth modification, load deformation, deformation of the spur gear shaft, system installation errors, bearing motion errors, etc.
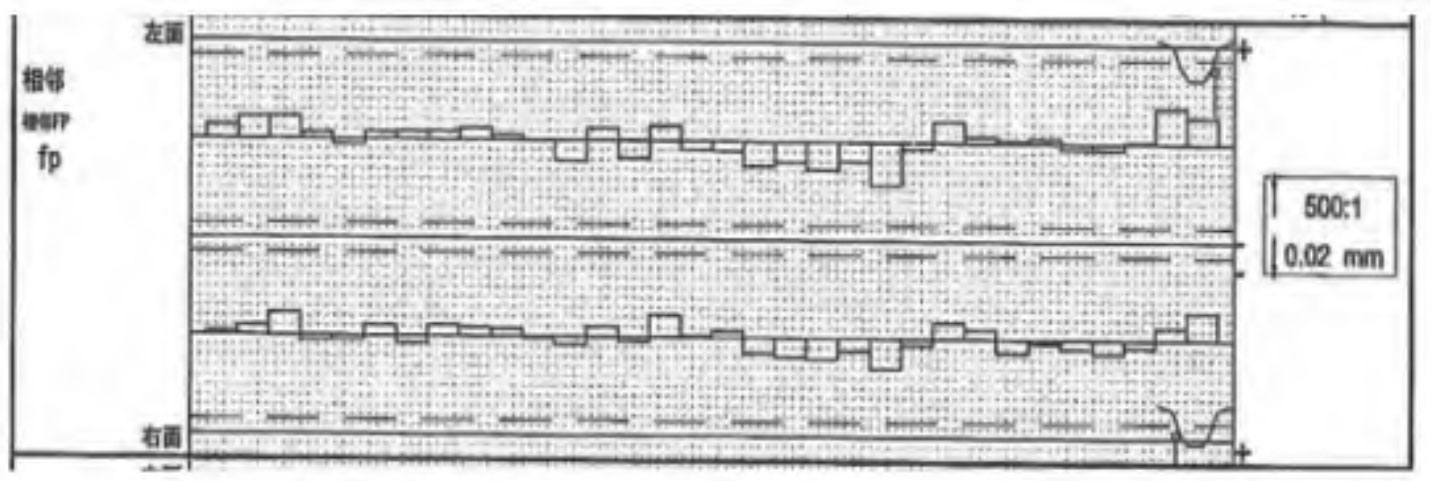
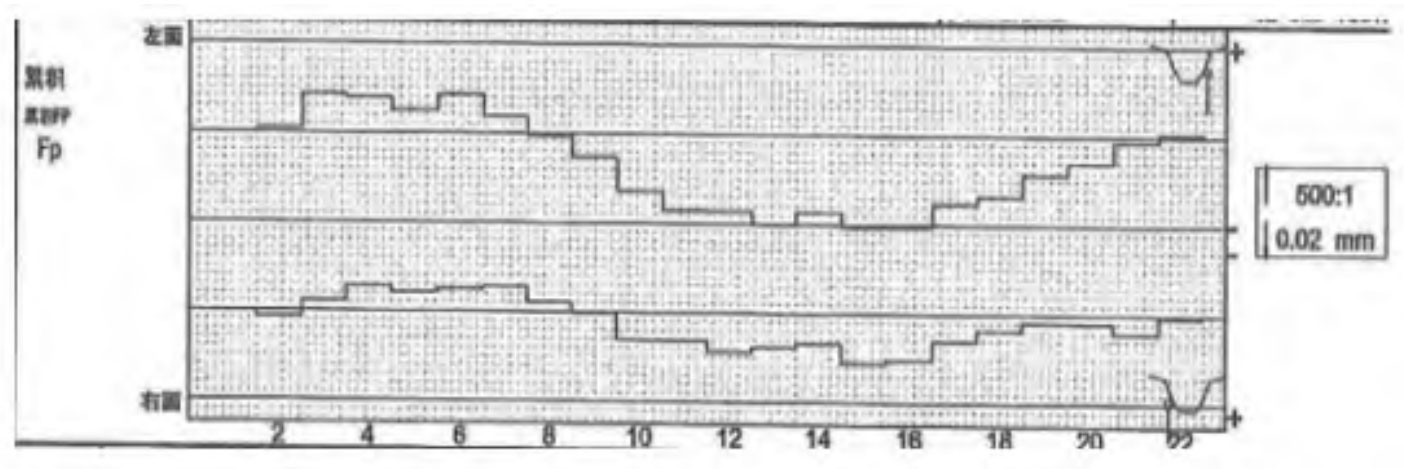
1. Accumulated error of tooth pitch Fp
Fp is mainly caused by factors such as installation eccentricity, grinding wheel wear, machine tool spindle diameter jump and swing during spur gear machining, presenting a sinusoidal periodic error and random error (tooth pitch error) superposition. As shown in Figures 1 and 2, the cumulative error Fp of a certain spur gear exhibits a typical sinusoidal pattern. Roughly, it can be represented by a sine curve.
δ p=Fpcos( φ+φ 0)
2. Single tooth pitch error fpt
Fpt is mainly caused by various factors such as tool errors and machining vibrations, and is a random error superimposed on Fp, which is difficult to express accurately with simple functions. Its numerical value is relatively small, comparable to the tooth shape error.
3. Tooth shape error ff α Tooth profile modification
ff α The formation of the tooth is mainly caused by factors such as tool shape, machine tool, material deformation, and processing methods, with a certain degree of randomness, but the tooth shape of each tooth is basically similar. The tooth profile modification shown in Figure 3 is a intentionally designed non involute modification of the tooth profile, used to counteract the uneven deformation (stiffness change) of the gear teeth under load. Both will repeat Z times within one cycle of the straight tooth gear rotation, so they can be represented by the Fourier expansion equation (usually 1 to 5 is sufficient):
δ f=∑ δ Ticos[iZ( φ+φ Ti0)](i=1~5)
4. Deformation of gear teeth under load δ a
Tooth deformation under load δ A is proportional to the unit load of the gear teeth, including gear tooth bending deformation and contact deformation, and has typical periodicity (tooth frequency and its higher-order frequency). It is the main content of transmission error analysis in spur gear design analysis software.
5. Eccentricity error between installation and shaft e, bearing motion error
The eccentricity e caused by installation eccentricity error and shaft bending (load bending and machining eccentricity) causes periodic errors in spur gears, which together with Fp seriously affect motion accuracy. It can be represented by the following equation:
δ e=etan( α t)cos( φ+φ e0)
The motion error of bearings is related to bearing accuracy, although it is still a periodic function, it is not easy to describe with simple formulas.
6. Numerical comparison and comprehensive description of various errors
Among manufacturing errors, the cumulative error of tooth pitch Fp and eccentricity e are the largest values among spur gear errors, which are approximately 3-4 times the other errors (see Table 1). They contribute the most to the transmission error of spur gears and are the main factors affecting the motion accuracy of spur gears. The error Fp and e have the same periodicity (axial frequency), but the phase may be different and can be combined as δ Acos( φ+φ 0A)。
| Error type | Fp | fpt | ffα | fHβ | etgαt | δa |
| Error/μm | 19 | 6 | 6 | 8.5 | 4-10 | 1-6 |
Tooth shape error ff α Its tooth profile modification and gear tooth deformation under load δ A has the variation characteristics of tooth frequency and its higher-order frequency, which can be merged into one term: Σδ Ti cos[iZ( φ+φ 0Ti)]。
In this way, the error of a single spur gear can be roughly described as:
δ Z= δ Acos( φ+φ 0A)+ Σδ Ti cos[iZ( φ+φ 0Ti)](i=1~5)
Among them, the first term is the shaft frequency, and the second term is the gear frequency and its higher-order frequency.
It can be seen that the characteristics of spur gear transmission error are: the transmission error amplitude with shaft frequency as the fundamental frequency is larger, and the frequency is lower; The amplitude of transmission error with tooth frequency as the fundamental frequency is relatively small, usually 1/2-1/10 of the shaft frequency fundamental frequency transmission error, but the frequency is higher and related to the number of teeth.