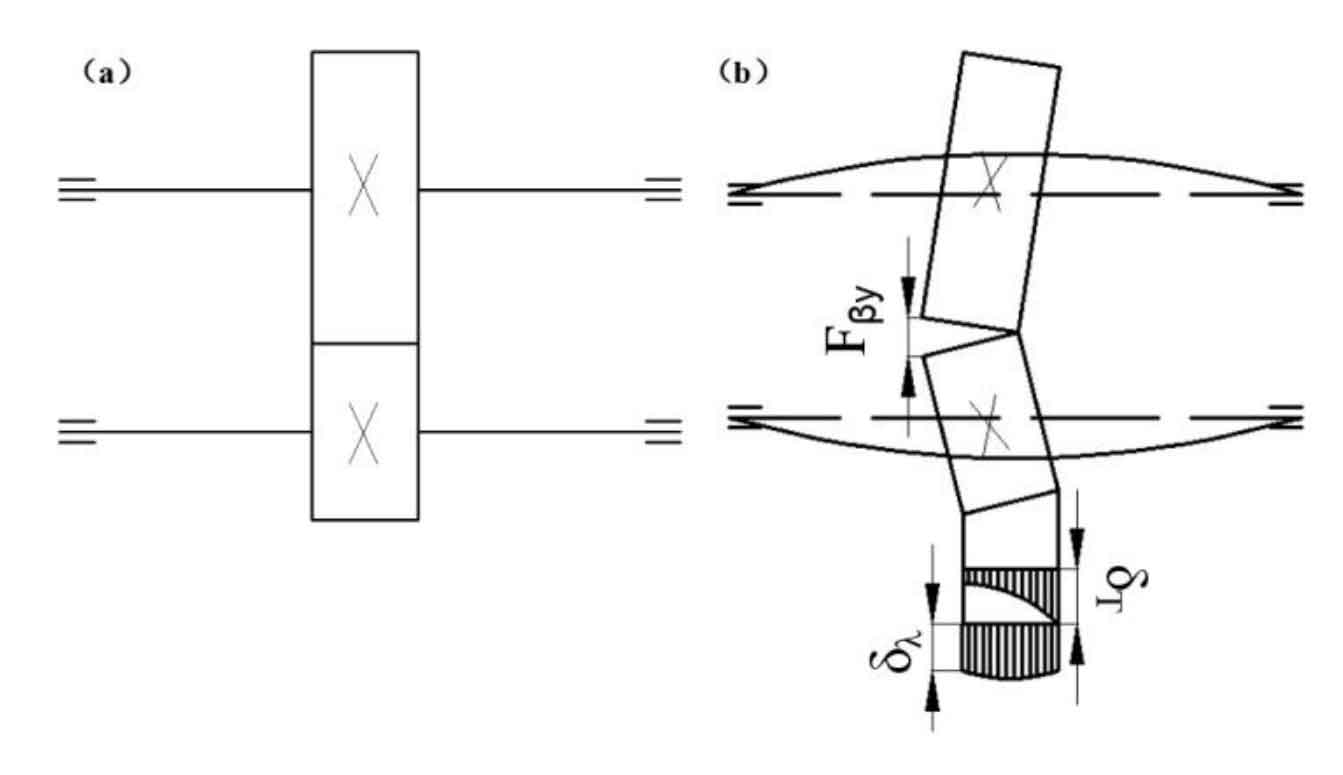
As shown in Figure 1 (a), under ideal or no-load conditions, the helical gear pair can mesh smoothly and bear uniform force, that is, a pair of meshing helical gear pairs can be regarded as two tangent pitch circles for pure rolling. However, the actual meshing process of helical gear pair will be affected by such factors as elastic deformation of gear teeth, processing and manufacturing errors, assembly errors, etc., resulting in serious eccentric load as shown in Figure 1 (b).
In the past, some enterprises would reduce the eccentric load of gear teeth by improving the accuracy of helical gear manufacturing and processing equipment, reducing human assembly errors and other means. However, these means often increase the cost significantly without addressing the symptoms and root causes. So many enterprises begin to modify the tooth direction of the eccentric load helical gear pair, which not only makes the stress distribution of the modified helical gear pair more uniform, but also saves costs to a certain extent. At present, there are up to 6 types of tooth modification, as shown in Figure 2.