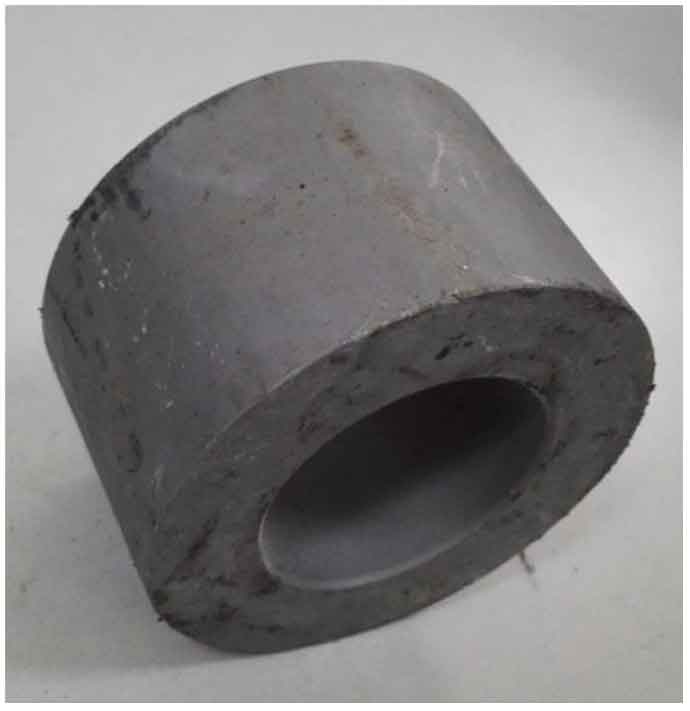
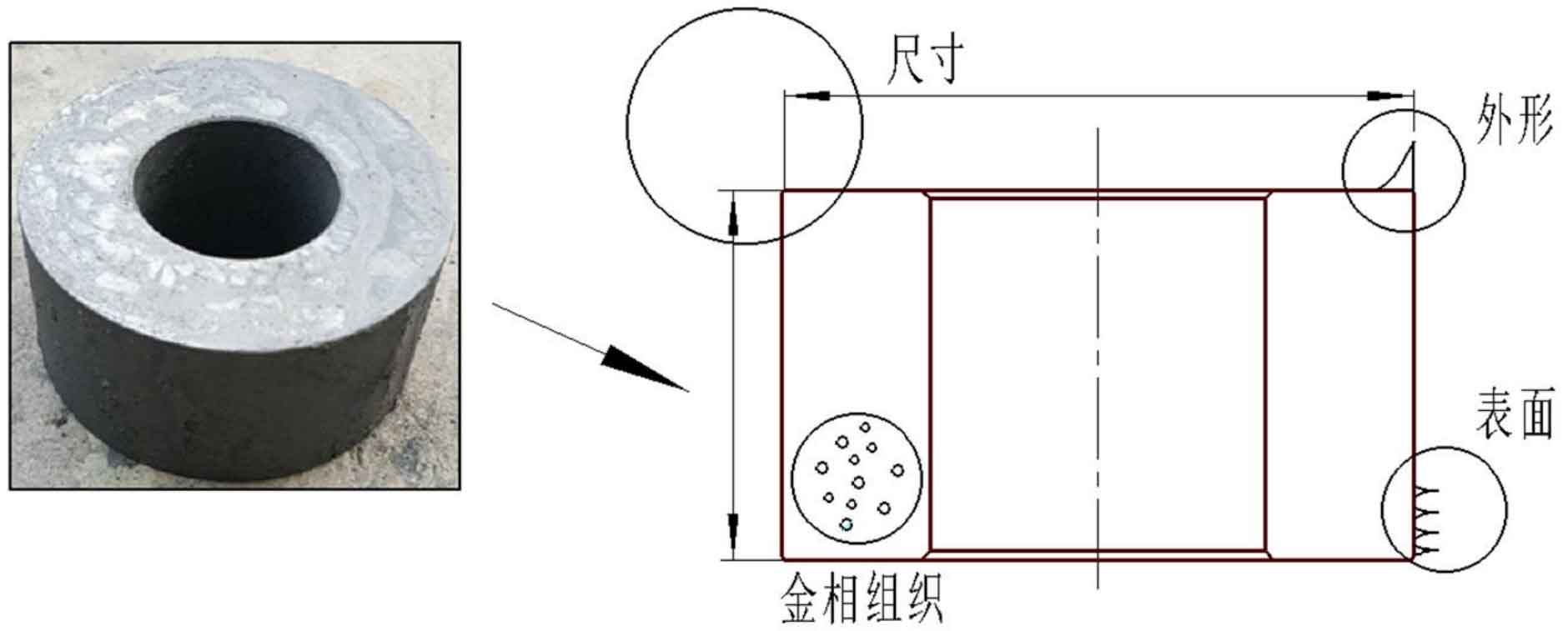
Cold extrusion process can produce extrusion parts quickly, continuously and in large quantities. In most cases, extrusion production has realized multi station full automation or semi automation. This manufacturing method requires the use of pre prepared blanks, as shown in Figure 1. The shape, size, metallographic structure and surface treatment of blank are one of the important factors to ensure the continuous production of high-quality spur gear by cold extrusion.
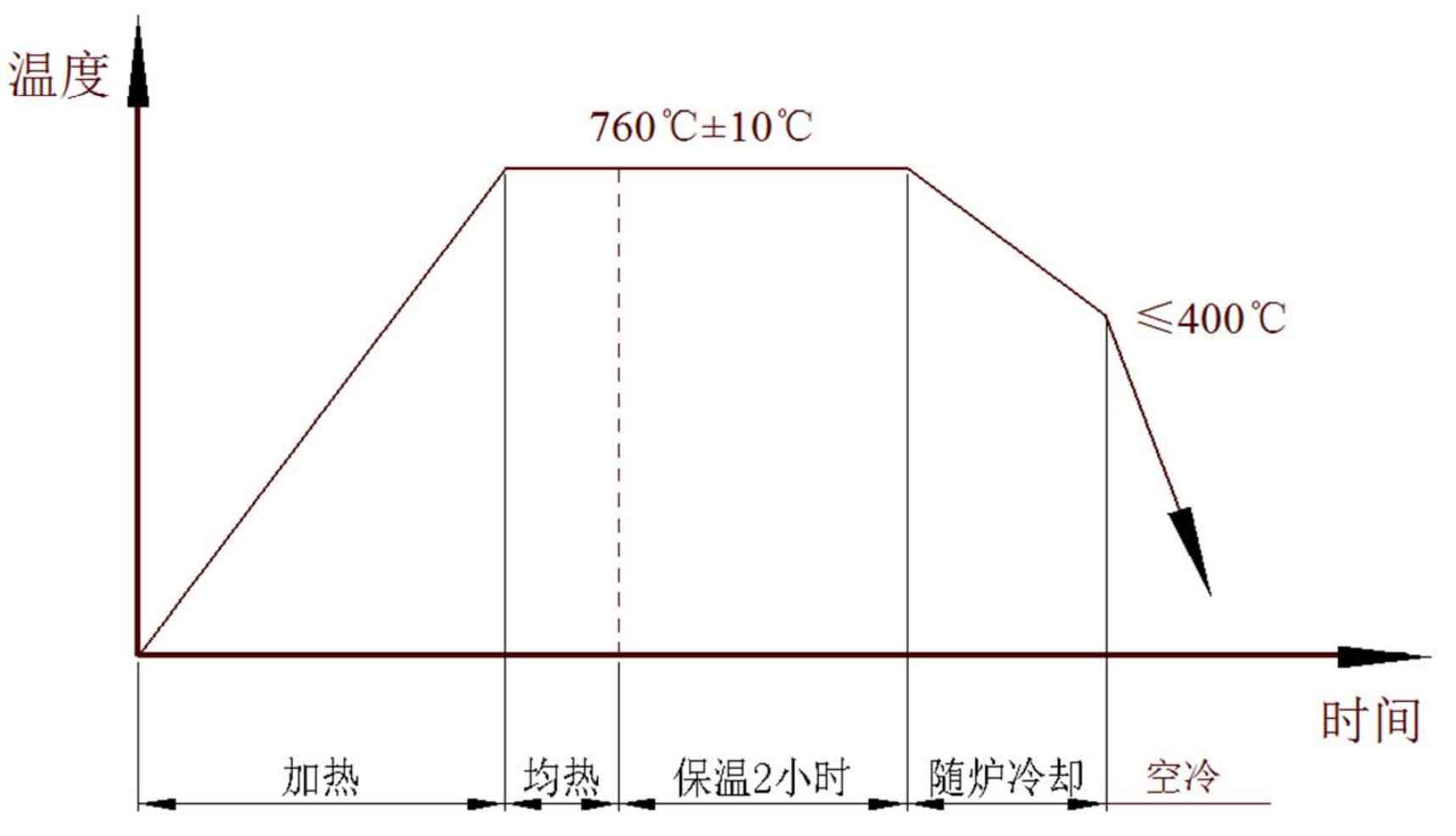
According to the structural characteristics of spur gear, the ring blank made of solid bar hot forging is selected as the cold extrusion blank of spur gear. In order to obtain the maximum deformation degree, the hot forging blank should be spheroidized and annealed before extrusion. Its purpose is to reduce the hardness of the blank before extrusion, improve its plasticity and ductility, eliminate internal structure, component defects and residual internal stress, reduce the unit extrusion force of the spur gear tooth concave die, and improve the stress condition of the die. Fig. 2 shows the spheroidizing annealing process of hot forging blank. Firstly, the blank is heated to 30 ~ 50 ℃ above AC1 and kept in the furnace for a period of time, then slowly cooled to 400 ℃ with the furnace, and finally discharged and air cooled to room temperature.
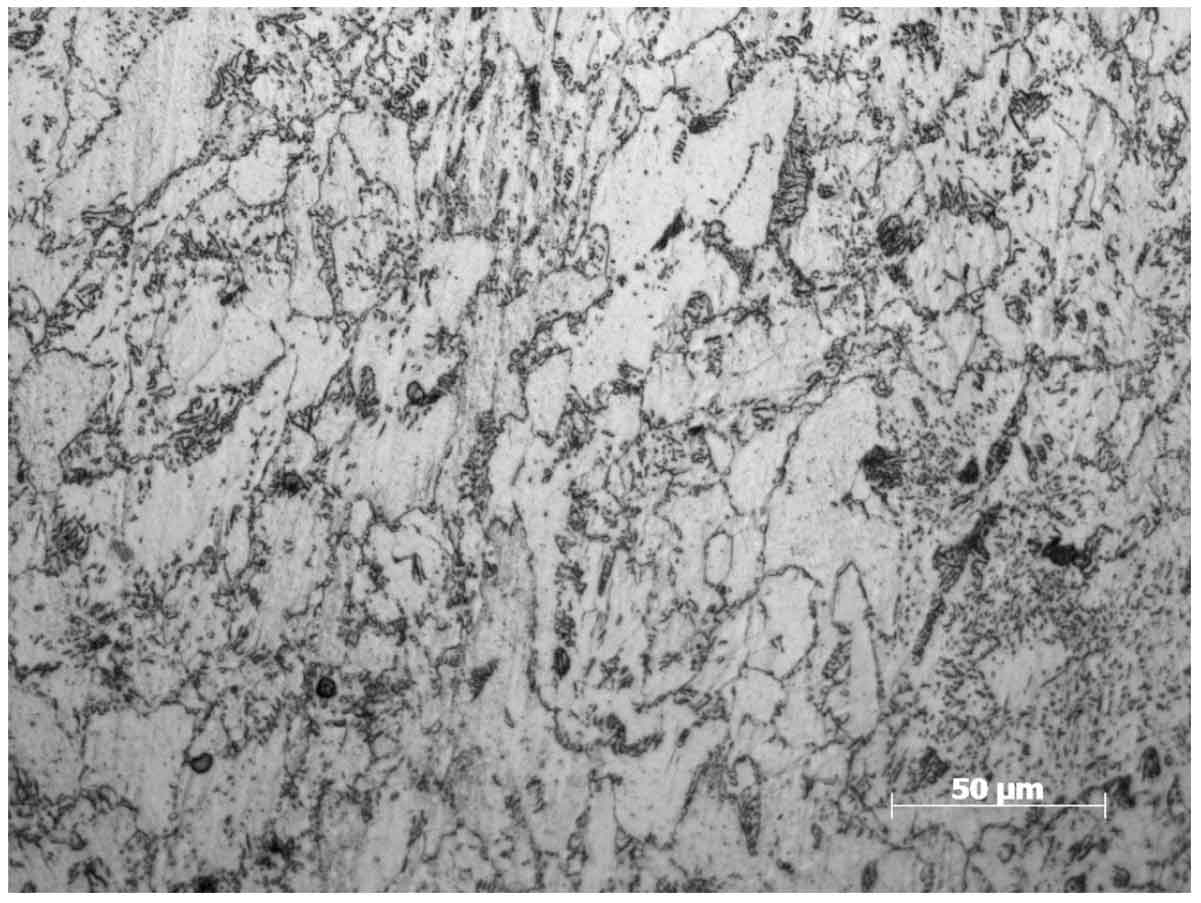
After spheroidizing annealing, the microstructure of the blank must be uniform without decarburization and carburization. The microstructure of the blank shall be tested after spheroidizing annealing, and the spheroidizing rate shall be greater than 90%. The spheroidized body after annealing shall meet the requirements of grade 5 ~ 6 according to JB / T 5074-2007 rating requirements for spheroidized body of low and medium carbon steel. As shown in Figure 3, the metallographic structure of hot forged ring billet after annealing is compared with the rating requirements. Its spheroidite rating is the highest level 6, and the structural characteristics are spheroidite + ferrite. Its hardness is in the range of 120 ~ 145 HBS.
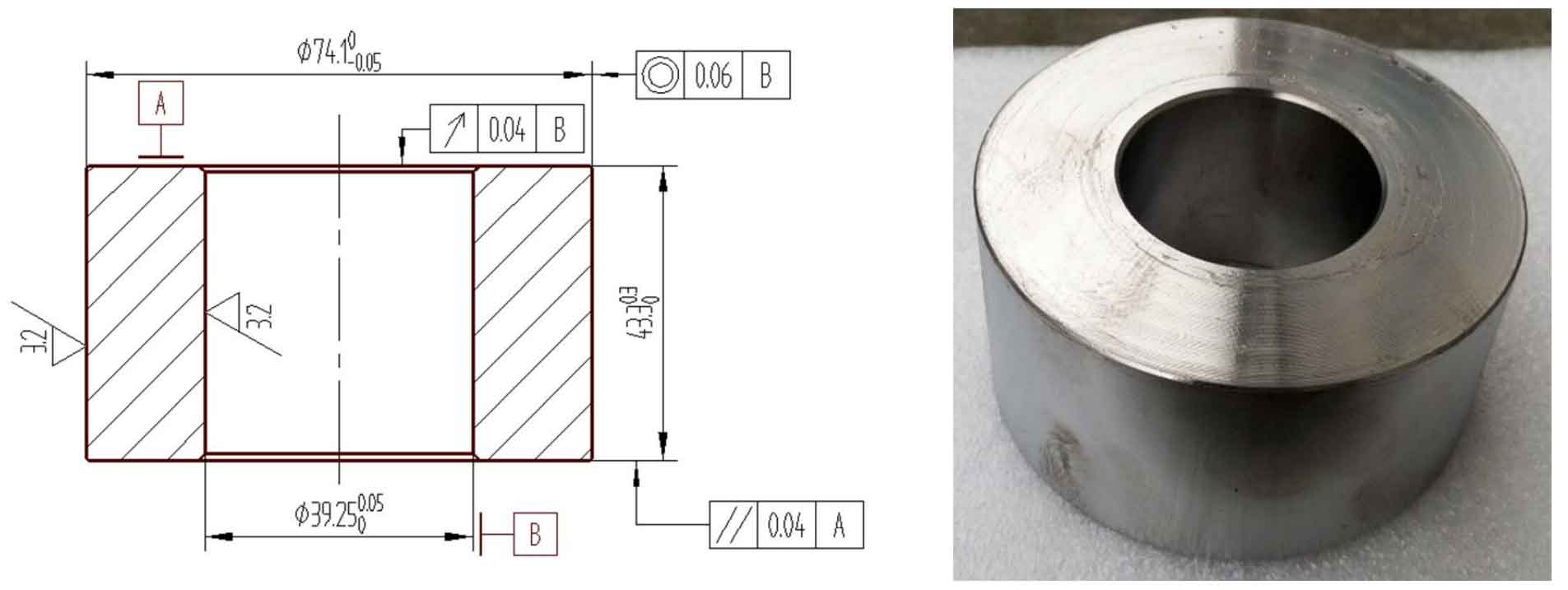
The surface quality of hot forged spur gear blank is poor, burr is left after cutting and punching, and oxide skin is left on the surface after annealing. In order to ensure the forming quality of cold extruded spur gear and prevent the die from being damaged due to the rough surface of the blank in the extrusion process, it is necessary to turn the blank after heat treatment. Cold extrusion blank has high requirements for surface quality and dimensional accuracy. After finishing turning, the blank surface is not allowed to have defects and oxide scale residue after forging, the parallelism of end face is not greater than 0.04mm, and the coaxiality of outer circle and inner hole is not greater than 0.06mm. At the same time, the outer circle and inner hole of the blank must be chamfered to prevent folding during cold extrusion, accelerate die wear and die sticking failure. The finished blank drawing and physical drawing are shown in Figure 4.
The surface treatment and lubrication of spur gear blank is the key link of gear cold extrusion. The quality of surface treatment and lubrication is directly related to the service life of spur gear tooth die, the filling effect of extrusion and the surface quality of extrusion. The pressure resistance of common lubricants is not enough to withstand the unit extrusion pressure of steel materials during extrusion. Therefore, the lubrication treatment of cold extrusion of steel materials is phosphate treatment and lubrication treatment, that is, a special lubrication support layer is formed on the blank surface and coated with lubricant. The lubrication support layer firmly bonds the lubricant with the outer surface of the blank. The lubricant layer is used as a sliding layer to reduce the friction between the extrusion and the die. Zinc phosphate layer is usually used as the lubricating support layer and zinc stearate as the lubricant. The surface treatment and lubrication process of spur gear blank mainly includes the following processes:
① Warm water washing the function of warm water washing is to “activate” the blank requiring coating through warm water washing, that is, form the so-called active center on the material surface, in order to form crystal nucleus for subsequent phosphating. The blank is placed in a warm water tank with a temperature of 60 ~ 80 ℃ for 3 ~ 5min. The temperature in the tank will affect the thickness of the phosphating layer. The phosphating layer formed when the water temperature in the tank is 60 ℃ is thinner, and the phosphating layer is thicker at 80 ℃.
② Phosphating treatment put the blank washed with warm water into dilute phosphoric acid solution containing zinc phosphate for treatment. Under the action of phosphoric acid, the metal iron on the blank surface is separated to form ferrous ions. At the same time, zinc phosphate grows and crystallizes on the blank surface to form zinc phosphate crystal layer. To form 8 ~ 15 μ For m-thick coating, the blank shall be immersed in the phosphating tank at 60 ~ 70 ℃ for 8 ~ 10min, and the solvent consumed during phosphating in the tank shall be replaced in time. After phosphating, immerse in the cold water tank for 1 ~ 2min to remove the residual phosphoric acid and phosphate in the zinc phosphate solution.
③ Saponification phosphating layer itself has almost no lubricity, and as a lubricating support layer, it also needs lubrication treatment. Zinc stearate, which is common in the factory, is selected as the lubricant in the cold extrusion process experiment of spur gear. When the blank is immersed in a warm pool with a temperature of about 70 ℃ for 3 ~ 4min, a covering layer with high lubrication and insoluble in water is formed on the surface of the blank. The existence of phosphating layer makes the lubricating layer easier to be adsorbed on the surface of the blank and integrated with the surface of the blank. A thin film can still be kept between the workpiece and the die under high pressure in extrusion forming. Figure 5 shows the blank after phosphorus saponification.