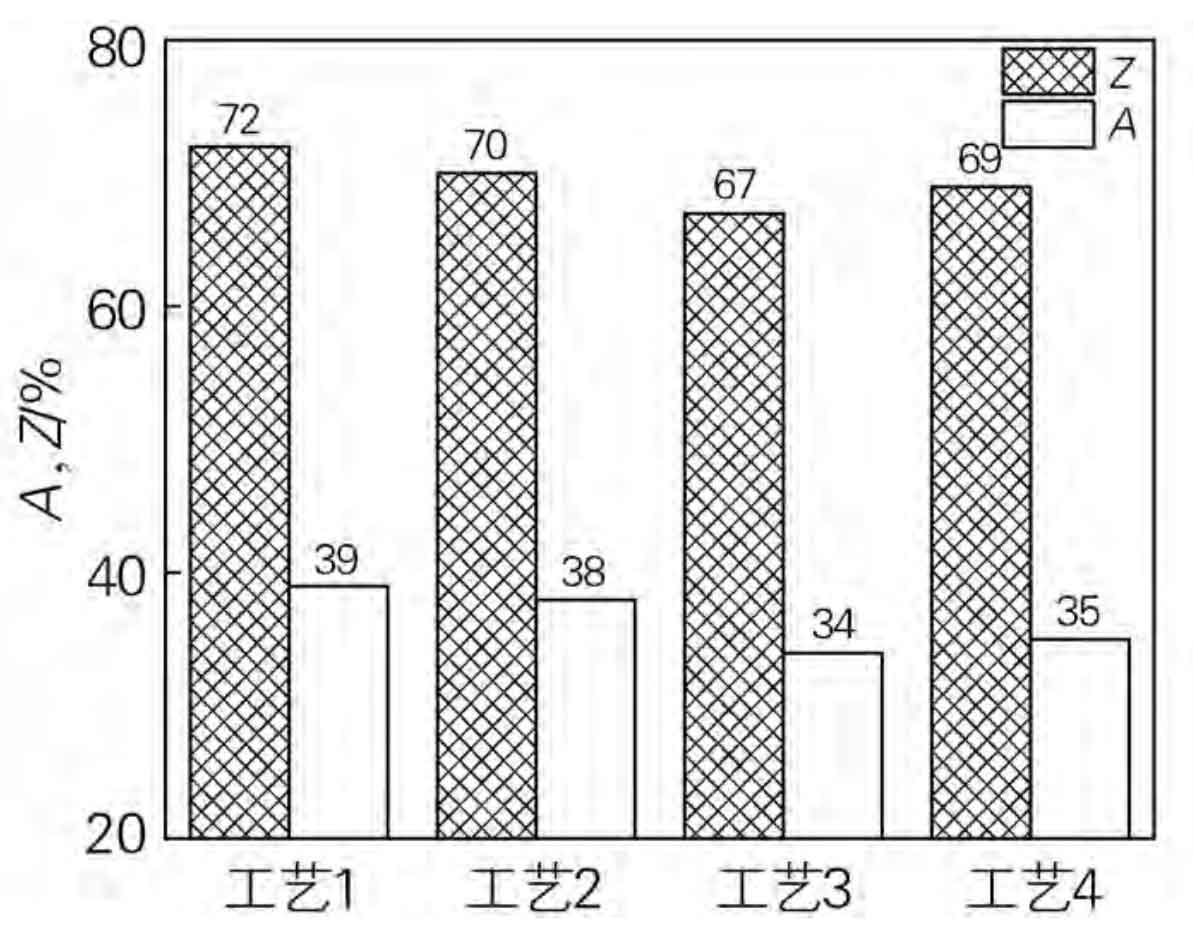
Reduction of area and elongation are one of the key parameters of material plasticity. As shown in the figure, the change of reduction of area and elongation of 16MnCrS5 steel under different spheroidizing annealing processes. Compared with other processes, 16MnCrS5 steel has the best plasticity under process 1 conditions, with a reduction of area of 72% and an elongation of 39%. Under process 3 conditions, the area shrinkage and elongation of the material are the lowest, which proves that the plasticity is effectively improved when the heating temperature is 760 ℃. After spheroidizing annealing, the higher the strength of the material, the worse the plasticity, the lower the strength, and the better the plasticity.
Combined with the microstructure analysis under each process, it can be seen that under the condition of process 1, the spheroidization rate of cementite is the highest and the proportion of ferrite in the matrix is the highest. In the process of plastic deformation, the main form of plastic deformation is slip. After the spheroidization of cementite, the resistance force in the process of ferrite slip is the smallest, and the deformation degree in the process of slip is up to 300%. Therefore, under the condition of process 1, 16MnCrS5 steel has the best plasticity.