(1) Influence of helix angle on transmission error of helical gears
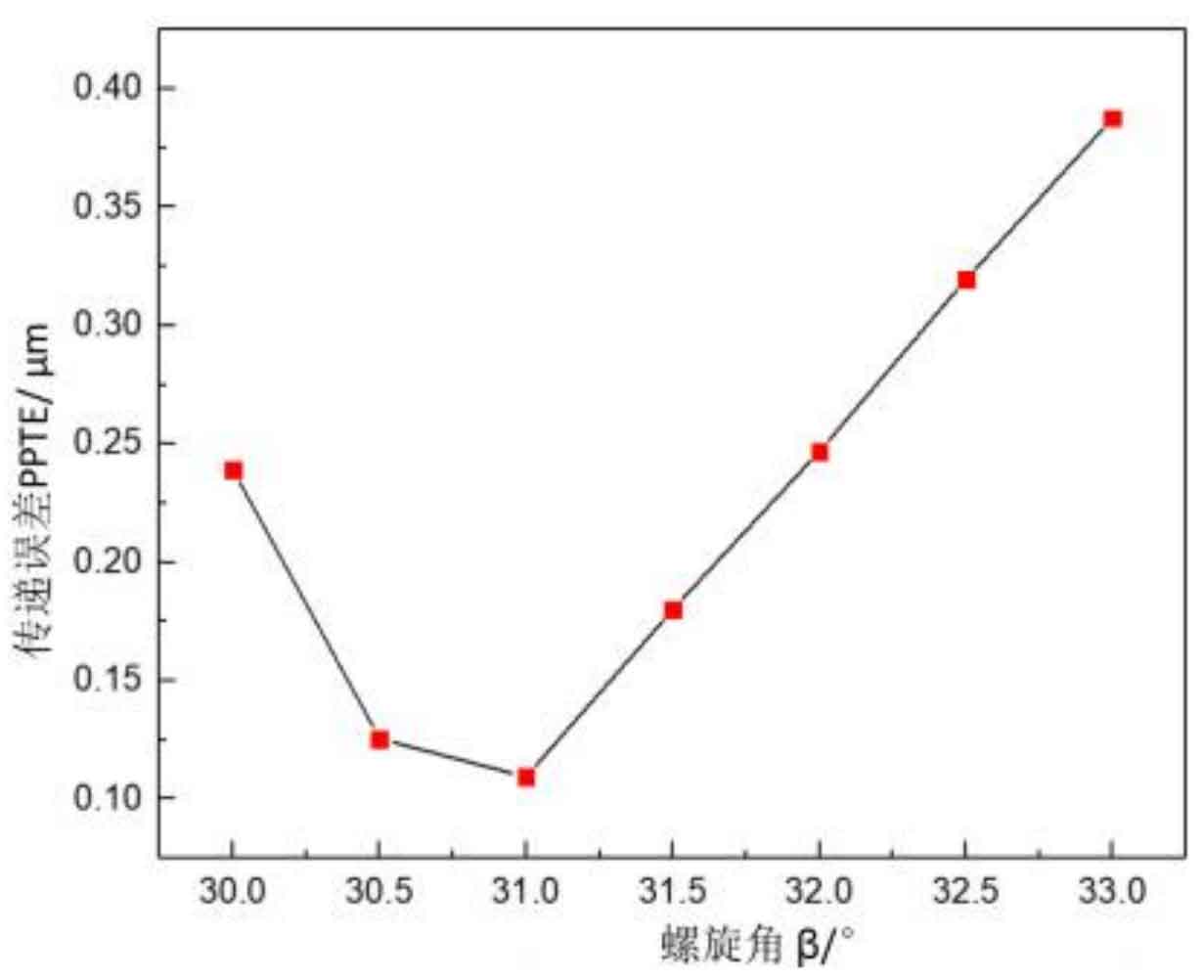
Figure 1 shows the relationship curve between the helix angle and the transmission error of helical gear. When the helix angle changes in the range of 30 °~33 °, the transmission error decreases first and then increases with the increase of the helix angle. When the helix angle is equal to 31 °, the transmission error of the helical gear pair is the minimum, 0.109 μ m。
(2) Influence of helix angle on hertz contact stress of helical gears
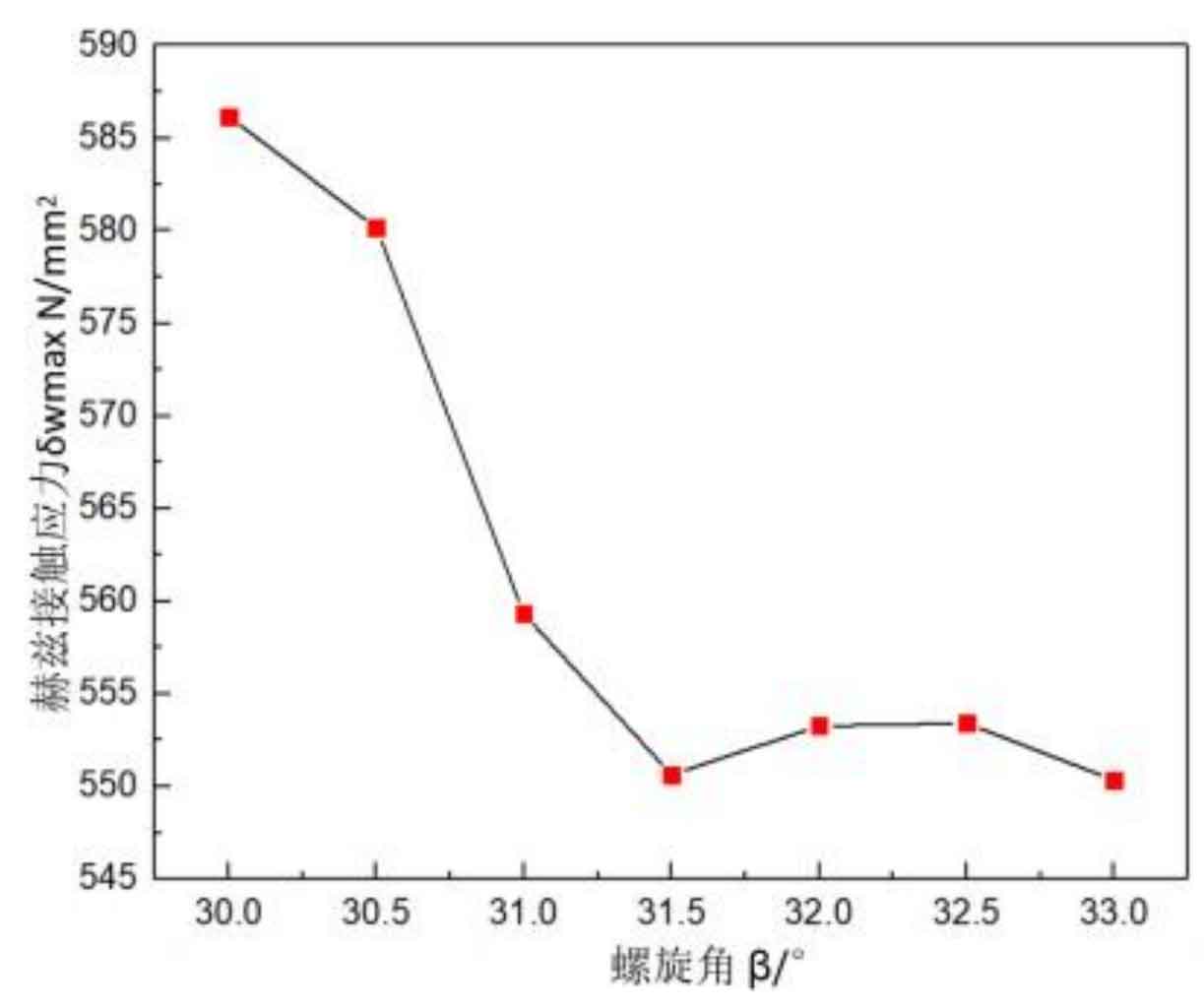
Figure 2 shows the Hertz contact stress curve of helical angle and helical gear. Within the range of 30 °~31.5 °, the overall trend is that Hertz contact stress continues to decrease, that is, the gear strength increases. However, in the range of 31.5 °~33 °, the Hertz contact stress first increases, then remains unchanged and finally decreases. When the helix angle of the gear pair is 31.5 ° and 33 ° respectively, the Hertz contact stress is the lowest, 550.645N/mm2.
(3) Influence of Helical Angle on Helical Gear Transmission Efficiency
Figure 3 shows the relationship curve between helix angle and helical gear transmission efficiency. When the helix angle is 30 °~31.5 °, the transmission efficiency of the helical gear pair remains unchanged; When the helix angle is 31.5 °~33 °, the transmission efficiency decreases with the increase of helix angle.
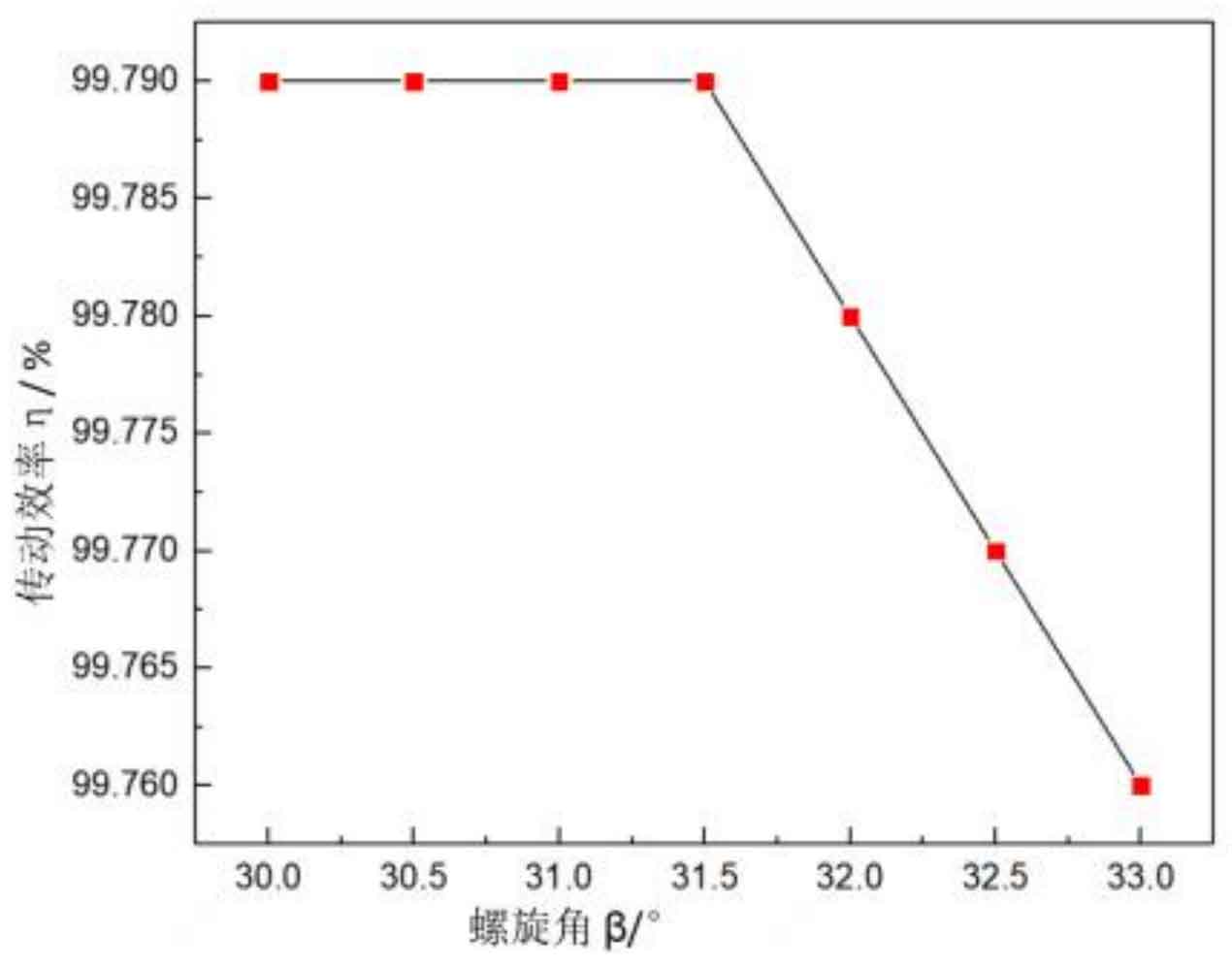
Therefore, except that the gear transmission efficiency will continue to decrease when the helix angle exceeds a certain range, that is, greater than 31.5 °, the helix angle has no obvious rule for the transmission error and Hertz contact stress of the helical gear pair. It is suggested that proper helix angle should be selected after comprehensively weighing the advantages and disadvantages of gear vibration noise and service life according to specific working conditions in engineering practice.
