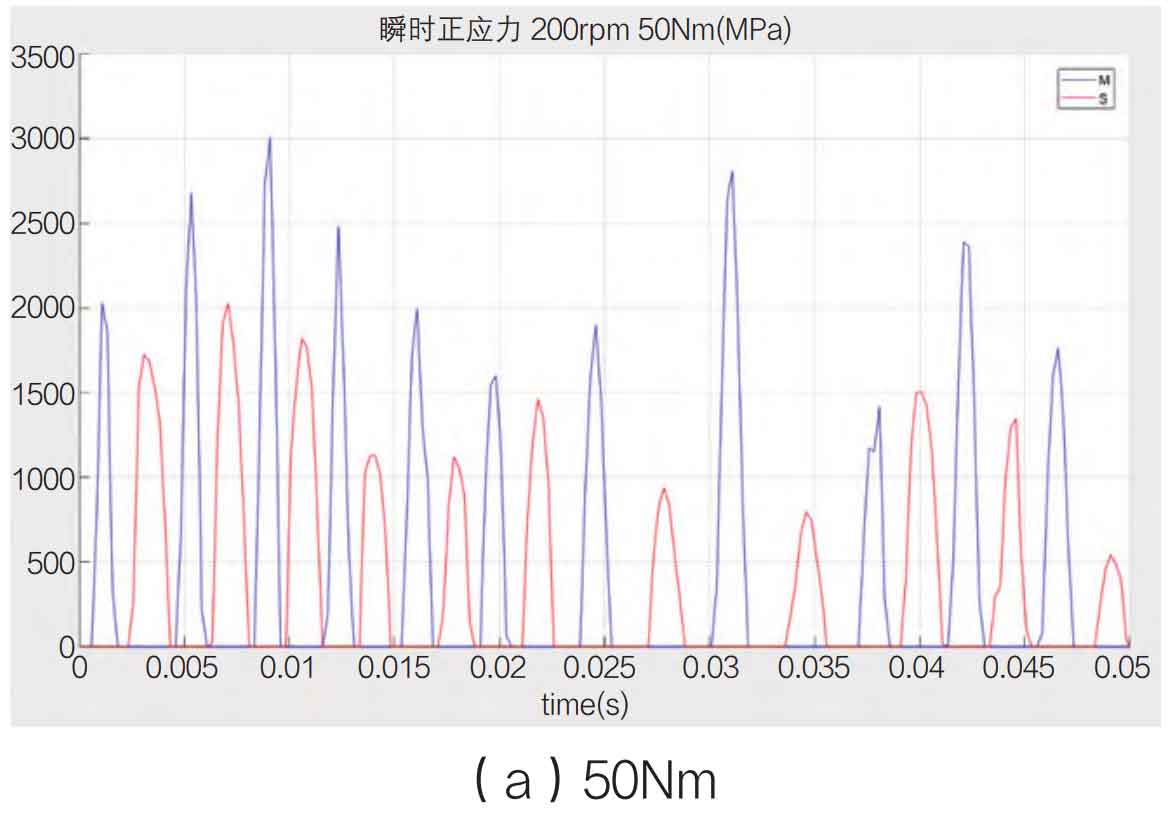
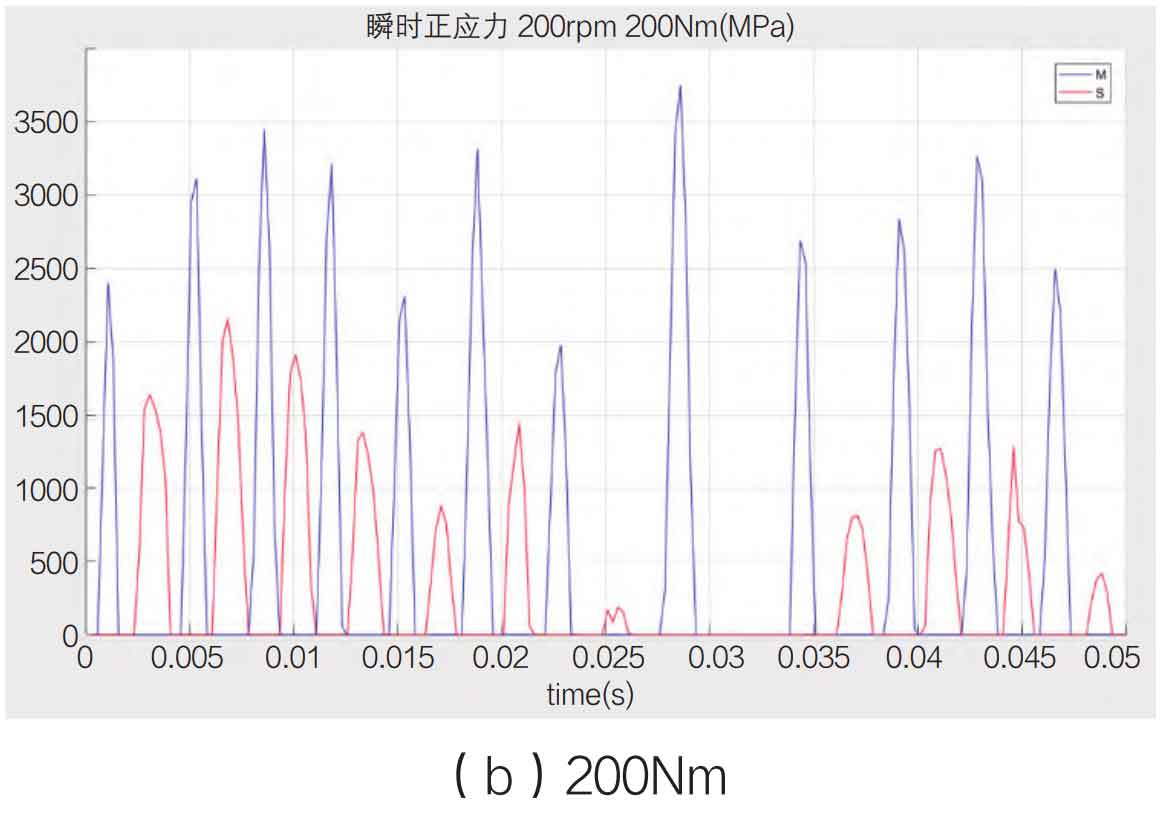
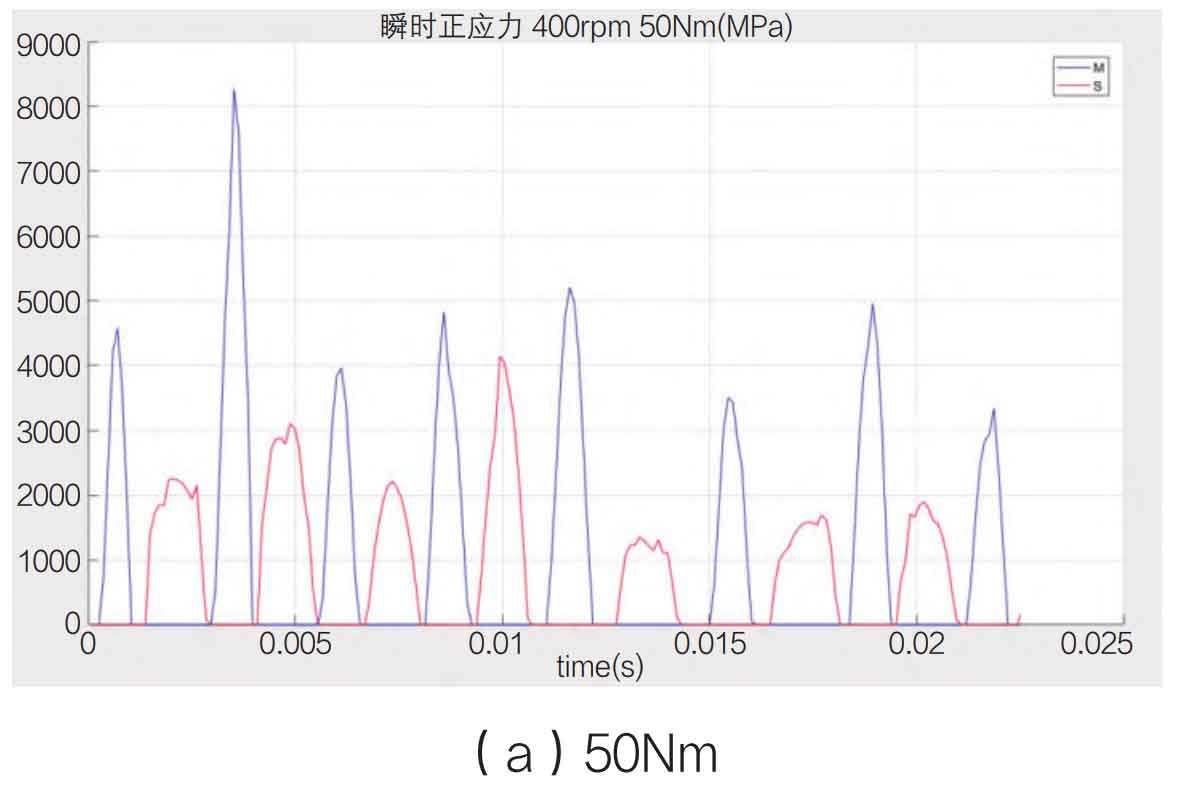
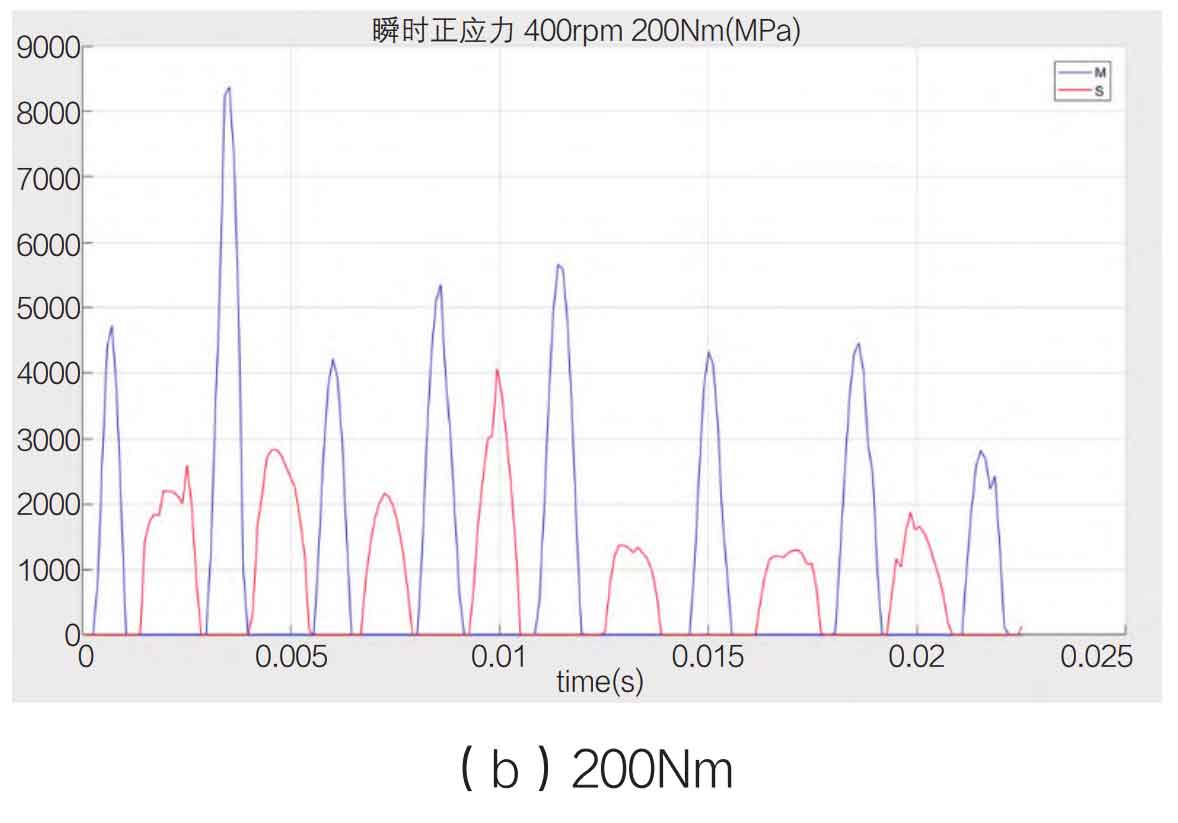
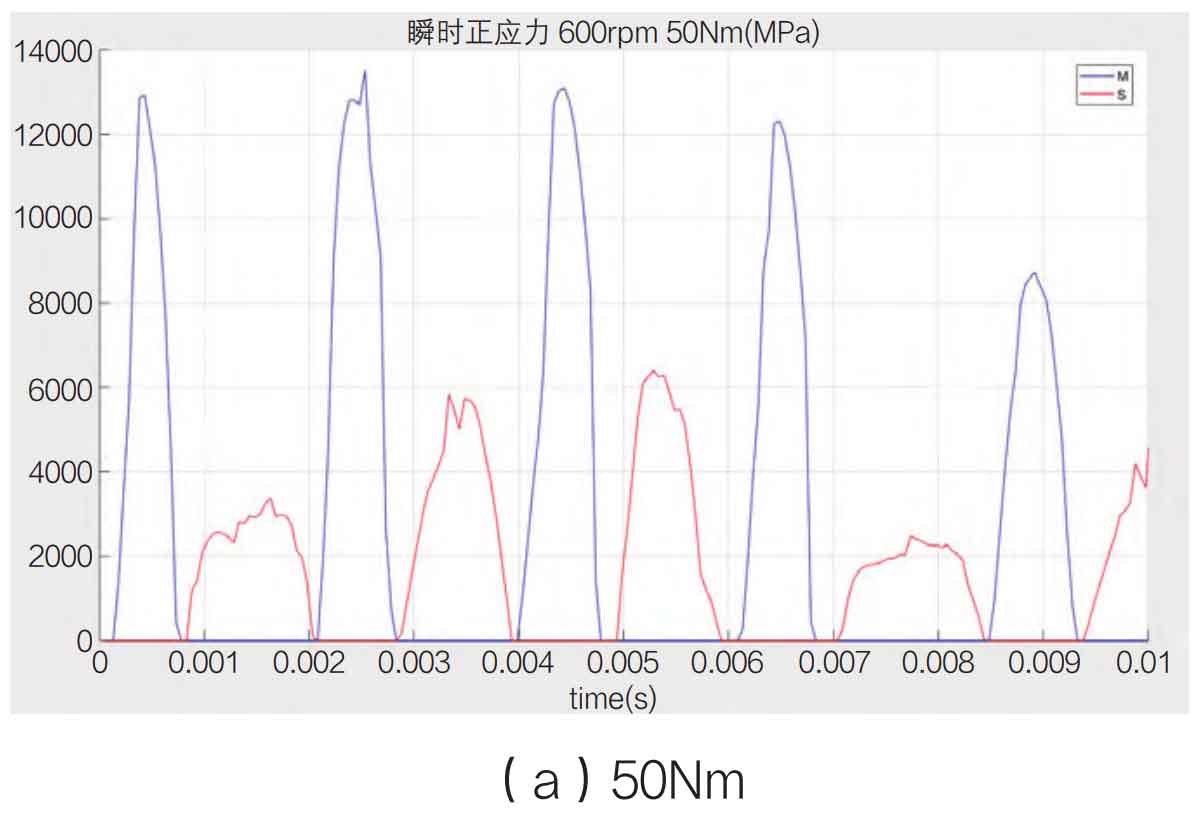
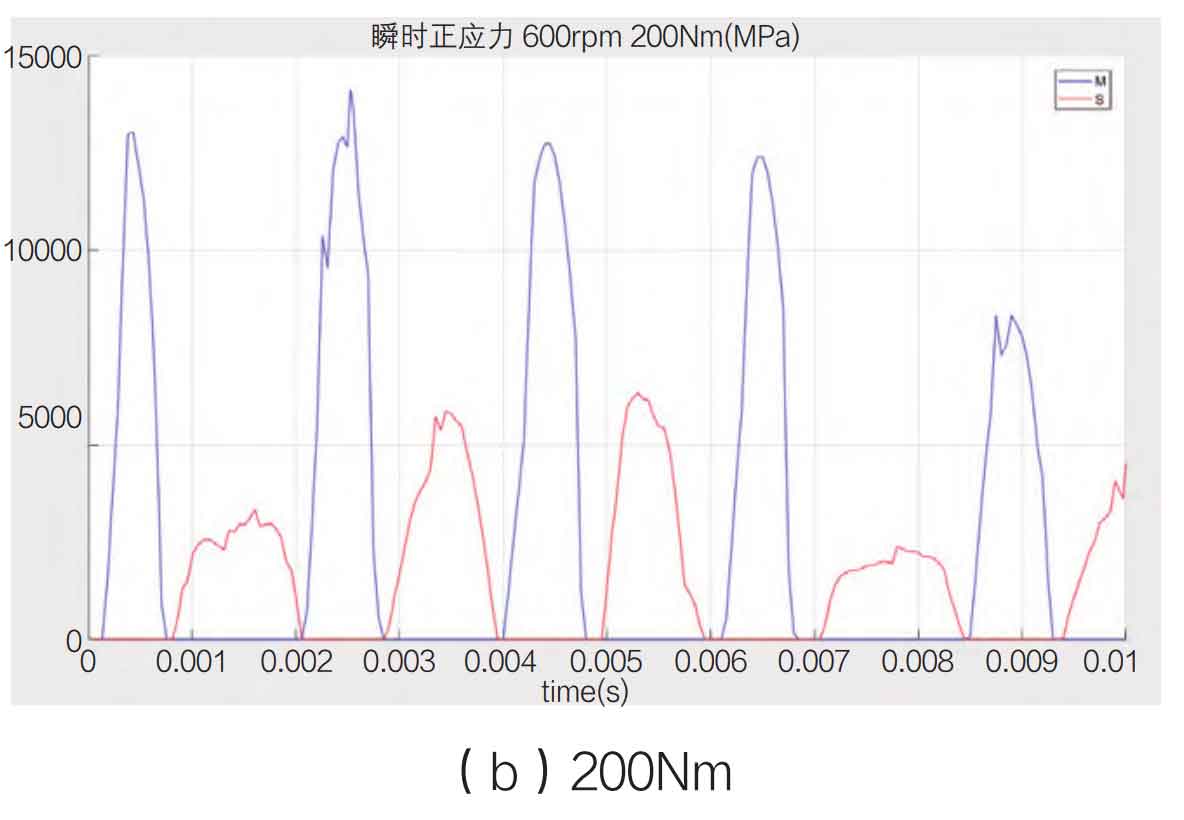
During the meshing and contact process of spiral bevel gears, the normal stress along the running direction is classified as the main contact surface, and vice versa, based on the running direction of spiral bevel gears. The normal stress value of the main contact surface represents the energy of the spiral bevel gear transmission, and the normal stress value of the secondary contact surface represents the energy consumed by the impact of the spiral bevel gear. Both values reflect the efficiency of the spiral bevel gear transmission. Take the speed of 200rpm, 400rpm and 600rpm as shown in Figure 1-3 below.
From the experiment, it is found that the main contact surface presents a thin and long numerical curve, and the secondary contact surface presents a squat shape, reflecting the characteristics of the main contact surface that bears the propulsion force on the front, the contact time is short and the output normal stress value is high, and the secondary contact surface is characterized by the impact rebound, the dynamic force is insufficient, and the contact time is long. At the same time, on the whole, the value of normal stress increases with the increase of speed, but the rate of normal stress increase of the main contact surface is much higher than that of the secondary contact surface, indicating that the higher the speed is, the more energy is consumed and the lower the transmission efficiency is. In this process, the rate of the driving spiral bevel gear and the reduction rate of transmission efficiency are inversely related.
After assembly, check the contact area. If it is not in the ideal design area, adjust it according to the contact area adjustment theory of spiral bevel gear. The stress distribution in the contact area is elliptical diffusion, which should be larger at the center and smaller around. The adjusted contact area is verified as shown in Figure 4 below.